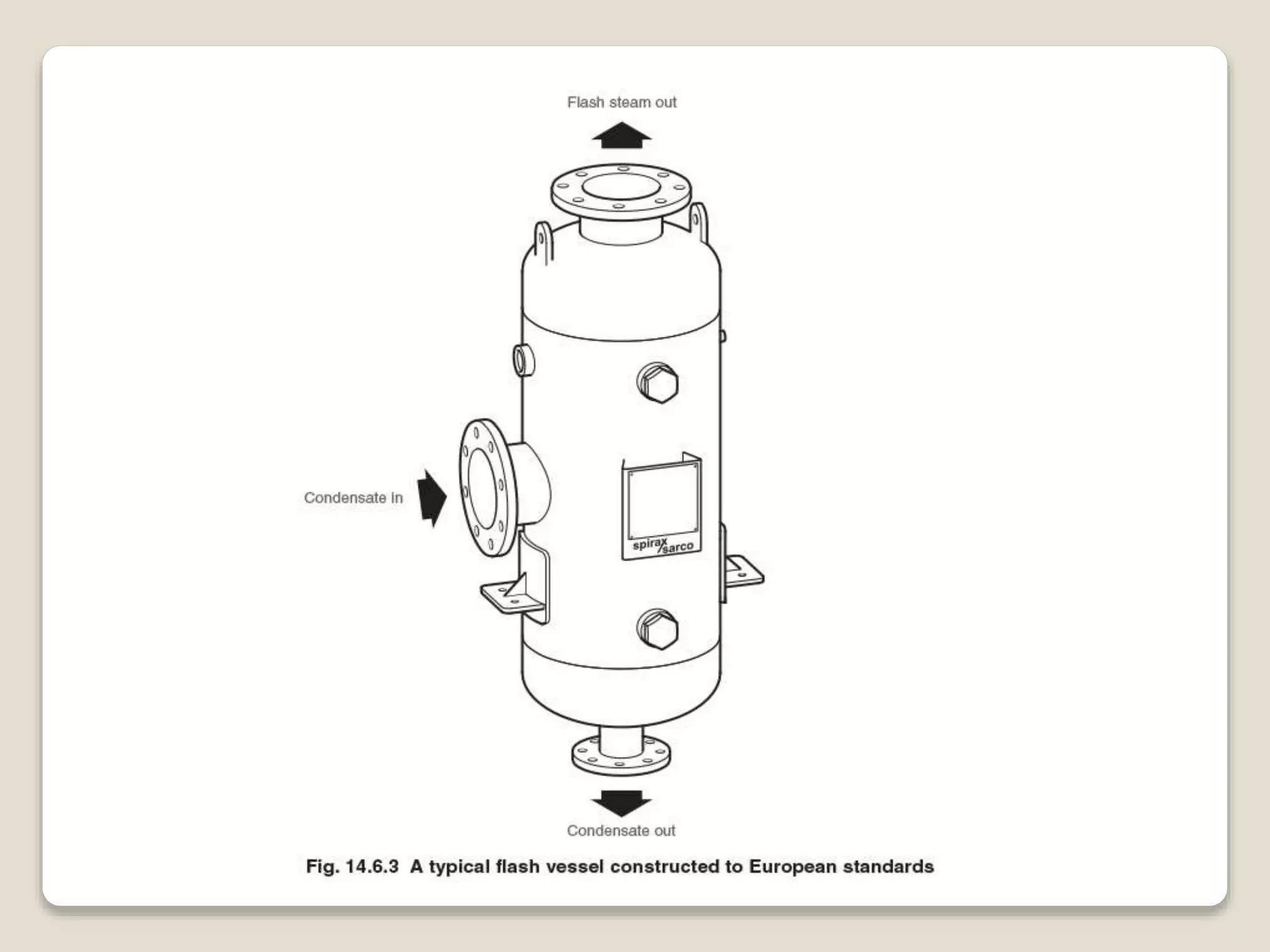
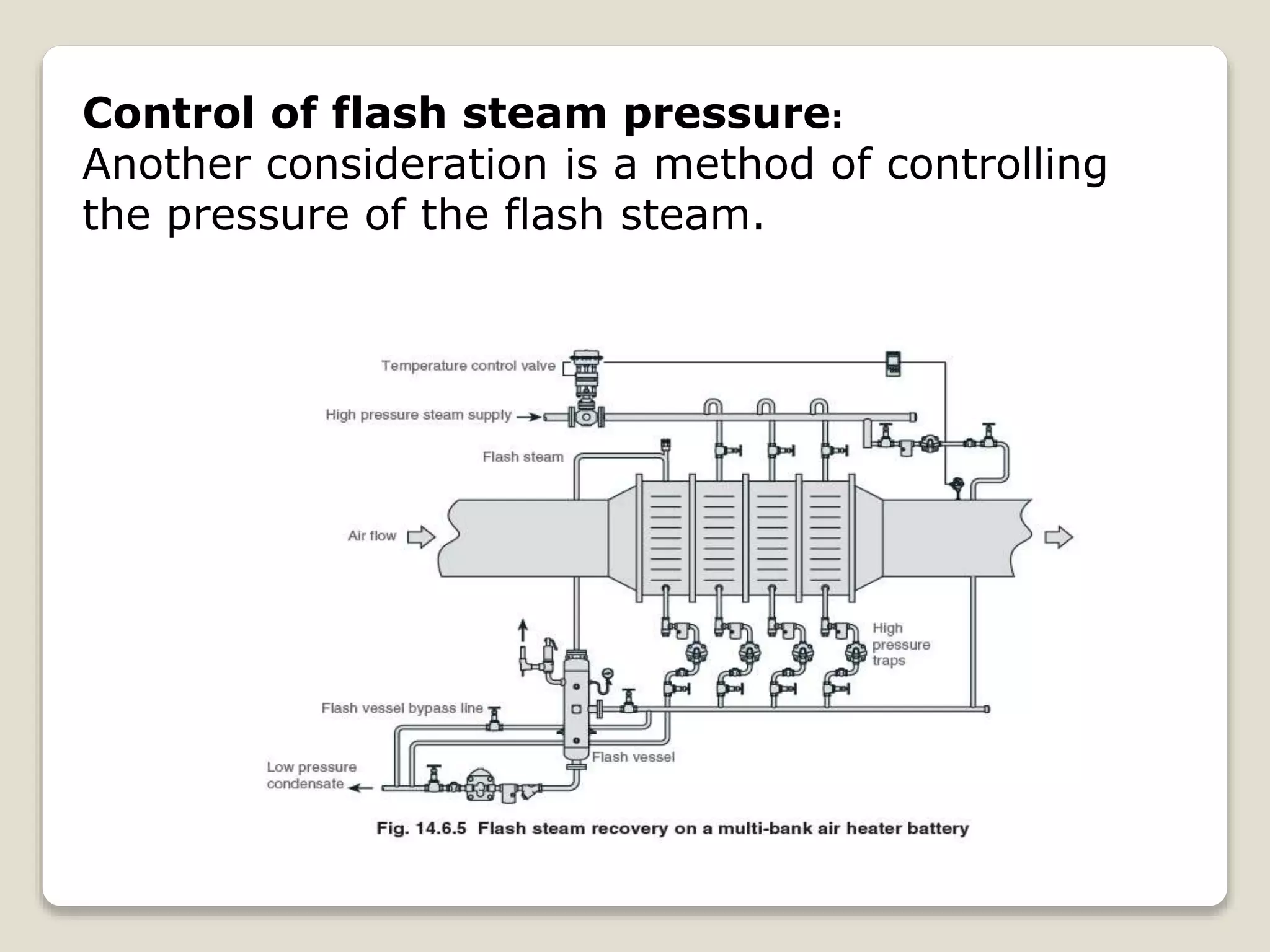
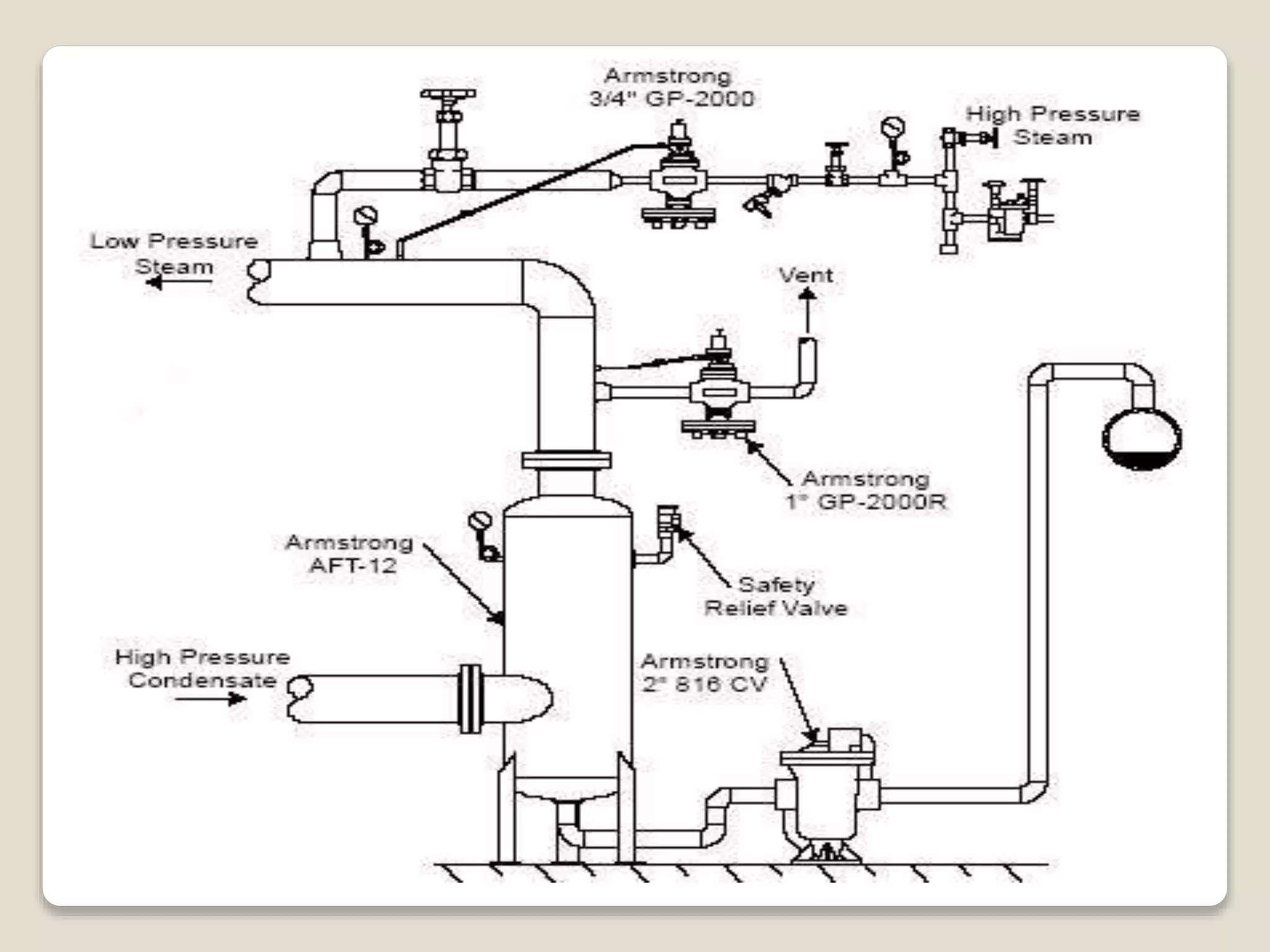
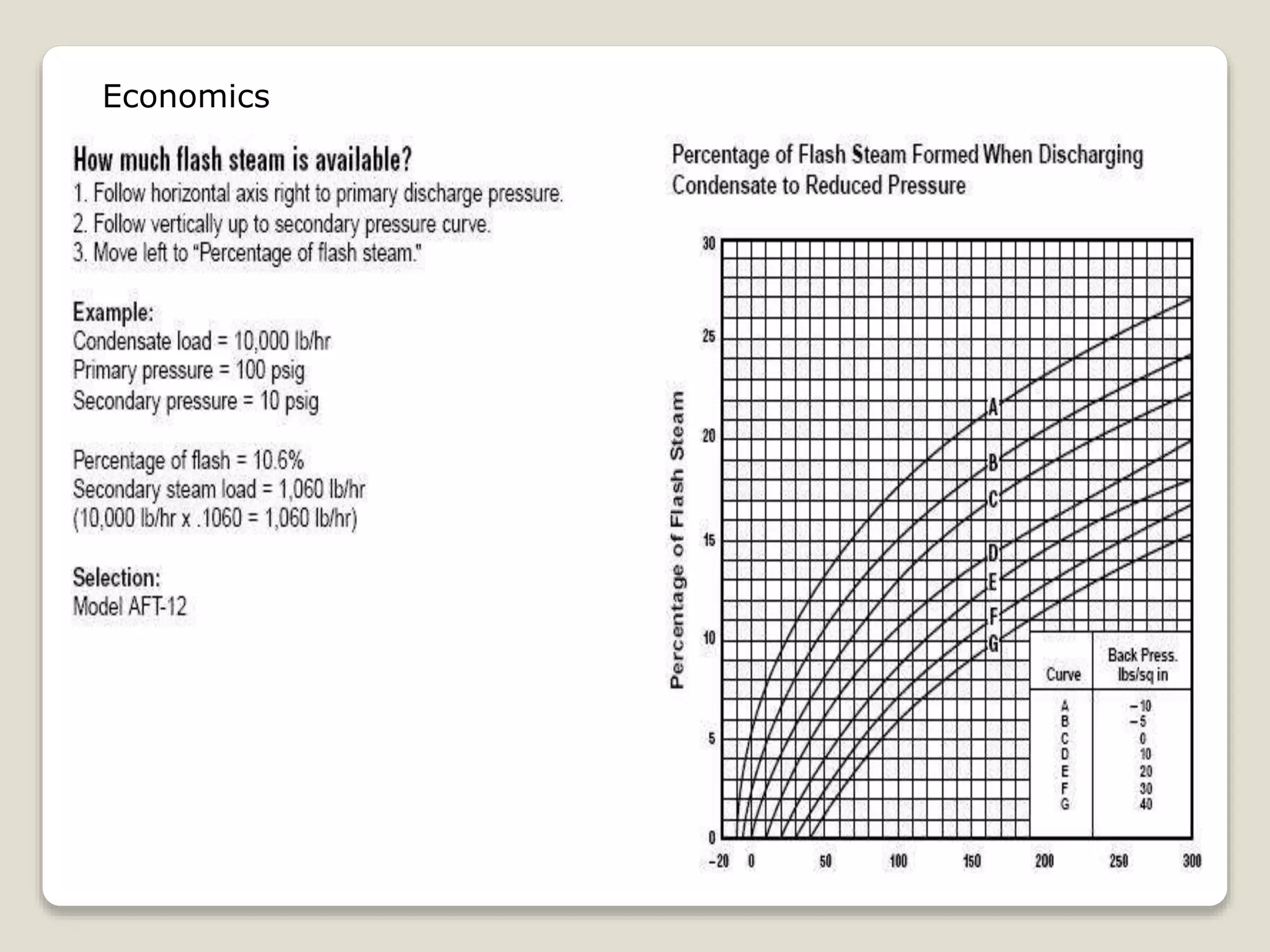
Flash steam is formed when high pressure condensate experiences a rapid drop in pressure, causing some of the condensate to flash into steam. Flash vessels are used to separate flash steam from condensate. They allow condensate to fall to the bottom where it drains out, while flash steam collects at the top and is piped to low pressure steam equipment. Recovering flash steam improves boiler efficiency and increases steam generation. It also provides economic benefits through reduced fuel costs and lower water-related expenses.