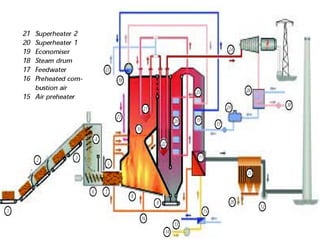
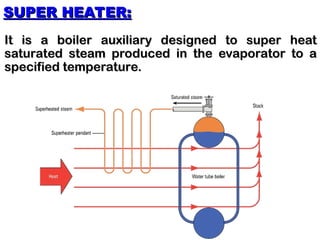
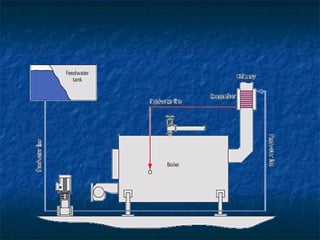
The document discusses various boiler auxiliaries and mountings essential for improving the efficiency and performance of steam generation plants. Key auxiliaries include super heaters, economizers, boiler feed pumps, and air pre-heaters, each serving specific functions to optimize boiler operation. It also covers safety features such as safety and relief valves, low-water cut-offs, and water feeders necessary for safe boiler operation.