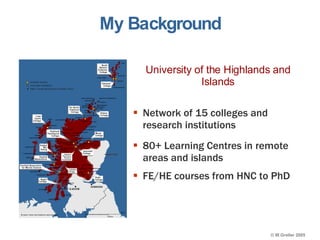
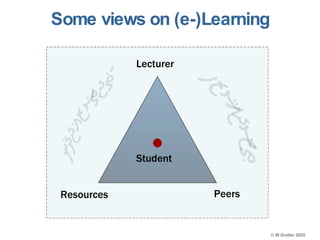
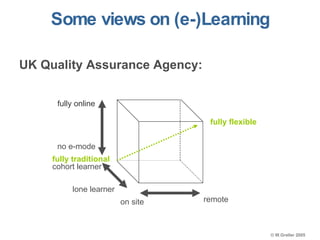
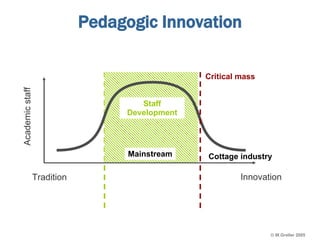
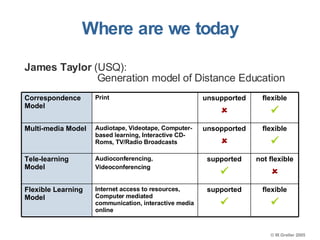
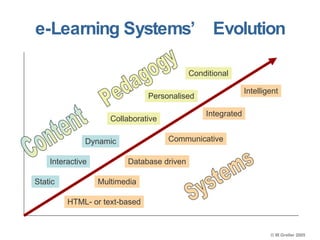
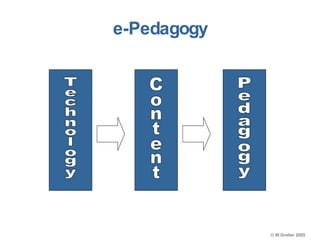
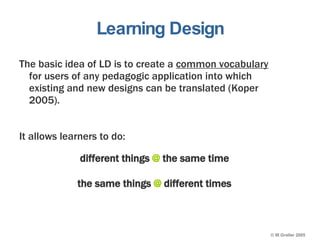
This document discusses e-learning pedagogy and trends. It notes that e-learning offers flexible learning opportunities but that current tools focus more on content than pedagogy. For e-learning to be effective, it must be driven by pedagogy rather than just technology. Learning design approaches aim to make teaching and learning processes more explicit and portable across systems to improve e-learning pedagogy and the student experience. However, fully implementing learning design approaches is still a major challenge.











![Learning Desing Implementation of LD: There is still a looooooooooong way to go……… Wolfgang Greller Head of Learning Environments UHI Millennium Institute Stornoway, Isle of Lewis SCOTLAND [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elearningandpedagogy25255-1218509064323207-9/85/Elearning-And-Pedagogy-20-320.jpg)