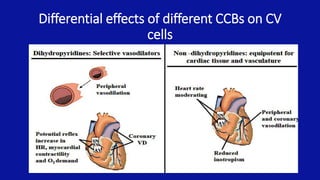
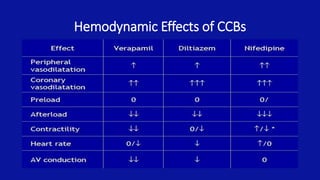
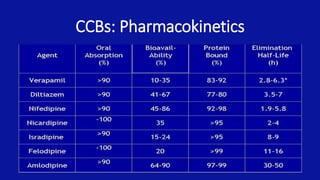
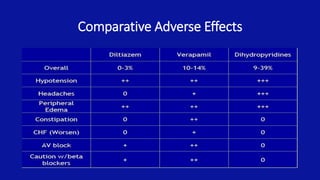
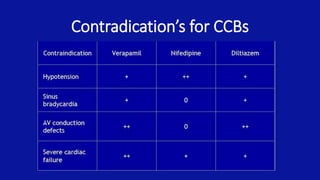
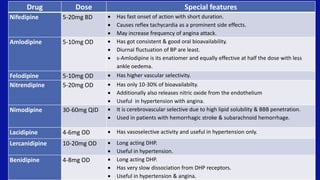
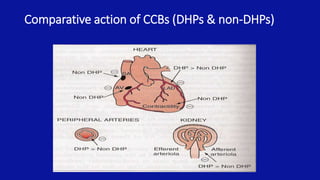
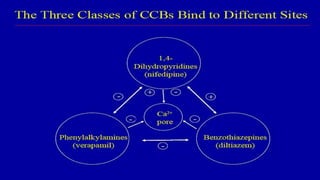
Calcium channel blockers (CCBs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the movement of calcium ions across cell membranes. There are three main classes of CCBs: dihydropyridines like nifedipine, phenylalkylamines like verapamil, and benzothiazepines like diltiazem. CCBs work by blocking L-type calcium channels in cardiac and vascular smooth muscle cells, which decreases calcium entry and inhibits contraction. This leads to vasodilation, reduced peripheral resistance, and decreased blood pressure and workload on the heart. Common uses of CCBs include hypertension, angina, arrhythmias, and migraines. Adverse effects vary between classes but can



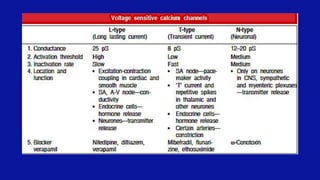






![CCBs Act Selectively on Cardiovascular Tissues
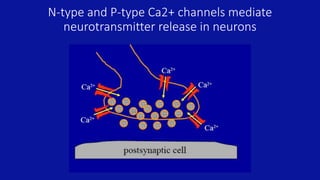
• Neurons rely on N-and P-type Ca2+ channels
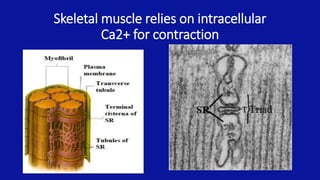
• Skeletal muscle relies primarily on [Ca]
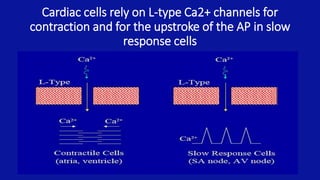
• Cardiac muscle requires Ca2+ influx through L-type
Ca2+ channels
• contraction (fast response cells)
• upstroke of AP (slow response cells)
• Vascular smooth muscle requires Ca2+ influx through
L-type Ca2+ channels for contraction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ccb-190608060507/85/calcium-channel-blocker-16-320.jpg)