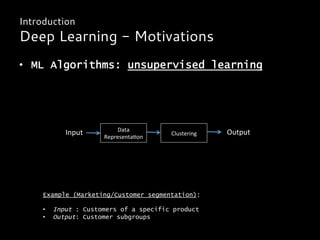
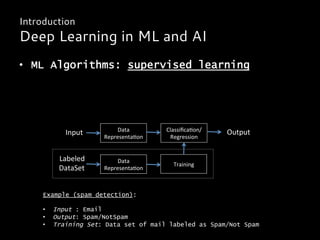
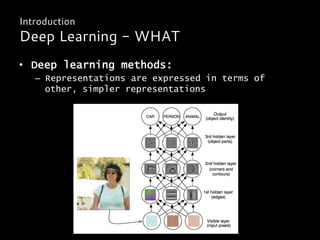
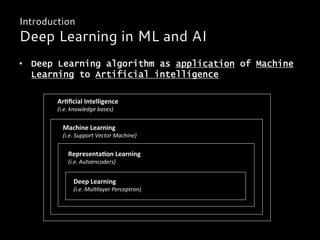
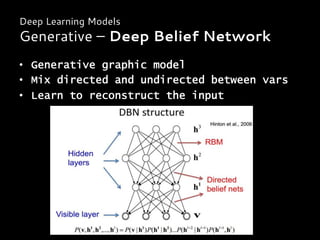
Deep learning is a class of machine learning algorithms that uses multiple layers of nonlinear processing units for feature extraction and transformation. It can be used for supervised learning tasks like classification and regression or unsupervised learning tasks like clustering. Deep learning models include deep neural networks, deep belief networks, and convolutional neural networks. Deep learning has been applied successfully in domains like computer vision, speech recognition, and natural language processing by companies like Google, Facebook, Microsoft, and others.








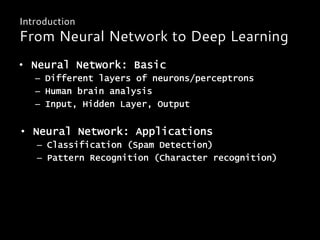
![• The core: Neuron
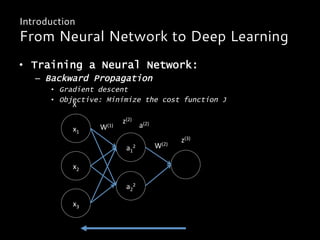
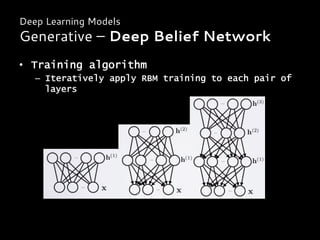
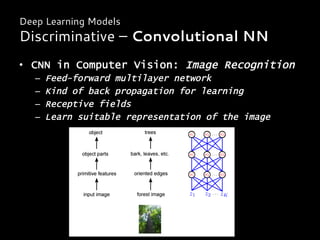
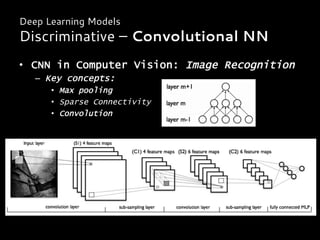
Introduction
From Neural Network to Deep Learning
W1
W2
W3
x1
x2
xn
Sigmoid
func)on
1/(1+e-‐z)
Output
hw(x)
x
=
[x0…xn]T
w
=
[w0…wn]T
z
=
wTx](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deeplearningruoccoshort-150316151934-conversion-gate01/85/Introduction-to-Deep-learning-14-320.jpg)
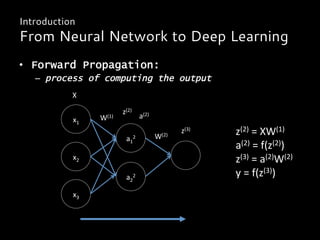






![• [Google] 2013
acquired DNNresearch of professor Geoff
Hinton to improve the state of the art in
image recognition in photos
• [Facebook] 2013
hired deep learning expert Yann to head up
the company’s new artificial intelligence lab
specialized in deep learning for computer
vision and image recognition
• [Pinterest] 2014
announced it has acquired Visual Graph
• [Google + Baidu]:
20G13 - Deep Learning Visual Search Engine
Deep Learning in the Real World
Facts](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deeplearningruoccoshort-150316151934-conversion-gate01/85/Introduction-to-Deep-learning-31-320.jpg)
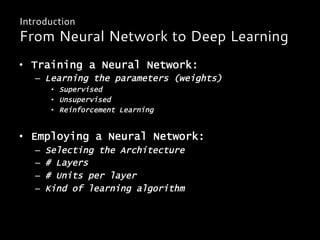
![• [Baidu] 2013:
Deep Learning Visual Search Engine
• [Google] 2013
Photo Search Engine
• [Microsoft] 2013
Search by voice on Xbox console
• [Google] 2014
word2vec for word tagging or text messaging
suggestion
Deep Learning in the Real World
Products](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deeplearningruoccoshort-150316151934-conversion-gate01/85/Introduction-to-Deep-learning-32-320.jpg)
