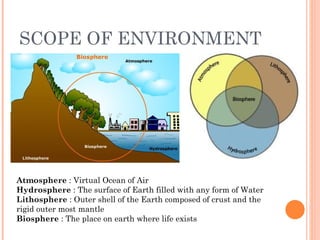
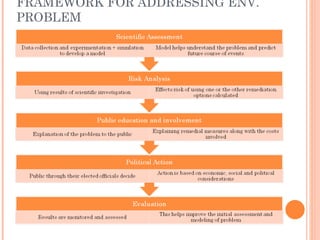
The document outlines the definition, significance, and multidisciplinary nature of environmental studies, emphasizing the need for public awareness and education regarding environmental issues. It discusses the importance of conservation, green technology, and the interdisciplinary approaches necessary for addressing major global environmental problems. The document also highlights various educational initiatives and programs aimed at enhancing awareness and promoting sustainable practices among individuals and communities.