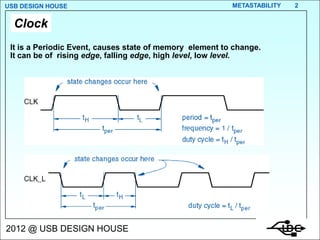
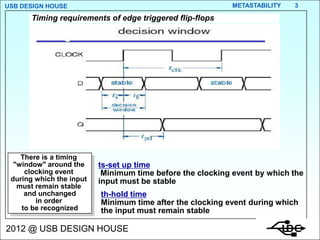
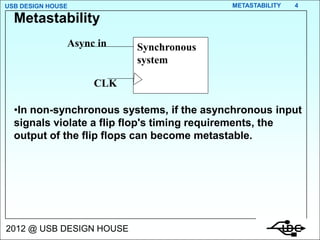
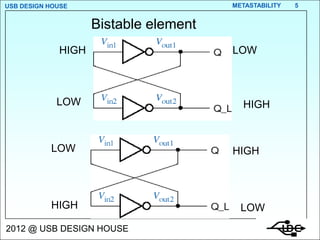
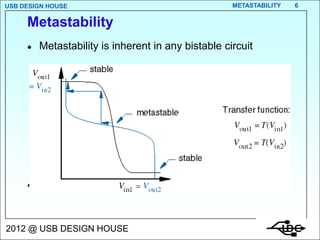
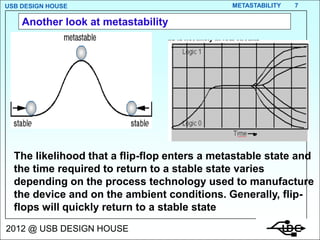
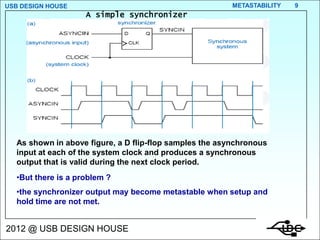
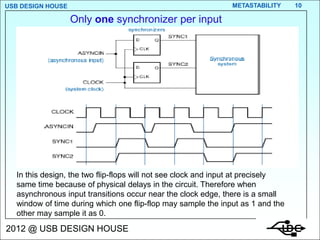
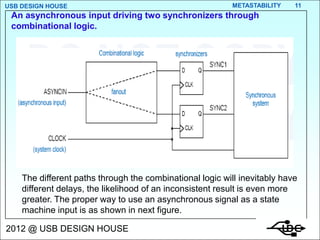
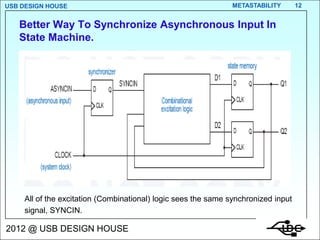
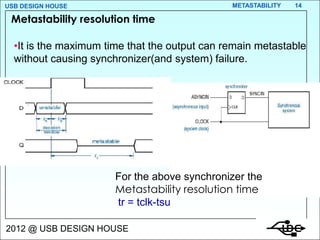
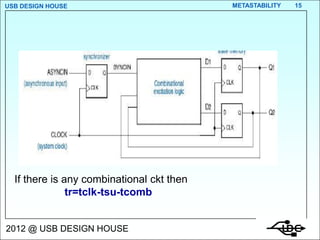
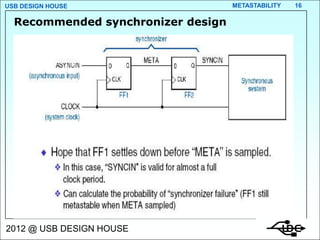
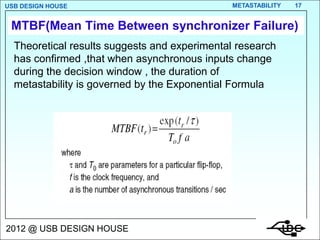
Metastability occurs when the inputs to a flip-flop violate the setup and hold timing requirements around the clock edge. This can cause the output to momentarily exist in an unstable intermediate state between logic 0 and 1. The likelihood of metastability increases when asynchronous inputs are sampled by a synchronous system. Well-designed synchronizers use multiple flip-flops in series to resolve metastability within the clock period and avoid failures. The mean time between synchronizer failures depends on factors like clock speed and input transition rate.