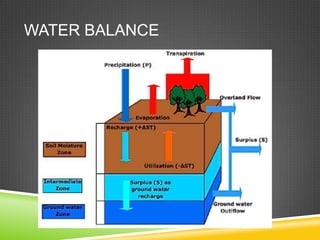
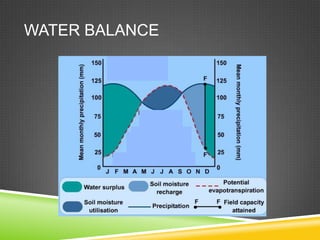
The document discusses the water balance of a drainage basin. It is made up of precipitation inputs, evapotranspiration outputs, and storage changes. Precipitation is the primary water input. Evapotranspiration is water released into the air by evaporation from wet surfaces and transpiration from plants. The water balance equation expresses that precipitation equals total streamflow discharge plus evapotranspiration, plus or minus changes in water storage.