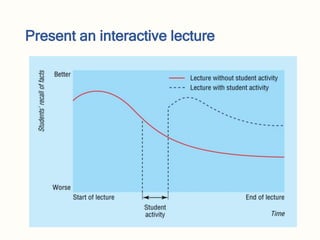
This document provides guidance on how to prepare and present an effective lecture. It recommends choosing 3-5 key concepts to focus on, designing slides with minimal text and clear visuals, and presenting material in a logical sequence while maintaining audience engagement through eye contact and questioning. The presentation should include an introduction to set expectations, the main content, and a conclusion to summarize key points. Creating interactivity through questioning techniques can help assess understanding and encourage discussion.