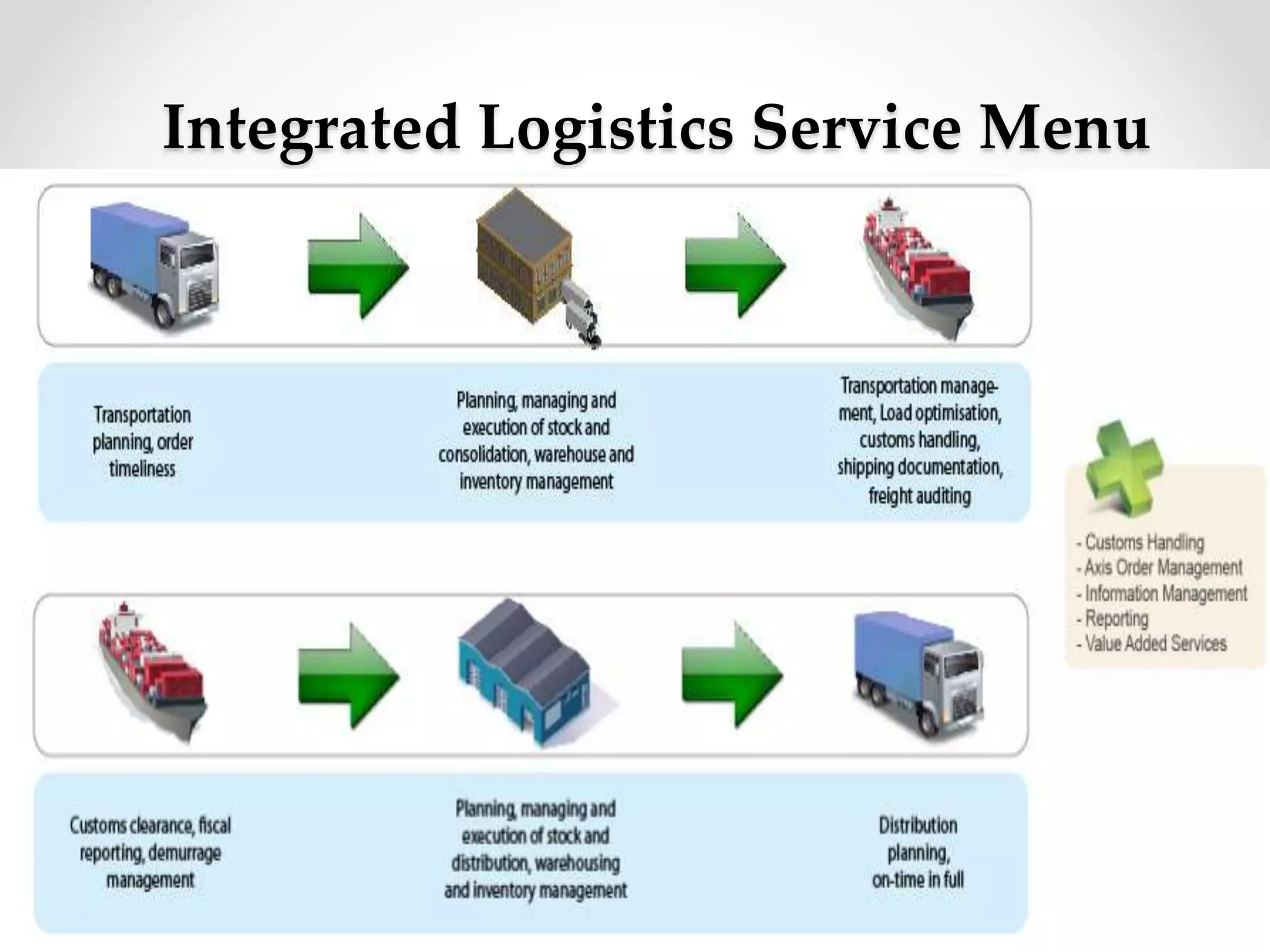
This document summarizes a class on integrated logistics management. It discusses key concepts like anticipating customer needs, acquiring resources to meet needs, and optimizing networks to fulfill requests. It also covers objectives like rapid response and minimum inventory/variance. Variables affecting evaluation include globalization, IT, and supply chain management growth. Operations involve inbound/outbound logistics. Key factors are shippers, suppliers, carriers, and government regulation. Integrated logistics provides advantages to companies by improving customer service and reducing costs through coordination across the supply chain.