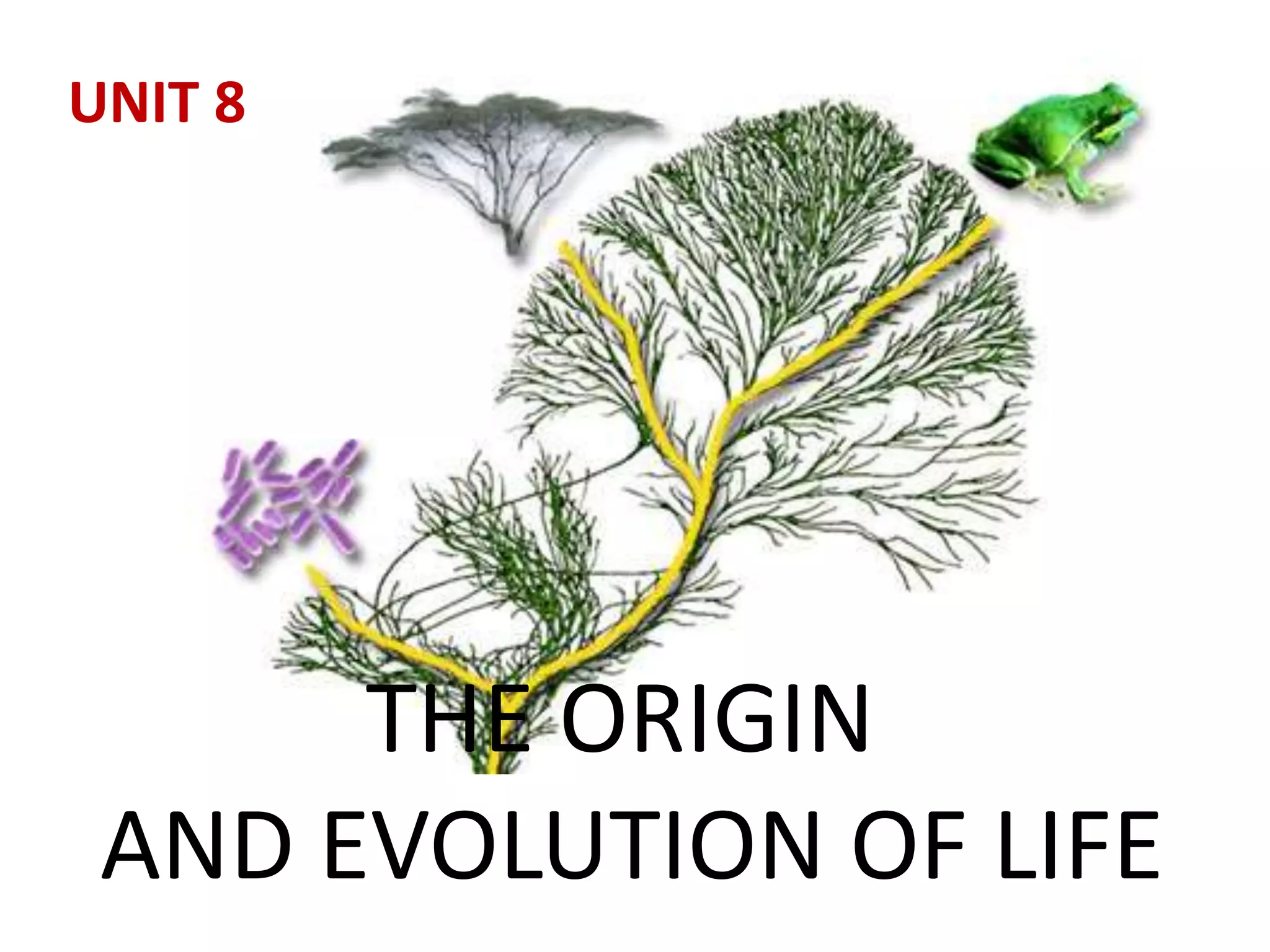
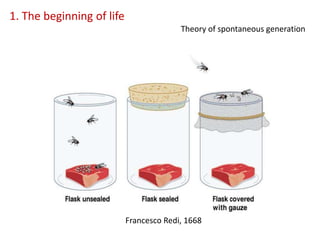
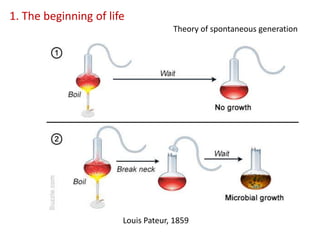
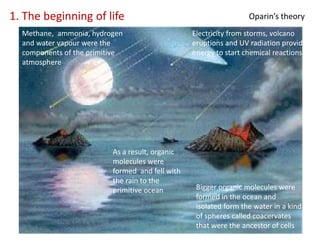
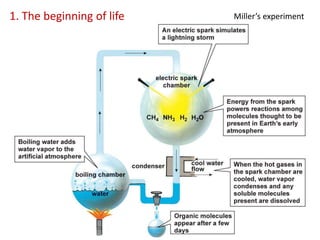
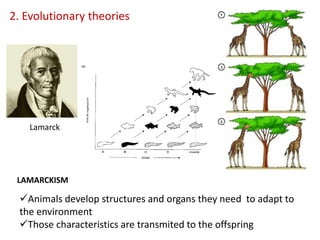
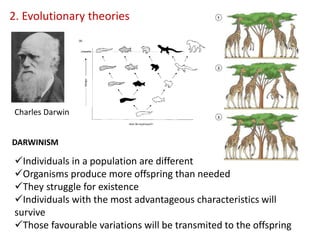
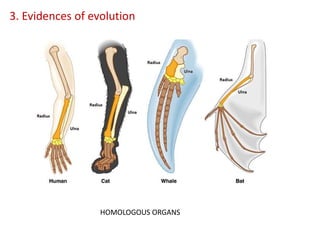
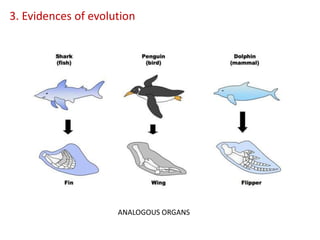
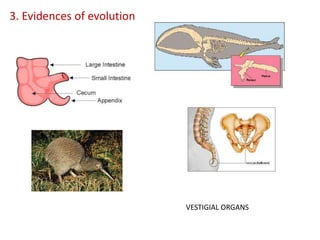
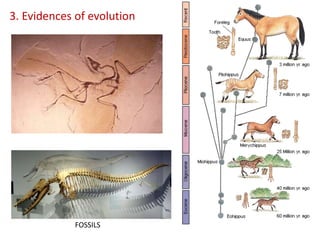
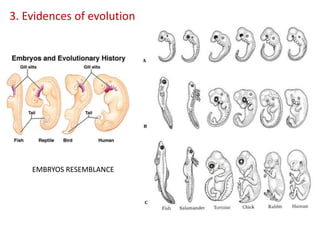
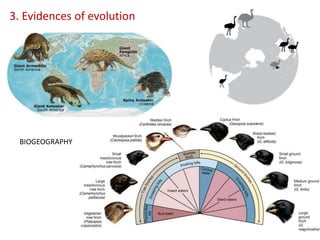
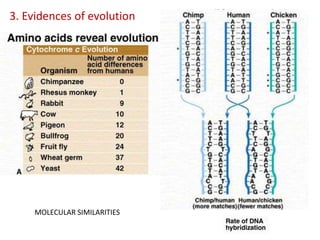
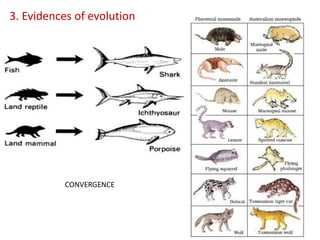
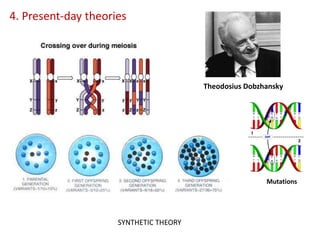
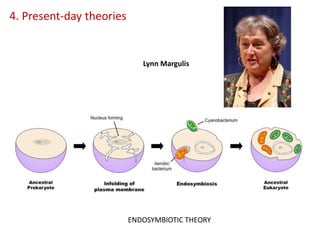
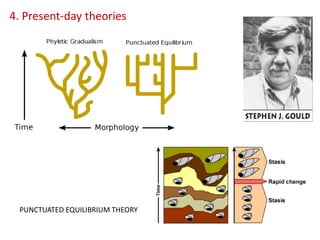
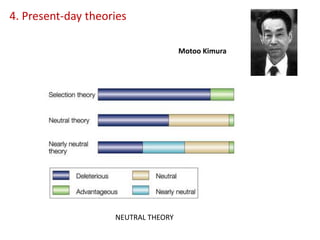
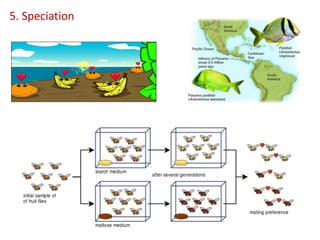
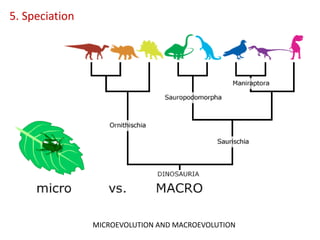
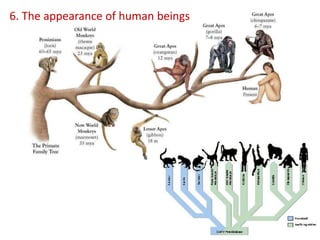
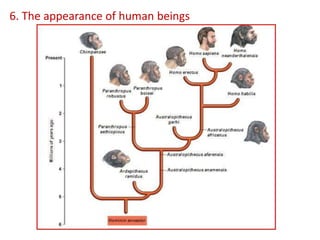
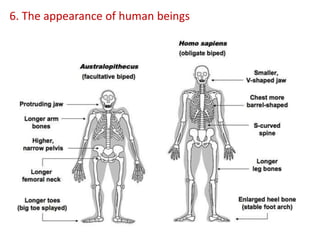
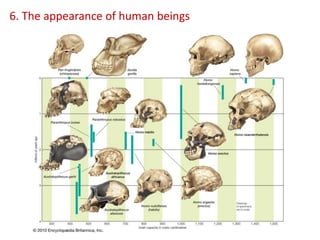
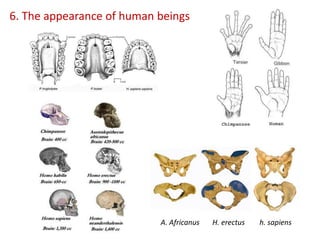
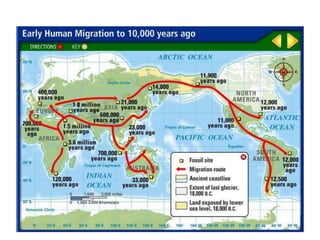
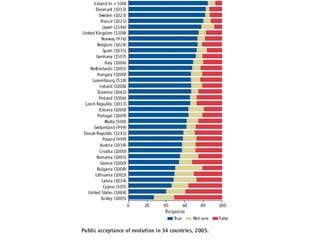
This document summarizes theories about the origin and evolution of life. It discusses early theories from the 1600s-1920s about spontaneous generation and the formation of organic molecules in the primitive atmosphere. It also describes the Miller experiment and panspermia theory. Current theories propose that hydrothermal vents provided energy and vesicles formed that could self-replicate, with RNA as the first nucleic acid. The document then outlines evolutionary theories from Lamarck to Darwin and modern synthesis. It lists evidence of evolution such as homologous/analogous structures, vestigial organs, fossils, and molecular similarities. Finally, it discusses present-day theories including punctuated equilibrium and neutral theory, as well as speciation and the appearance of human beings