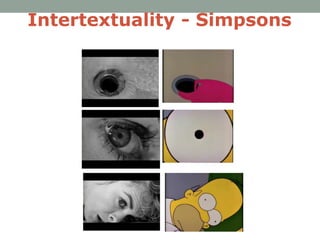
This document defines and provides examples of intertextuality. Intertextuality refers to the shaping of a text's meaning by another text through references, allusions, and transformations between texts. It is based on the idea that texts do not exist independently, but rather absorb and transform influences from other texts. Examples provided include film remakes, references between TV shows and other media, and how genre conventions create intertextual frameworks that link texts together through shared influences.