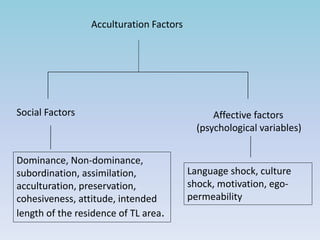
The Acculturation Model, developed by John H. Schumann in 1978, posits that second language acquisition is influenced by social-psychological integration and the extent of learners' acculturation to the target language group. Key factors include social dominance between groups, integration strategies, and affective factors such as motivation and cultural shock. While the model highlights the relationship between social factors and language learning, it faces criticism for not specifying combinations of factors or adequately addressing how they affect language proficiency over time.