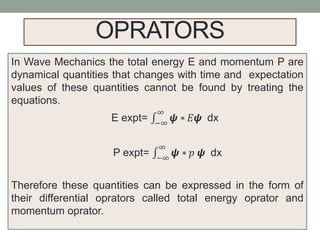
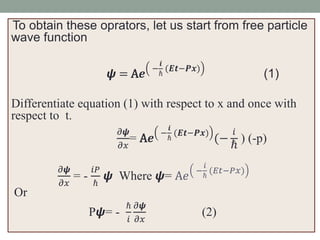
The document discusses the formulation of operators in wave mechanics, specifically the total energy and momentum operators based on the wave function of a free particle. It derives these operators through differentiation and verifies their validity using the Schrödinger equation. The expressions for the momentum and total energy operators are provided, highlighting their role in quantum mechanics.