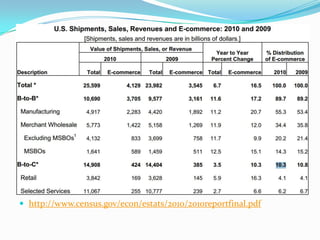
This document defines key terms related to e-business and discusses various aspects of conducting business online. It defines e-business as businesses that utilize internet technologies, and discusses business intelligence, e-commerce, CRM, SCM, and ERP. It outlines different types of e-business models including B2B, B2C, C2C, and others. The document also distinguishes between e-business and e-commerce, describing how e-business aims to improve overall business performance through connectivity, while e-commerce focuses on online marketing, selling and buying. Finally, it discusses advantages and disadvantages of e-business, as well as examples of e-marketing activities.