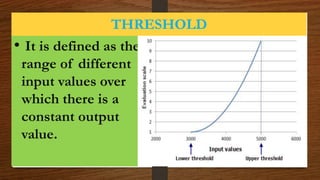
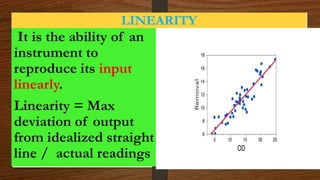
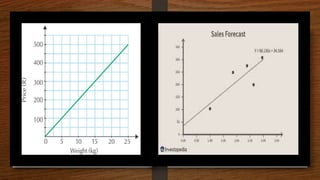
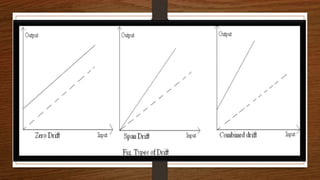
This document discusses the static and dynamic characteristics of measurement systems. Static characteristics refer to a system's performance when the input is constant or changing slowly, and include accuracy, precision, resolution, and sensitivity. Dynamic characteristics refer to how a system responds when the input is changing rapidly over time, and include speed of response, fidelity, lag, and overshoot. The document provides definitions and explanations of these key static and dynamic terms.