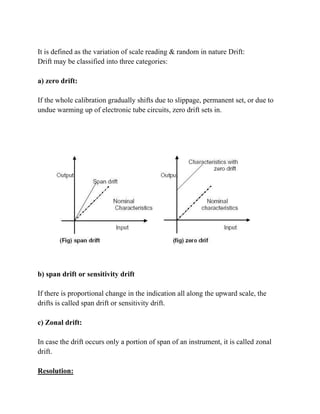
The document discusses the static and dynamic characteristics of measurement systems. Static characteristics include accuracy, precision, sensitivity, linearity, reproducibility, repeatability, resolution, threshold, drift, stability, tolerance, and range. These define how instruments measure quantities that do not vary much over time. Dynamic characteristics include speed of response, measuring lag, fidelity, and dynamic error, and describe how instruments respond to rapidly changing quantities. Accuracy measures closeness to the true value, while precision refers to reproducibility of measurements. Sensitivity is the smallest detectable change and resolution is the minimum detectable increment.