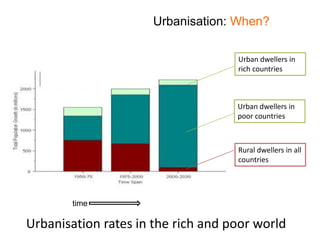
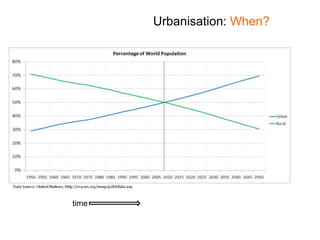
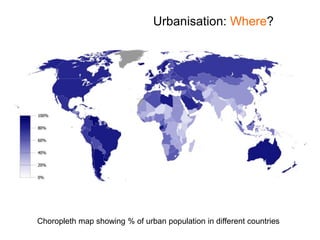
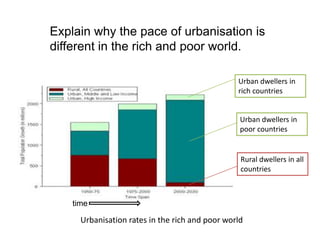
Urbanisation refers to the increasing proportion of people living in cities and urban areas. It began rapidly in poor countries in the mid-20th century as people migrated from rural areas to cities at a rate of 20% per year, driven by difficult rural living conditions and the concentration of jobs and services in urban centers. In rich countries, urbanisation accelerated during the Industrial Revolution as new factory and shipyard jobs drew people to towns and cities, while mechanized farming led to rural job losses. More recently, urbanisation has slowed in rich nations and some have experienced counter-urbanization, though cities are now attracting residents back to redeveloped inner areas.