Embed presentation
Downloaded 231 times


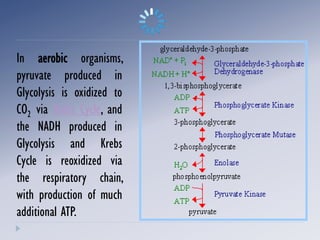
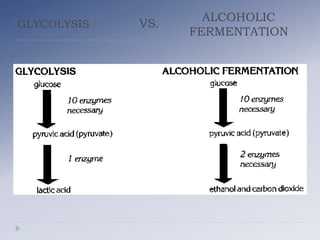
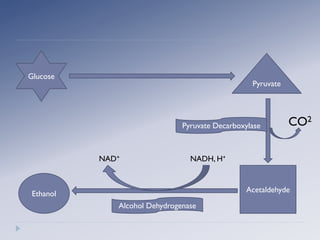
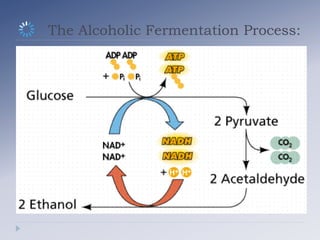
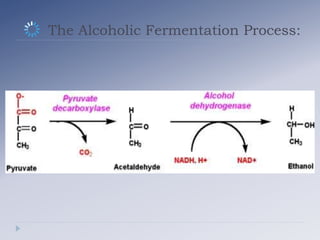
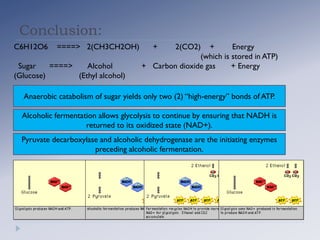


Alcoholic fermentation is a biological process whereby sugars are converted into cellular energy and produce ethanol and carbon dioxide as waste products. It occurs in the cytosol of yeasts and other anaerobic organisms. The process involves glycolysis producing pyruvate, which is then converted to acetaldehyde by pyruvate decarboxylase and further converted to ethanol by alcohol dehydrogenase, regenerating NAD+ needed for glycolysis to continue without oxygen present. In conclusion, alcoholic fermentation allows glycolysis to continue under anaerobic conditions by oxidizing NADH back to NAD+ through the production of ethanol and carbon dioxide from sugars like glucose.








