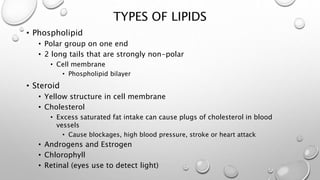
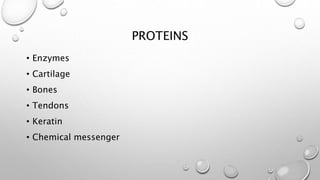
This document discusses the four major macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) that make up living things. It explains that macromolecules are polymers formed from smaller monomers through dehydration synthesis. Carbohydrates such as starch and glycogen store energy, lipids are used for long-term energy storage and insulation, proteins have many functions like enzymes and structure, and nucleic acids like DNA and RNA control cell functions and store genetic information. All macromolecules are made through the same process of joining monomers like amino acids or nucleotides.