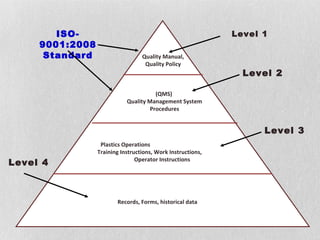
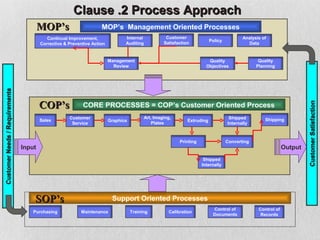
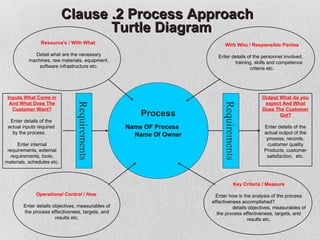
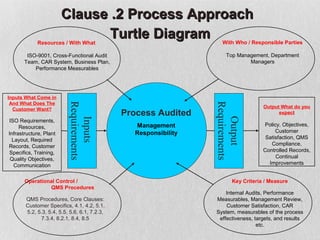
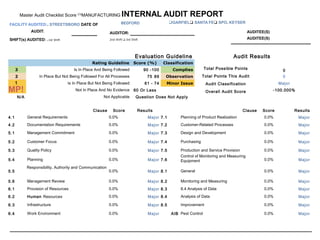
The document discusses documentation requirements for ISO 9001 certification. It notes that some organizations see ISO certification as simply a way to get a certificate, but that the true value comes from implementing an effective quality management system. It emphasizes that top management must plan and implement the QMS. The document also discusses reducing documentation requirements in the revised ISO 9001 standard and taking a lean approach to documentation to avoid creating an unnecessary paperwork burden. It proposes a tiered documentation structure with a high-level quality manual at the top level and more detailed procedures, instructions, and records at lower levels.