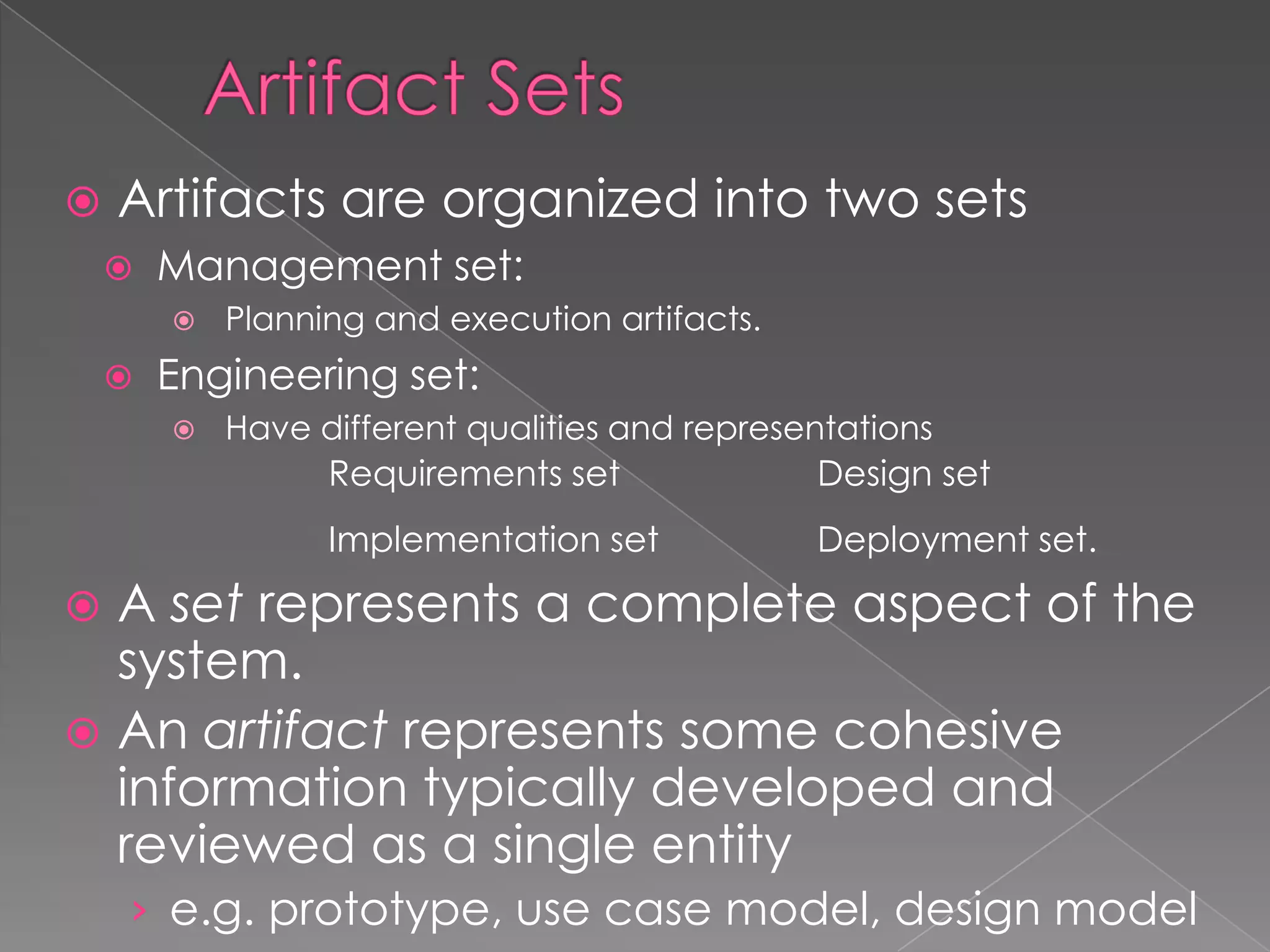
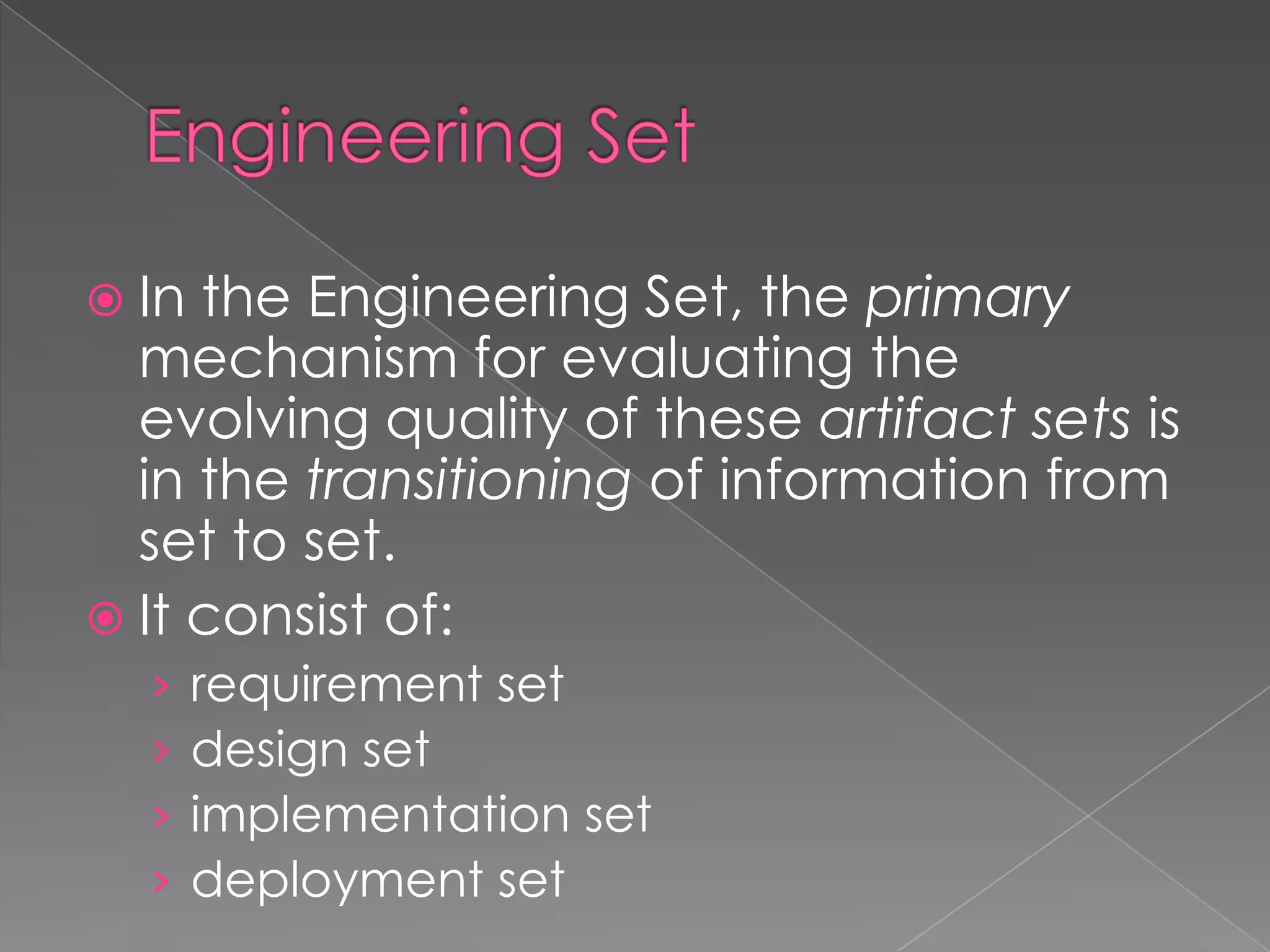
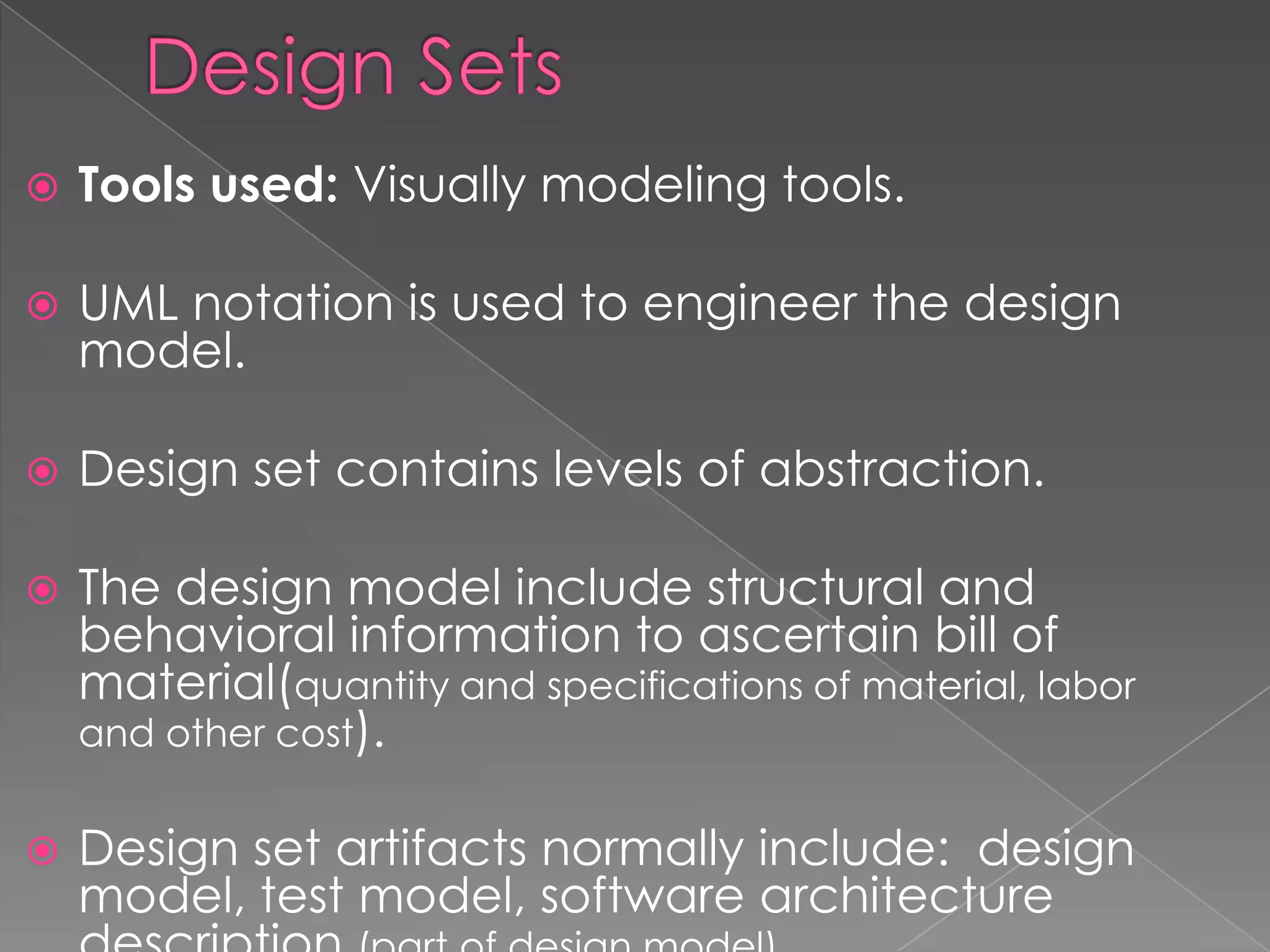
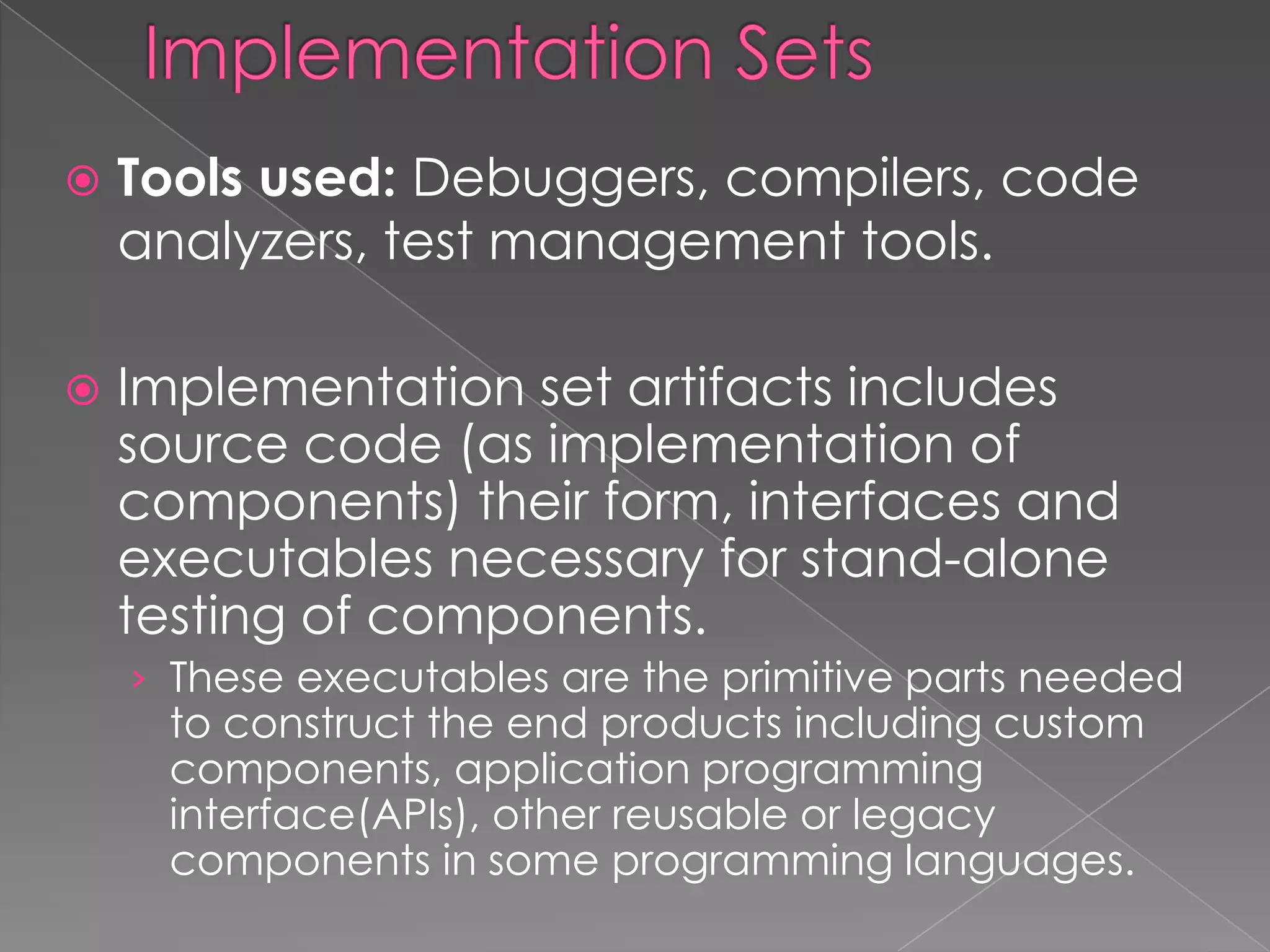
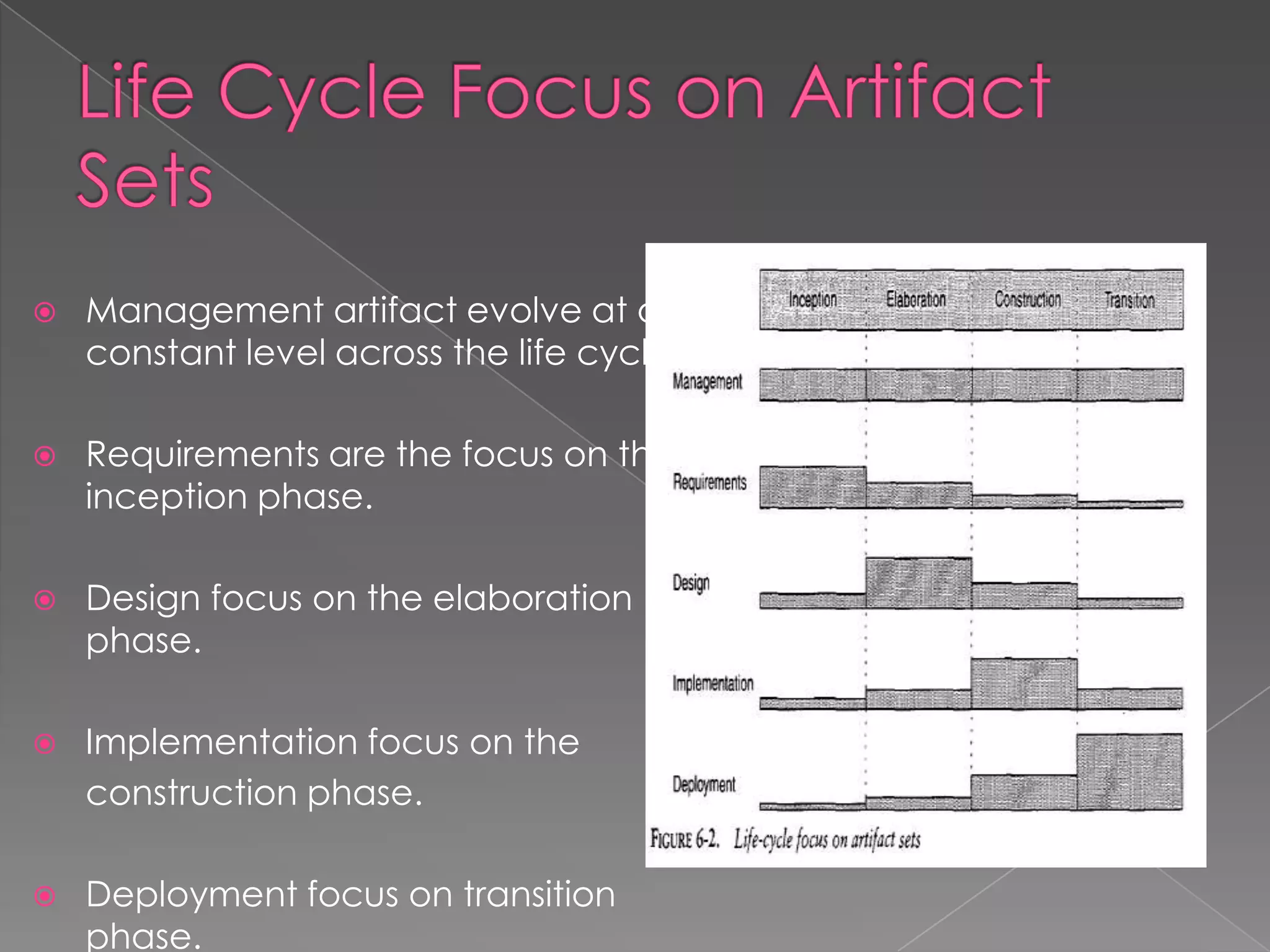
This document discusses software project management artifacts. Artifacts are organized into management and engineering sets. The management set includes artifacts like the work breakdown structure, business case, and software development plan. The engineering set includes requirement, design, implementation, and deployment artifact sets. Each set captures information through various notations and tools to manage the software development lifecycle.