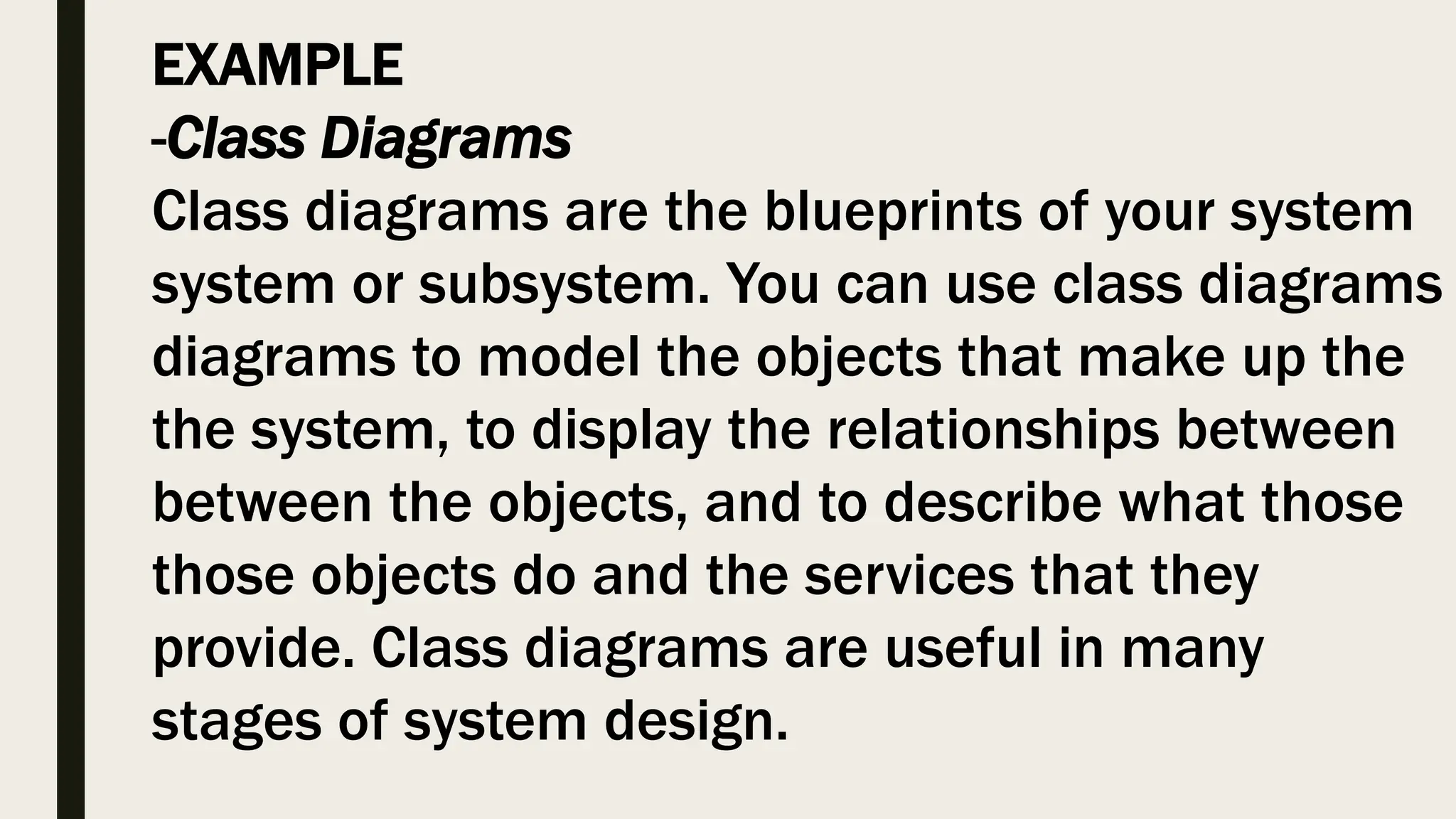
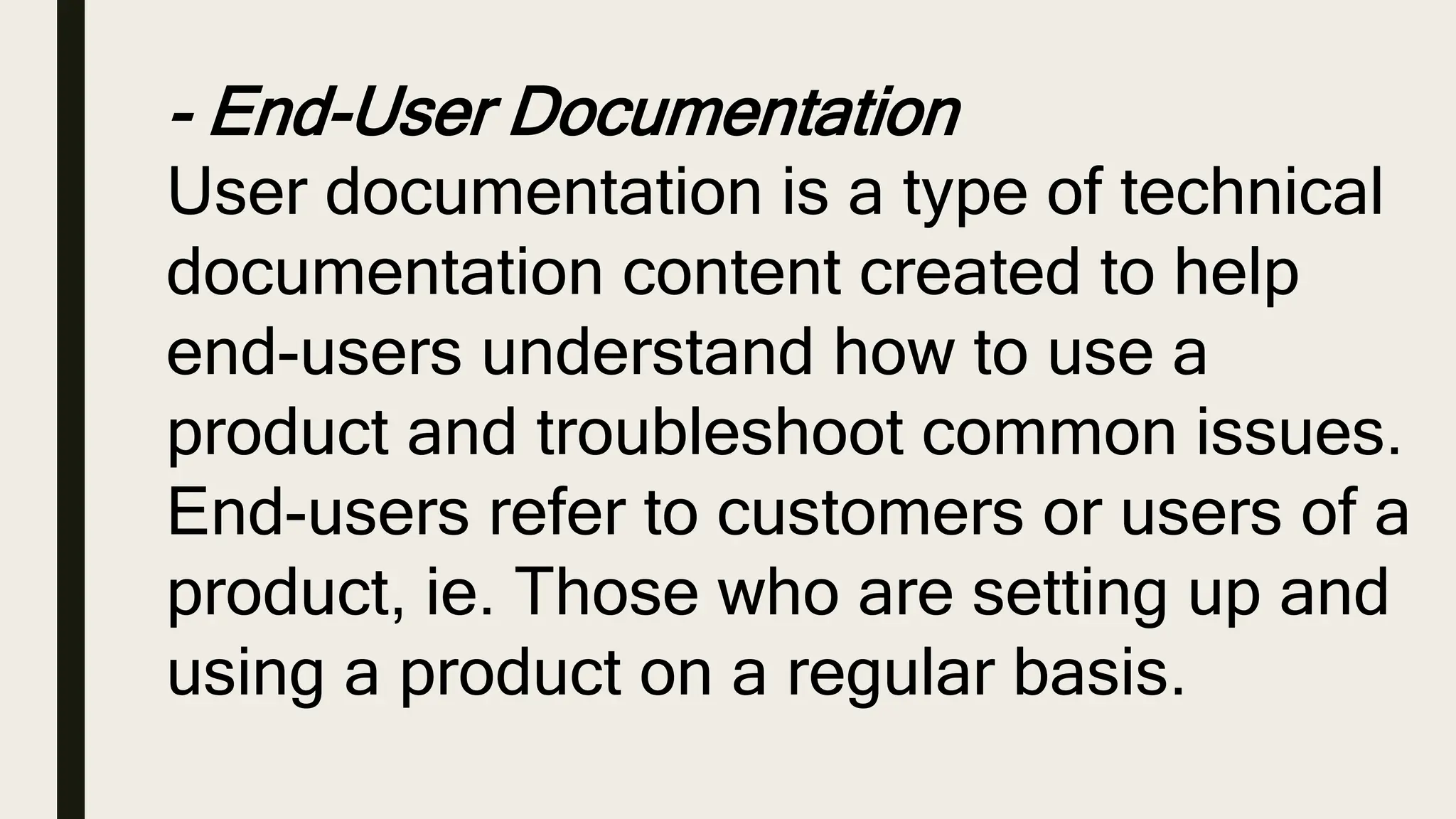
An artifact is any tangible by-product created during the software development process, including documents, files, diagrams, and code. There are several types of artifacts like project management artifacts that help plan and organize a project, code artifacts created by developers like test suites and compiled code, and documentation artifacts for end-users and internal teams. Artifacts help describe the architecture and design of the software, aid the development process, and provide documentation for users.