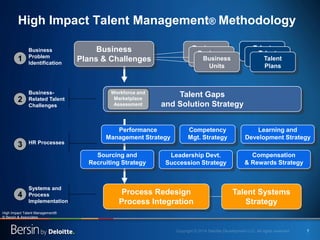
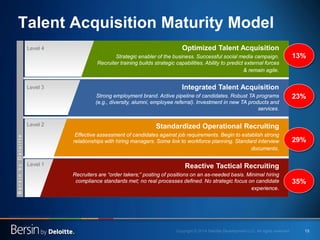
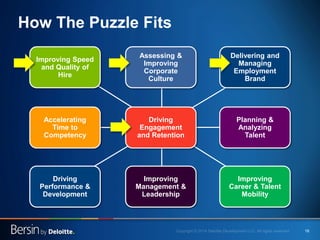
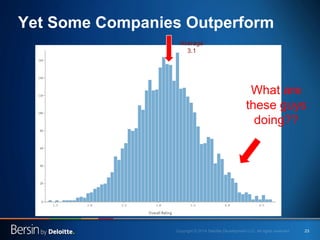
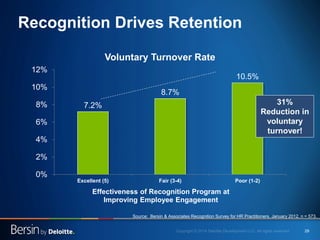
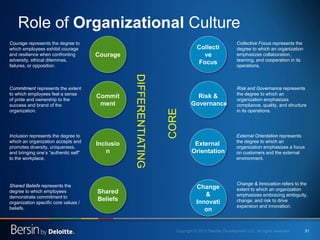
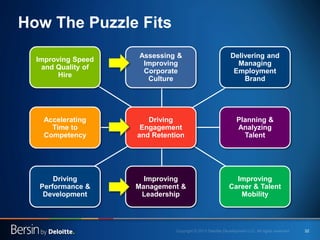
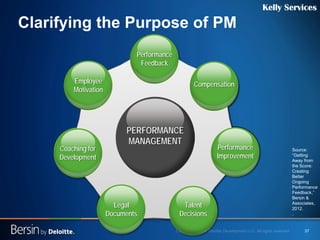
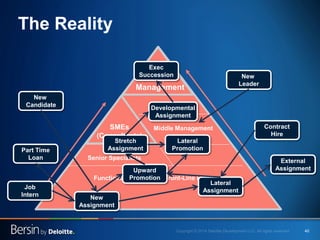
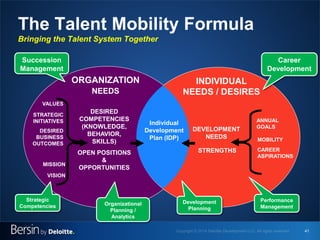
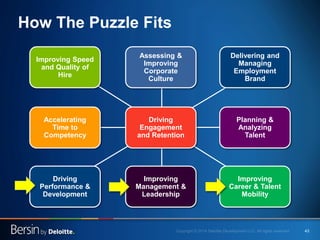
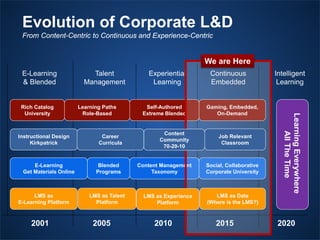
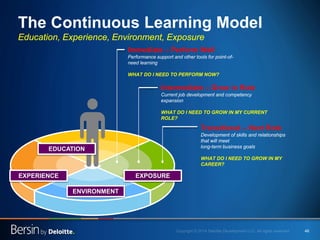
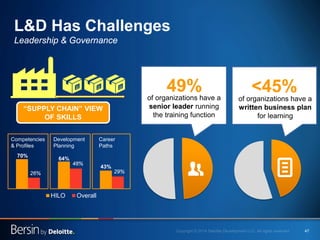
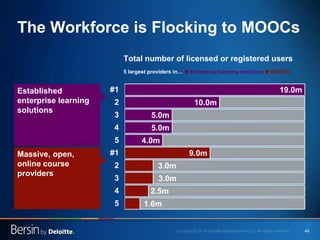
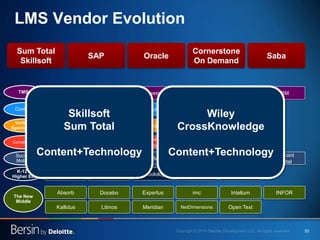
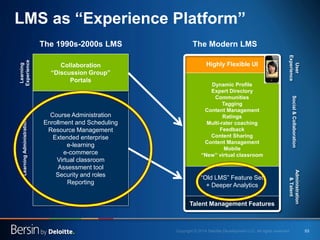
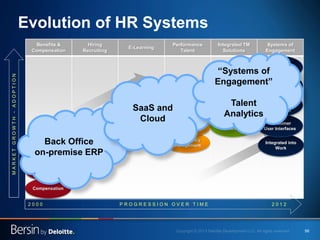
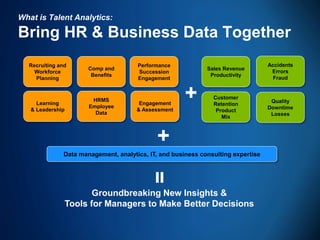
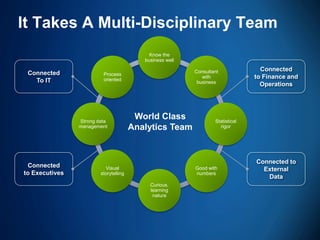
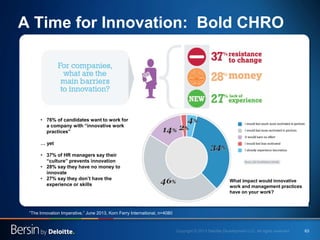
The document outlines the evolving landscape of talent management and the need for organizations to adopt integrated and high-impact talent management strategies. Key priorities for global talent management include diversity, retention, employee engagement, performance management, and talent acquisition, all driven by the shift in employee expectations towards career experiences rather than traditional career paths. It emphasizes the necessity for organizations to create an adaptive workforce culture and modernize learning and development approaches to enhance employee engagement and overall organizational performance.