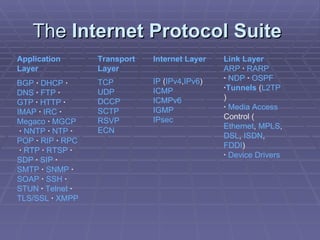
The document summarizes the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP), which is the set of communication protocols used for the Internet and similar networks. It consists of four layers - link, internet, transport, and application layers. Some important protocols included in each layer are IP, TCP, UDP, and higher-level protocols like HTTP, FTP, and SMTP. The TCP/IP model uses encapsulation, adding headers at each layer to abstract the protocols and allow communication across networks.