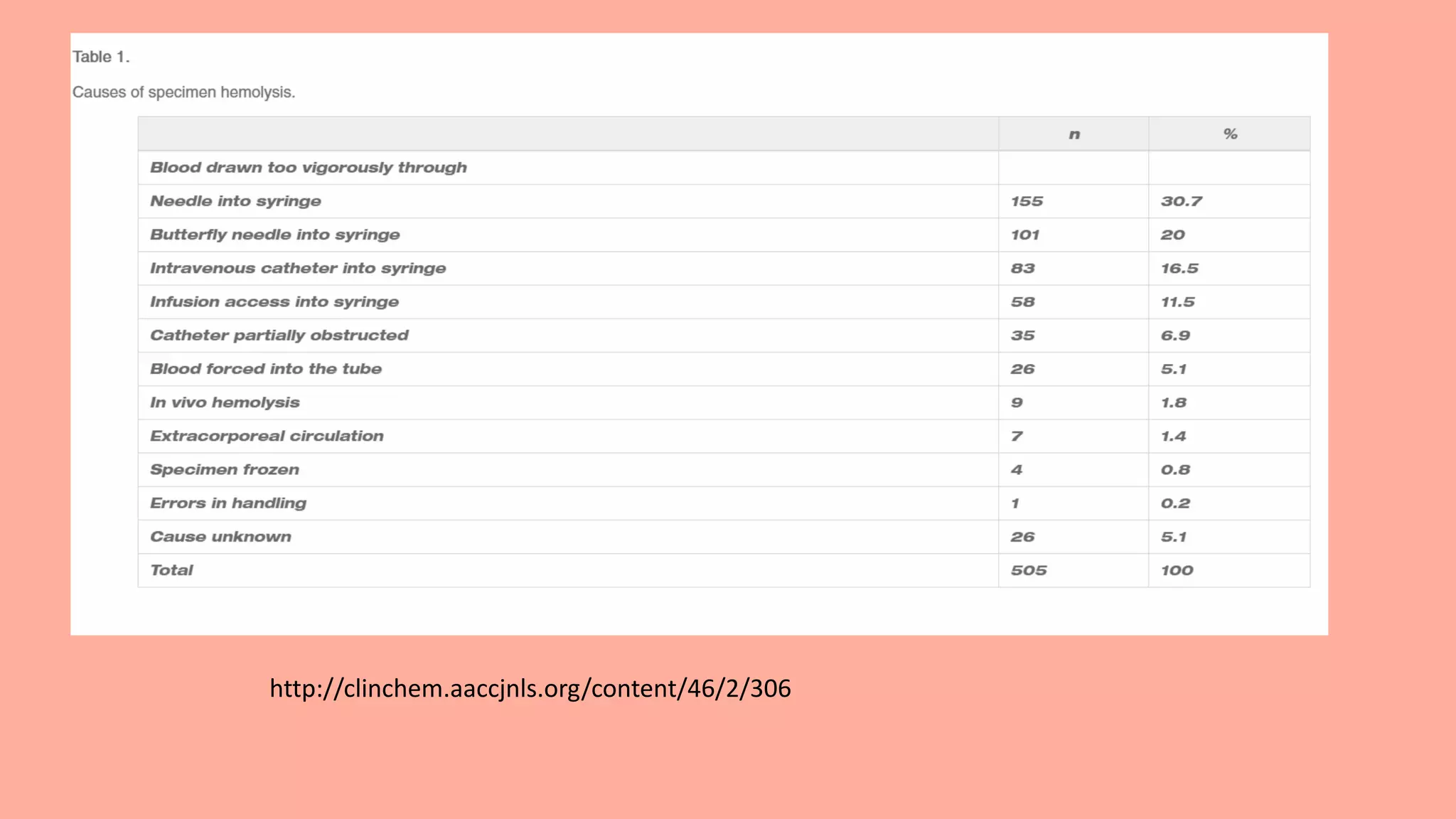
Hemolysis, or the rupturing of red blood cells, can occur in vivo or in vitro and is caused by hemolysins damaging the cell membrane. It accounts for about 60% of rejected blood specimens and can be caused by improper collection or handling techniques. Hemolysis causes problems in chemistry, hematology, and blood bank testing due to interference from the released cell contents. Careful venipuncture and avoidance of techniques that can damage cells, such as using too small a needle or leaving a tourniquet on too long, can prevent hemolysis.








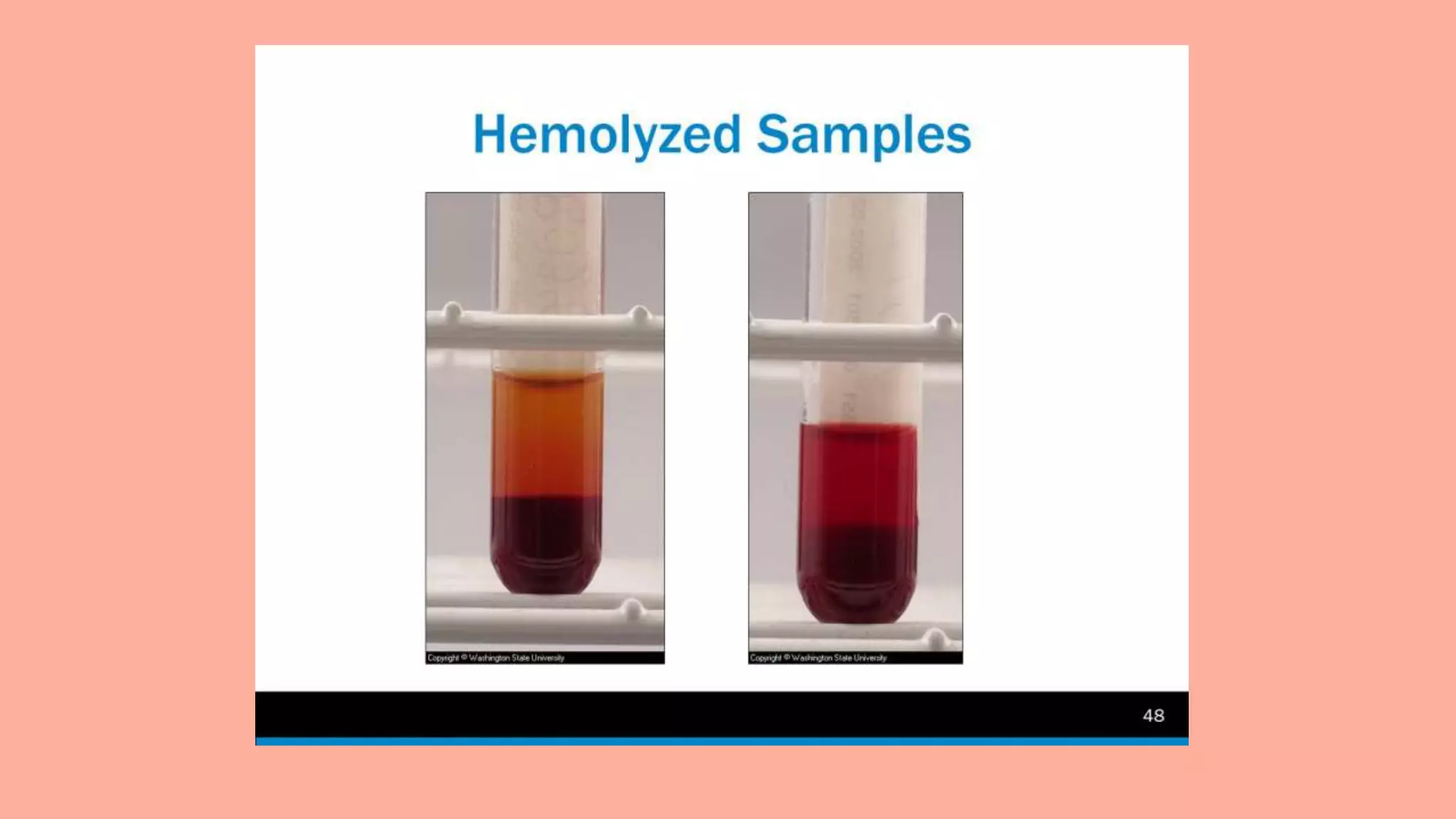

![Hemolysis of blood
samples. Red blood cells
without (left and middle)
and with (right) hemolysis.
If as little as 0.5% of the red
blood cells are hemolyzed,
the released hemoglobin
will cause the serum or
plasma to appear pale red
or cherry red in color.[5]
Note that the hemolyzed
sample appears clearer,
because there are
significantly fewer cells to
scatter light.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hemolysis-190203042328/75/Hemolysis-12-2048.jpg)

