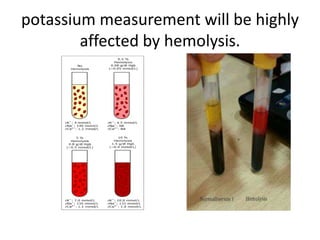
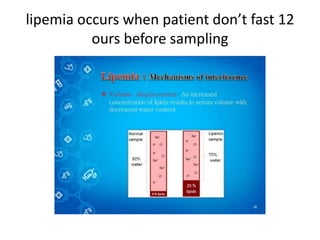
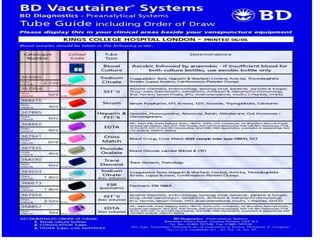
The document discusses the pre-analytical phase of laboratory medicine. It describes the proper procedure for blood collection, including identifying the vein, cleaning the area, inserting the needle at a 15-30 degree angle, and releasing the tourniquet within one minute of drawing blood. It also discusses effects of factors like age, sex, diet, drugs, exercise and diagnostic procedures on blood samples and potential issues like hemolysis, lipemia, and effects of anticoagulants on electrolyte measurements. Proper collection techniques and use of dry heparinized tubes are recommended to avoid interference in test results.