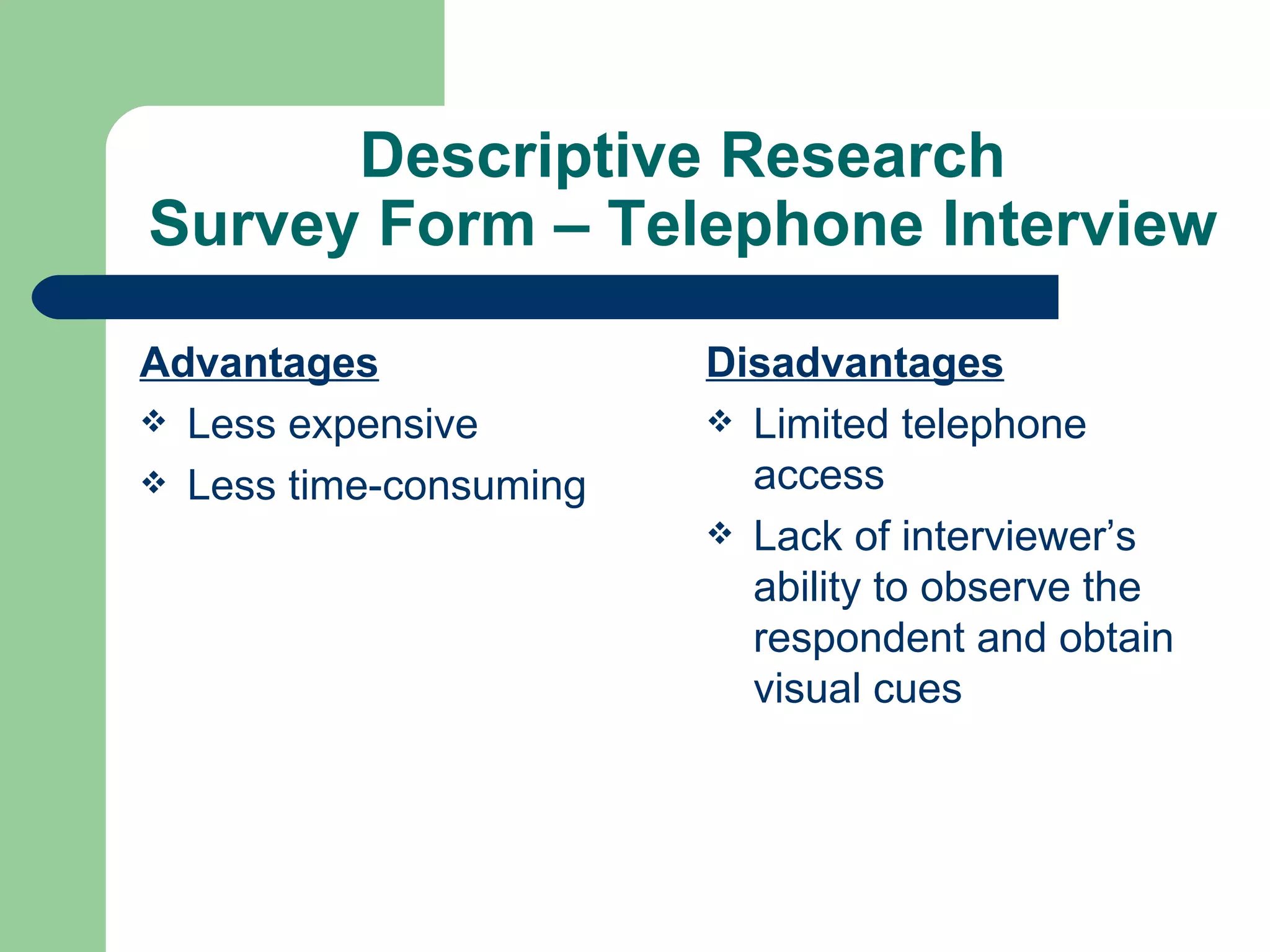
Descriptive research involves collecting and organizing quantitative and qualitative data to describe events or situations without looking for relationships or causes. It aims to answer questions about what currently exists, such as teachers' attitudes toward technology or how students interact with educational programs. Common descriptive research methods include surveys, interviews, observations, and collecting student portfolios. Descriptive research provides an understanding of current conditions that can help identify areas for improvement.