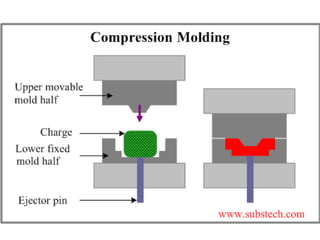
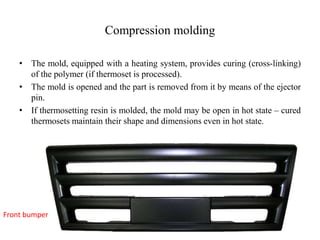
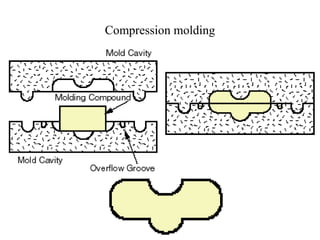
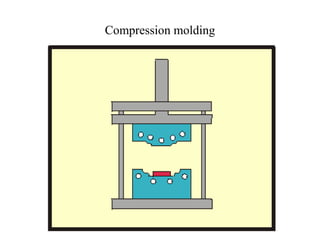
Compression molding is a process where a preheated polymer material is placed into a heated mold cavity. The mold closes with force to push the material against all areas of the mold. Heat and pressure are applied to cure the material into the shape of the mold cavity. Both thermoset and some thermoplastic materials can be molded in this way. The process is used to make large, intricate parts for various applications like electronics casing, appliances, automotive parts, and more. Key factors for success include the amount of material, heating time and technique, applied force, and cooling time and technique. Common materials molded are epoxies, urea formaldehyde, melamine formaldehyde, and phenolics.