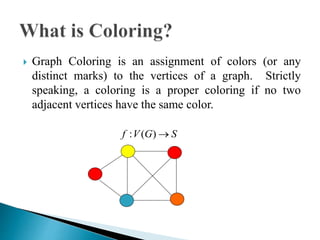
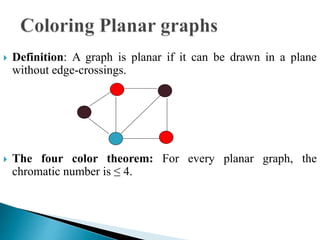
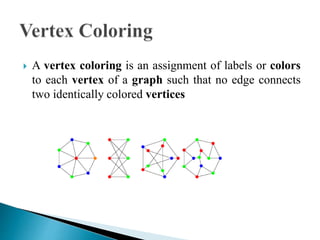
The document discusses graph coloring and its applications. It defines graph coloring as assigning colors to graph vertices such that no adjacent vertices have the same color. It also discusses the four color theorem, which states that any planar map can be colored with four or fewer colors. Finally, it provides an overview of backtracking as an algorithmic approach for solving graph coloring problems.