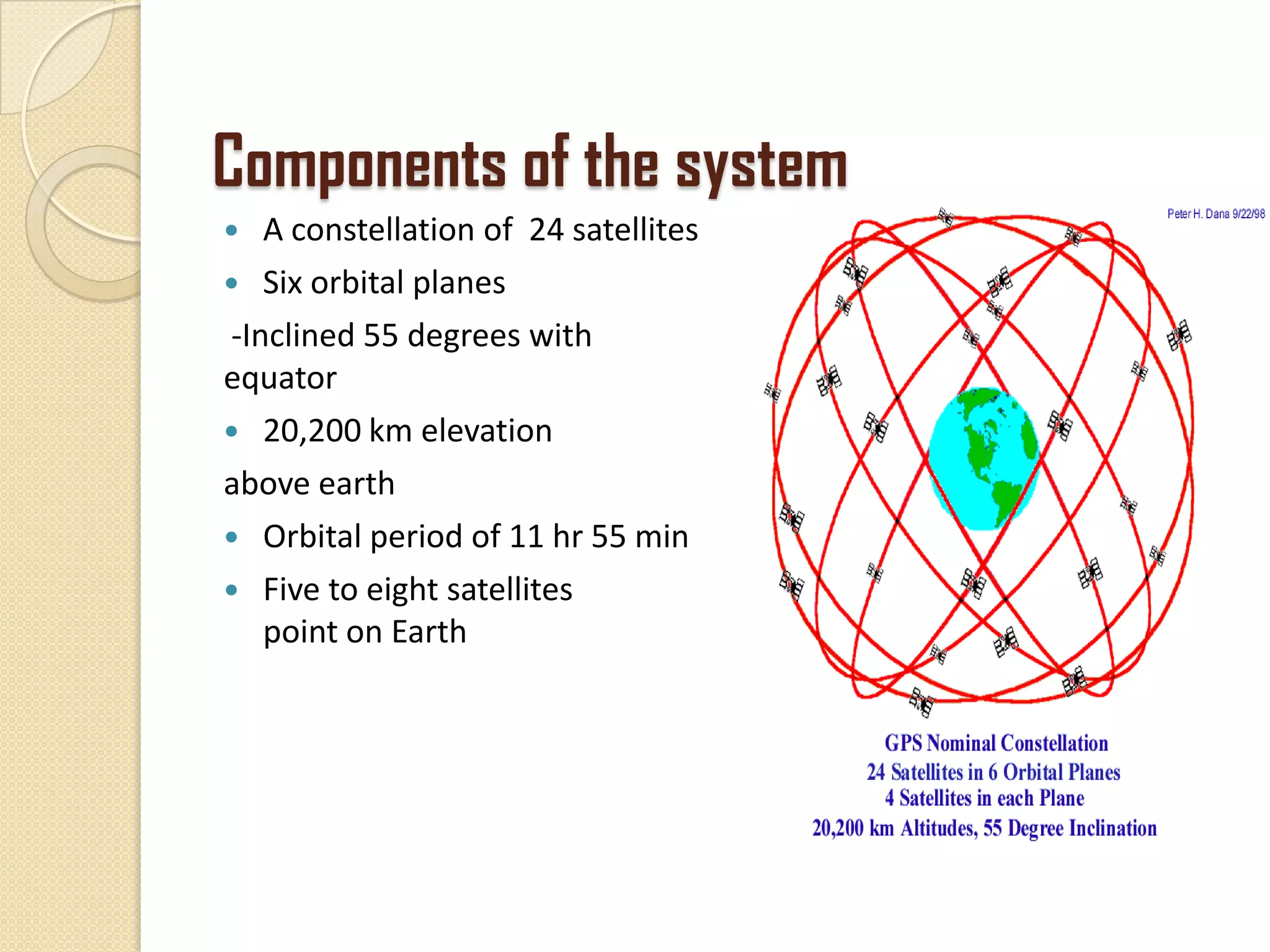
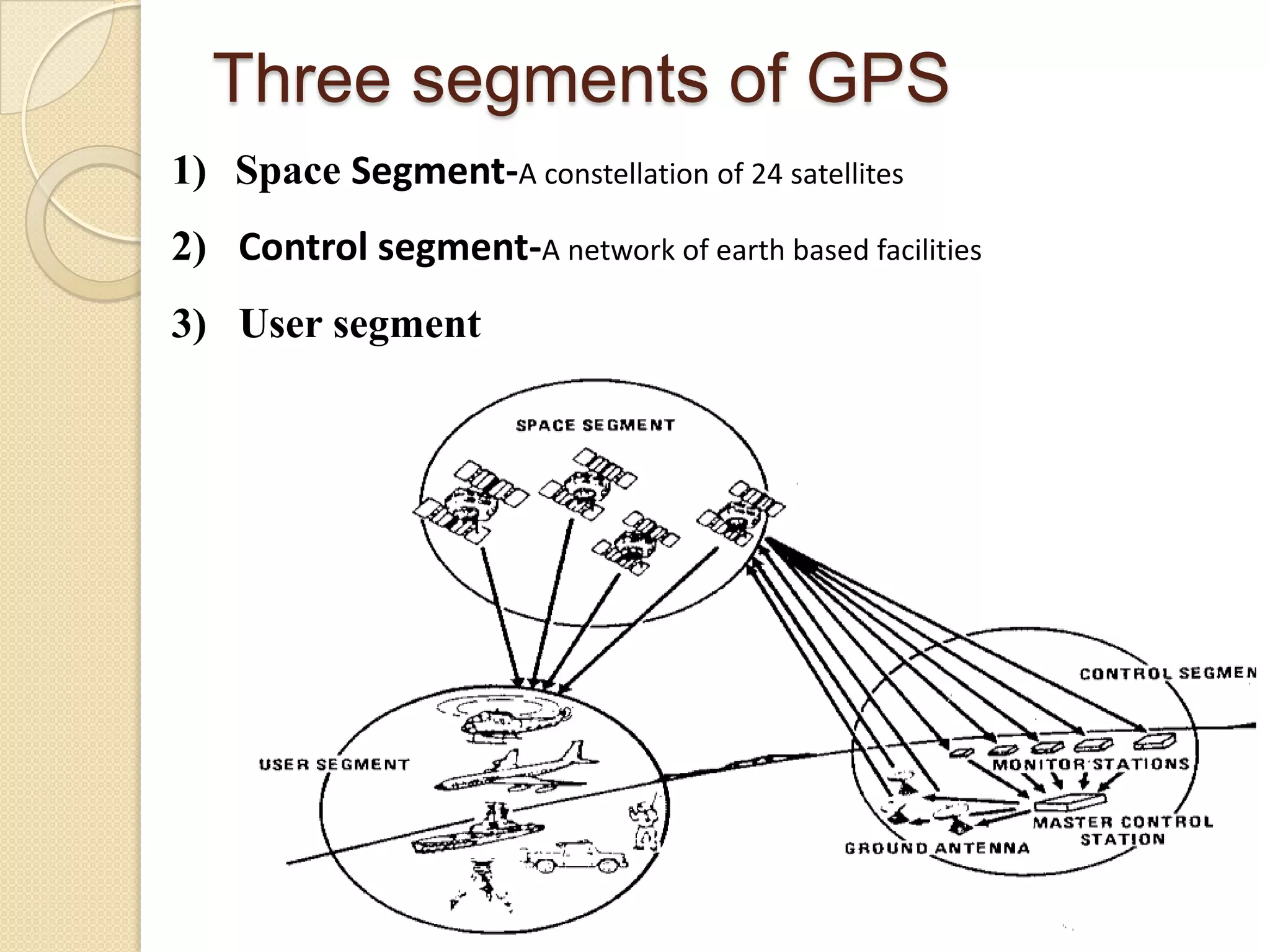
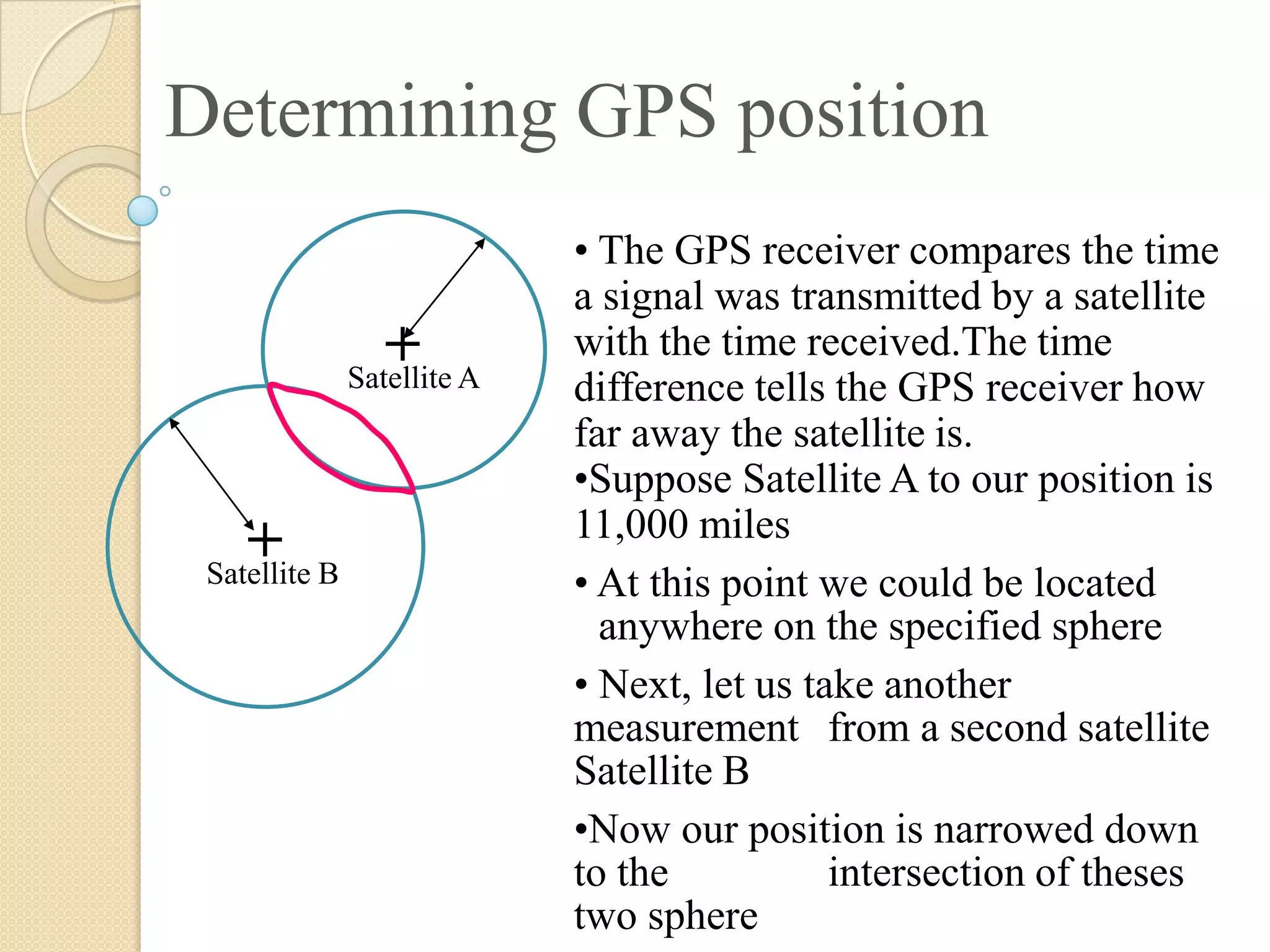
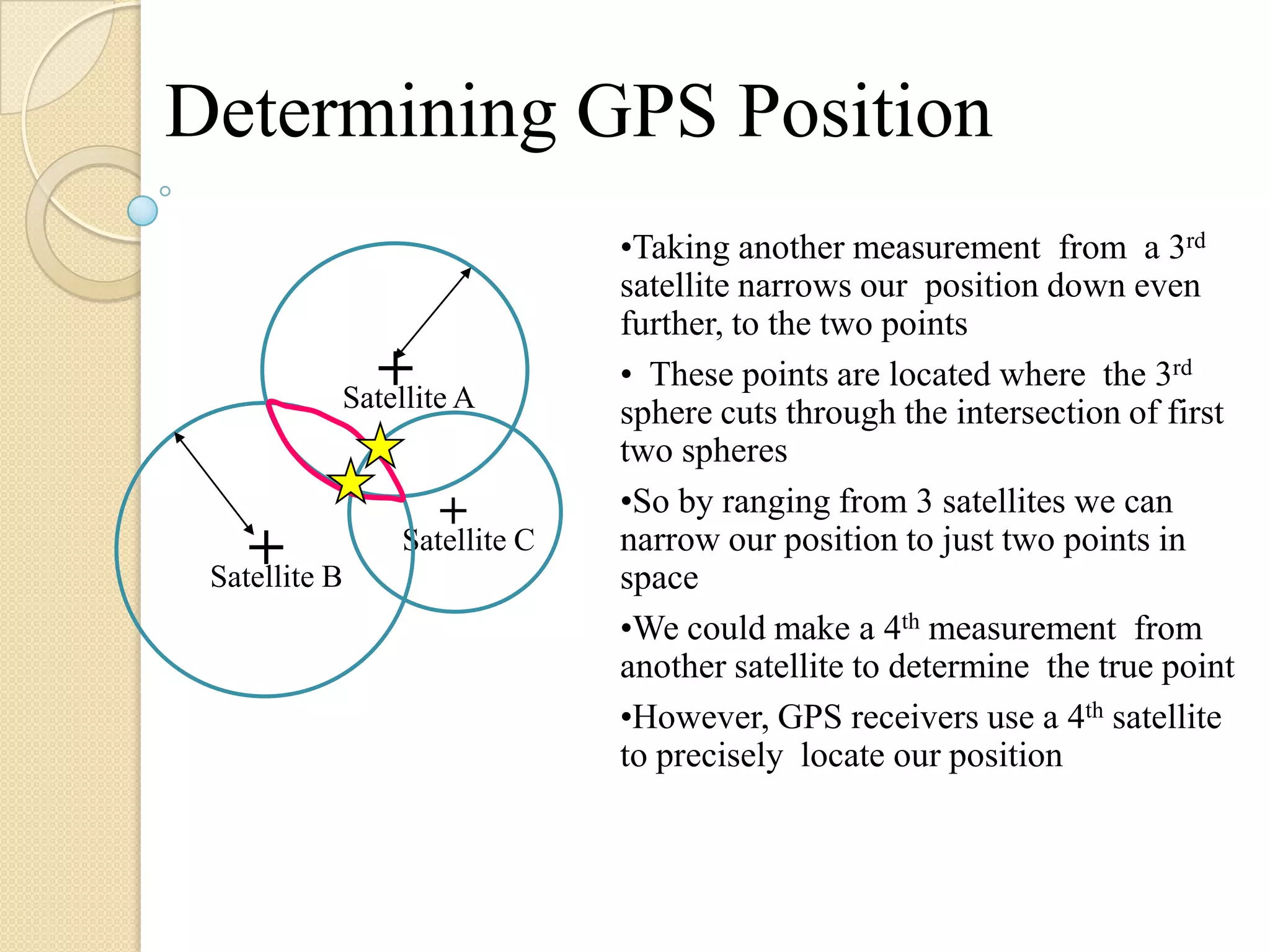
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based navigation system that provides location and time information to users with GPS receivers. It was developed by the U.S. Department of Defense in the 1970s to overcome limitations of previous navigation systems. GPS uses 24 satellites that orbit the Earth and transmit signals that allow receivers to determine their precise location, speed and direction. The system works by calculating the time delay of signals from at least 3 satellites to determine the user's position through trilateration. GPS has both military and civilian applications including vehicle navigation, map-making, tracking valuable assets, and outdoor recreational activities.