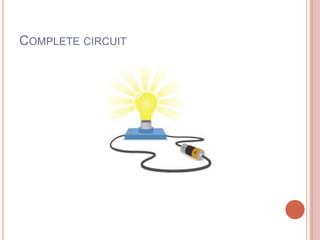
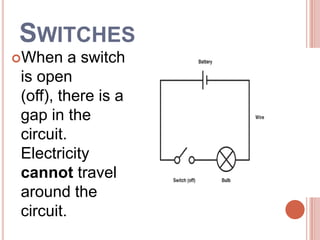
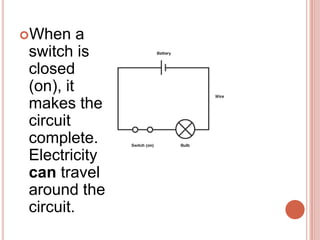
Electricity has dramatically changed daily life over the past 100 years. Scientists like Benjamin Franklin, Thomas Edison, and Nikola Tesla helped uncover the principles of electricity. A battery produces electricity through a chemical reaction between two different metals in a solution, generating a flow of electrons. This electricity can power devices when wires provide a complete circuit between the battery's positive and negative terminals. Switches allow control of whether a circuit is complete or incomplete to regulate the electricity's flow.