This document provides information on using modifiers including:
- Defining good and well as modifiers and their proper uses
- Explaining the three types of modifiers: adjectives, adverbs, and phrases/clauses
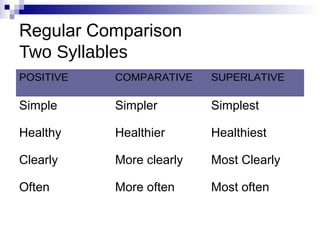
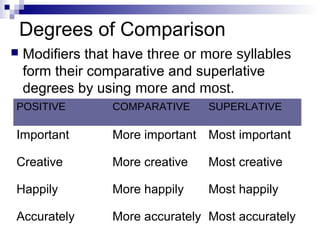
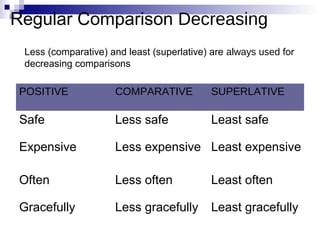
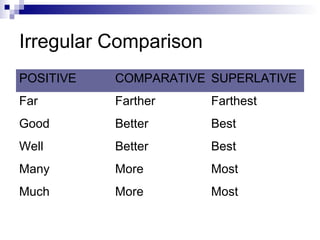
- Detailing the three degrees of comparison for modifiers: positive, comparative, superlative
- Guiding when to use more/most and less/least versus -er/-est for irregular comparisons