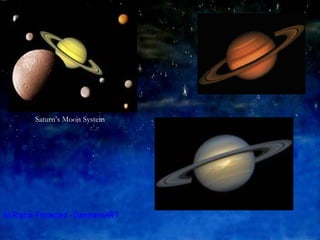
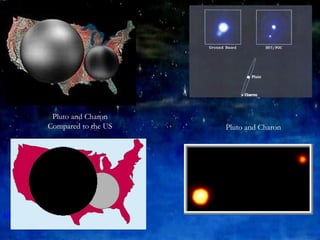
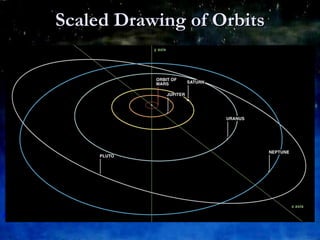
The document discusses the outer planets of our solar system including Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune and Pluto. It provides details on the size, composition, atmosphere and visibility of each planet as well as notable features like Jupiter's Great Red Spot and Saturn's rings. Key facts are given for each planet's moons and comparisons are made between the sizes of the outer planets and Earth.