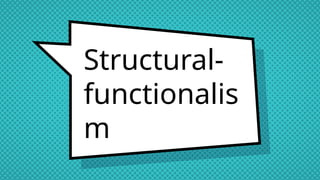
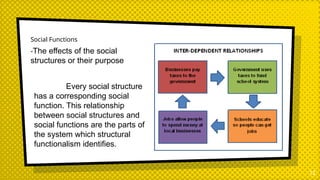
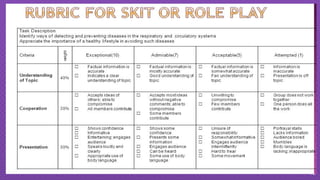
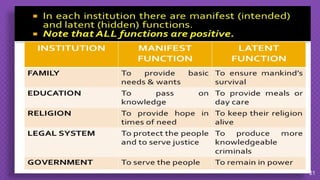
The document discusses structural functionalism, a sociological theory that views society as a system of interconnected parts with specific functions that maintain stability. It explains key concepts such as manifest and latent functions and dysfunctions, and identifies notable theorists like Auguste Comte, Herbert Spencer, and Talcott Parsons who contributed to this theory. The document also highlights strengths and weaknesses of structural functionalism, emphasizing its focus on social stability while acknowledging its limitations in addressing societal changes and inequalities.