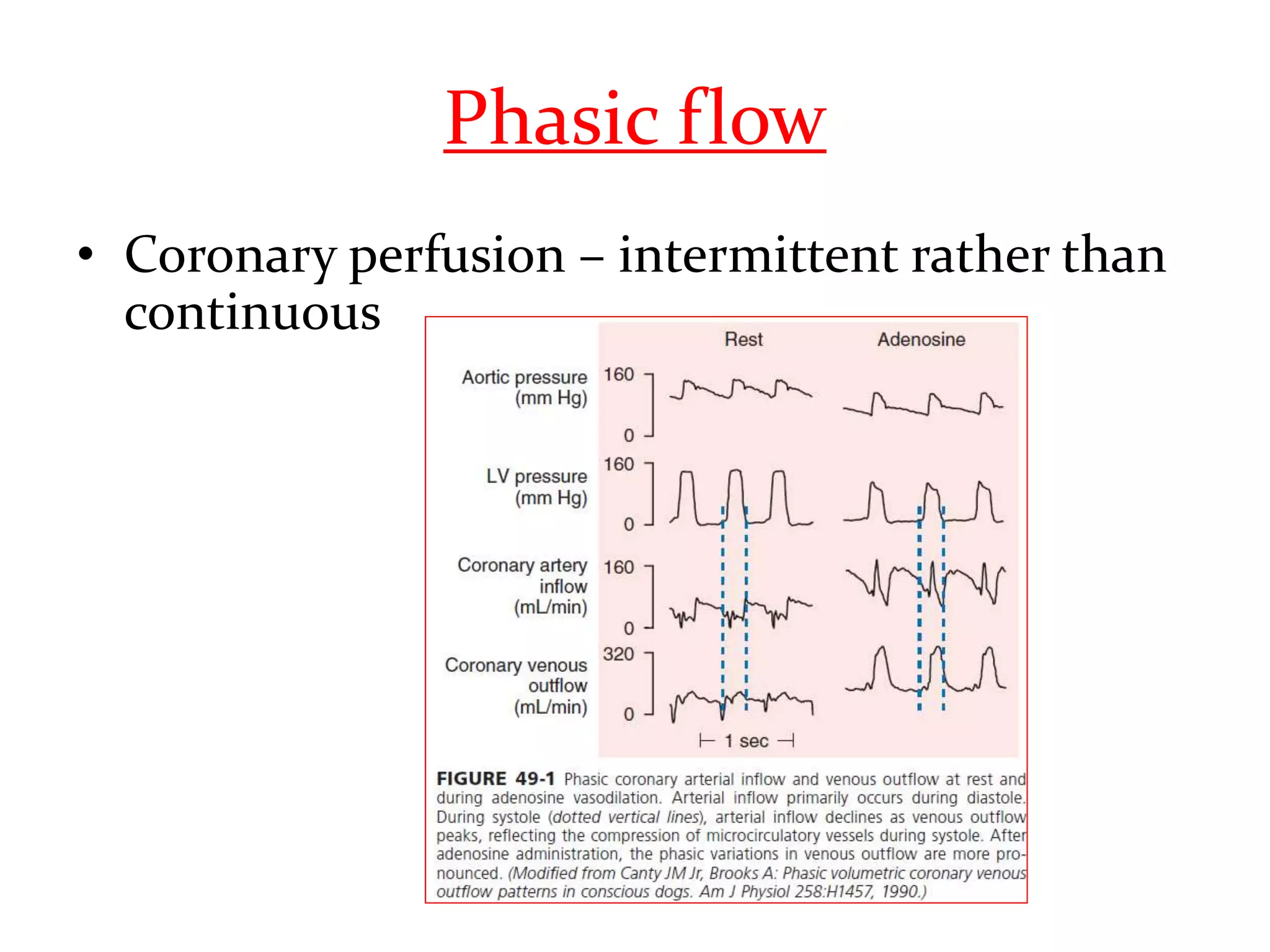
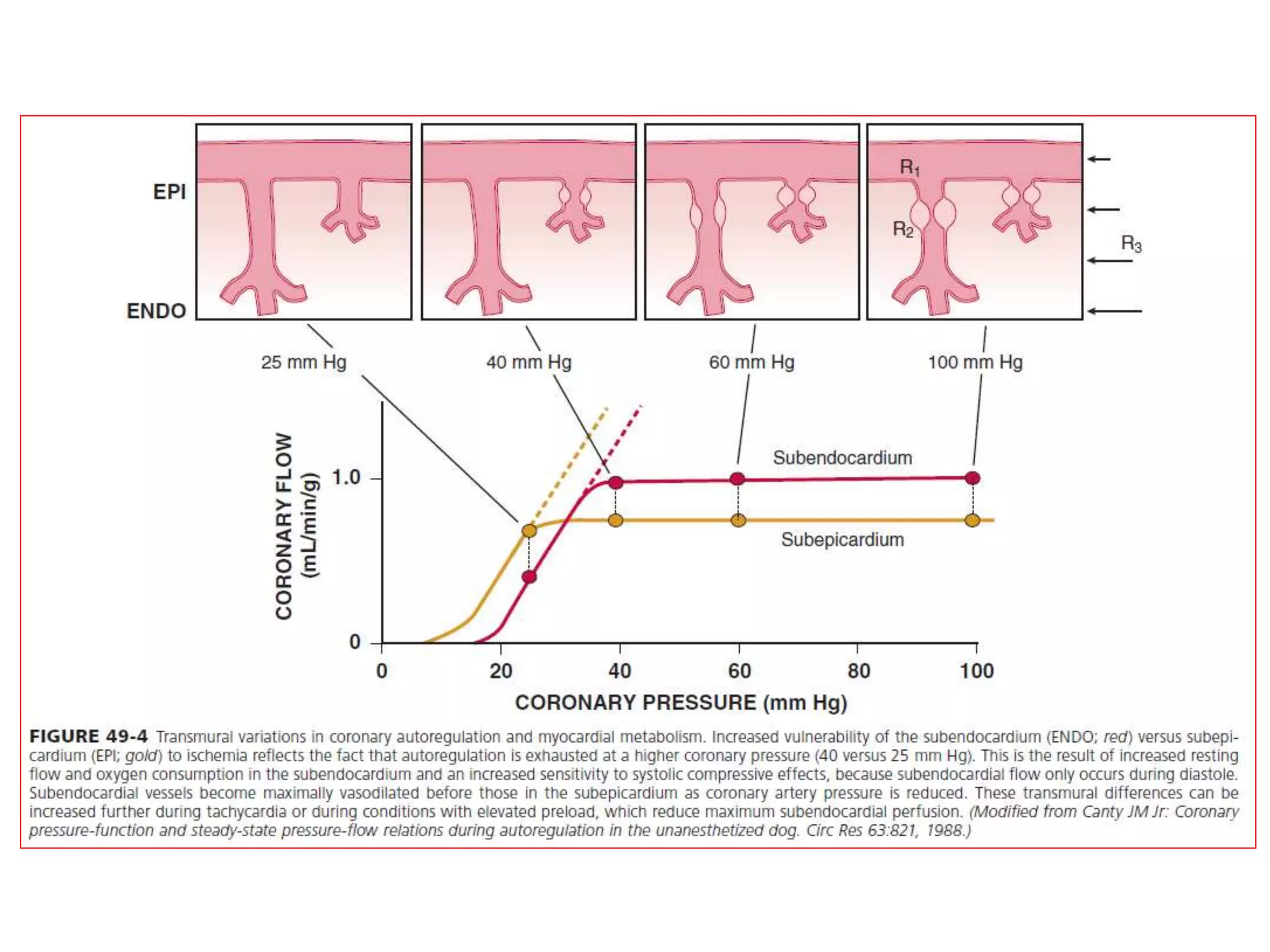
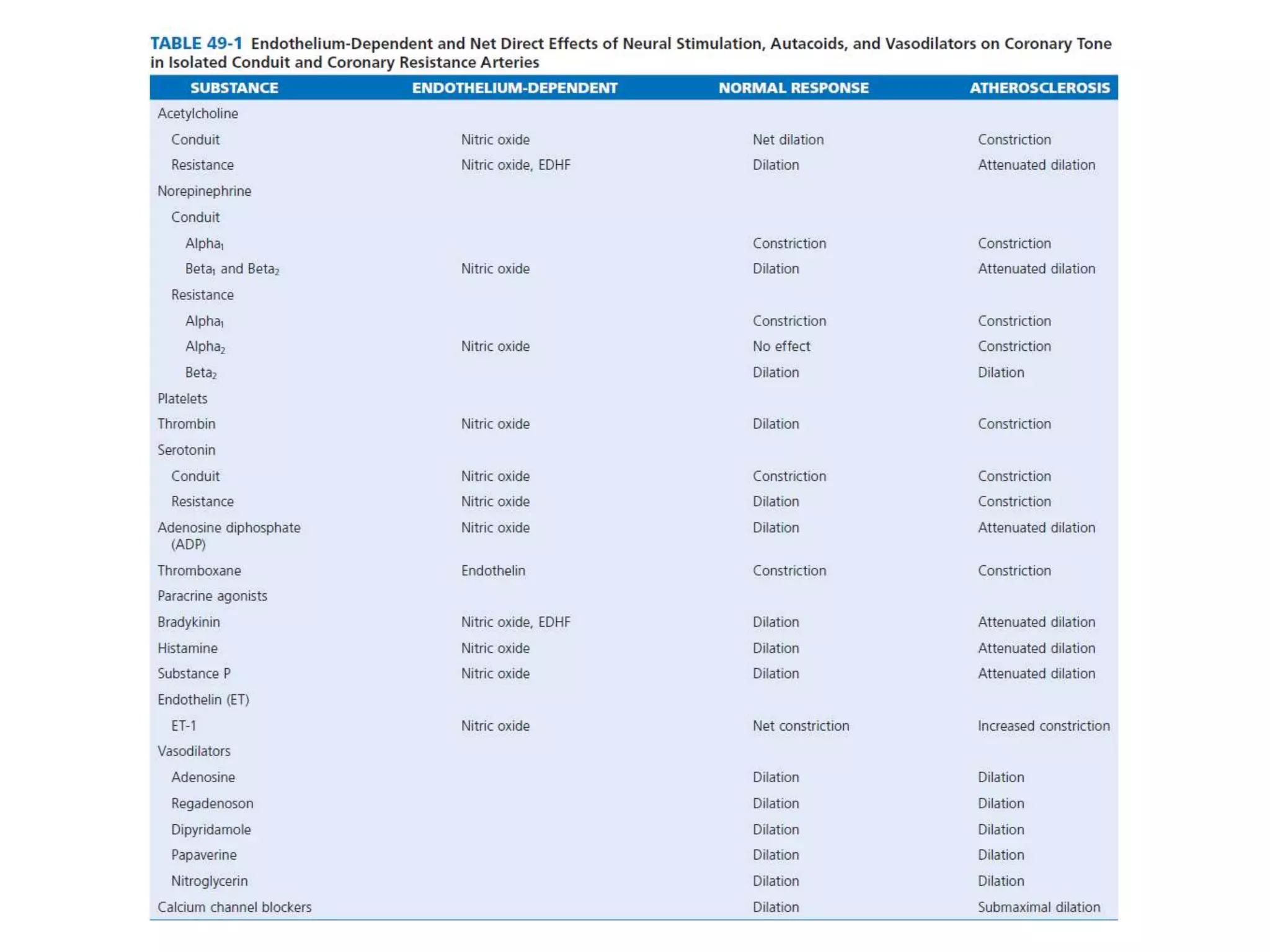
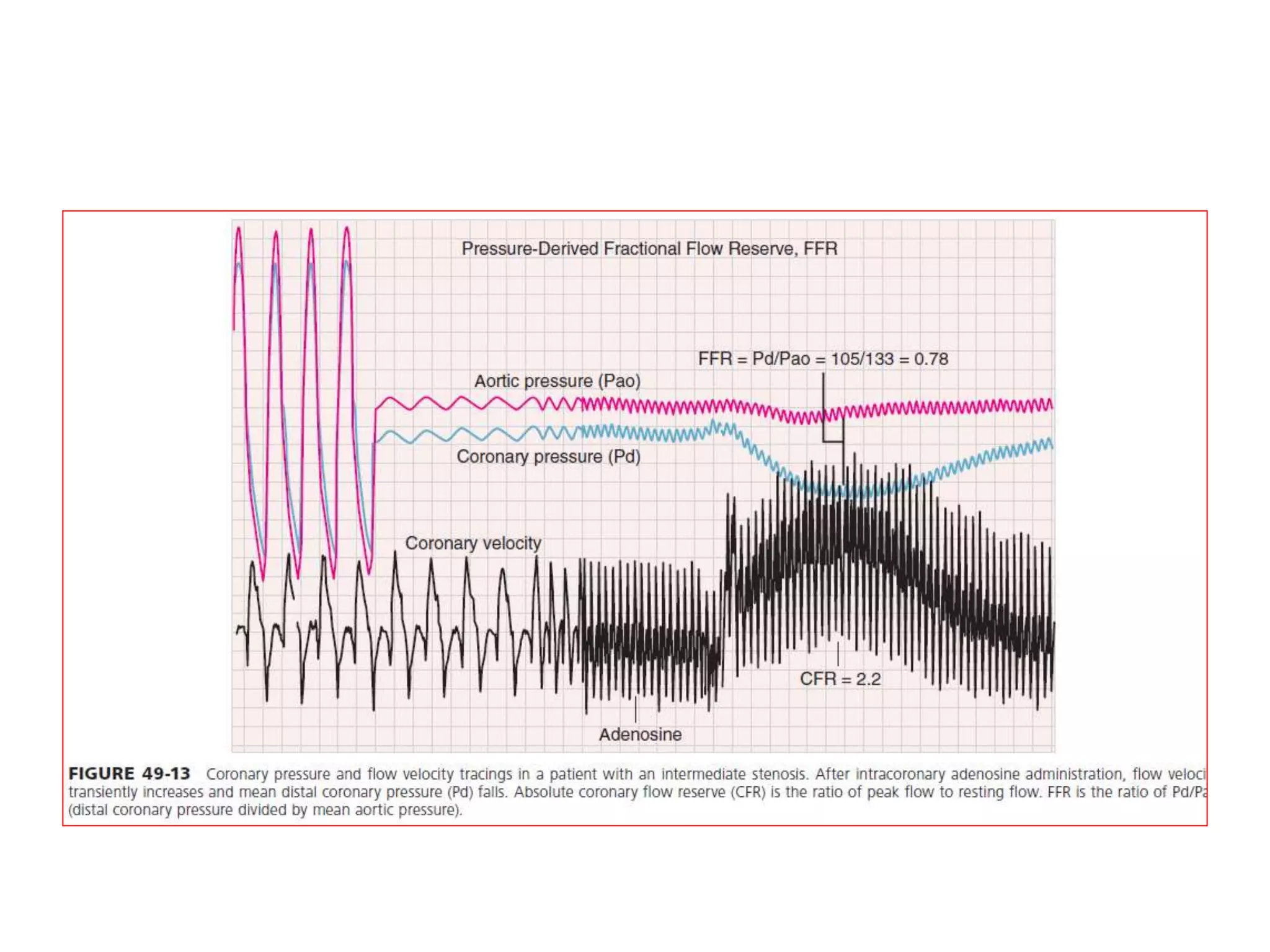
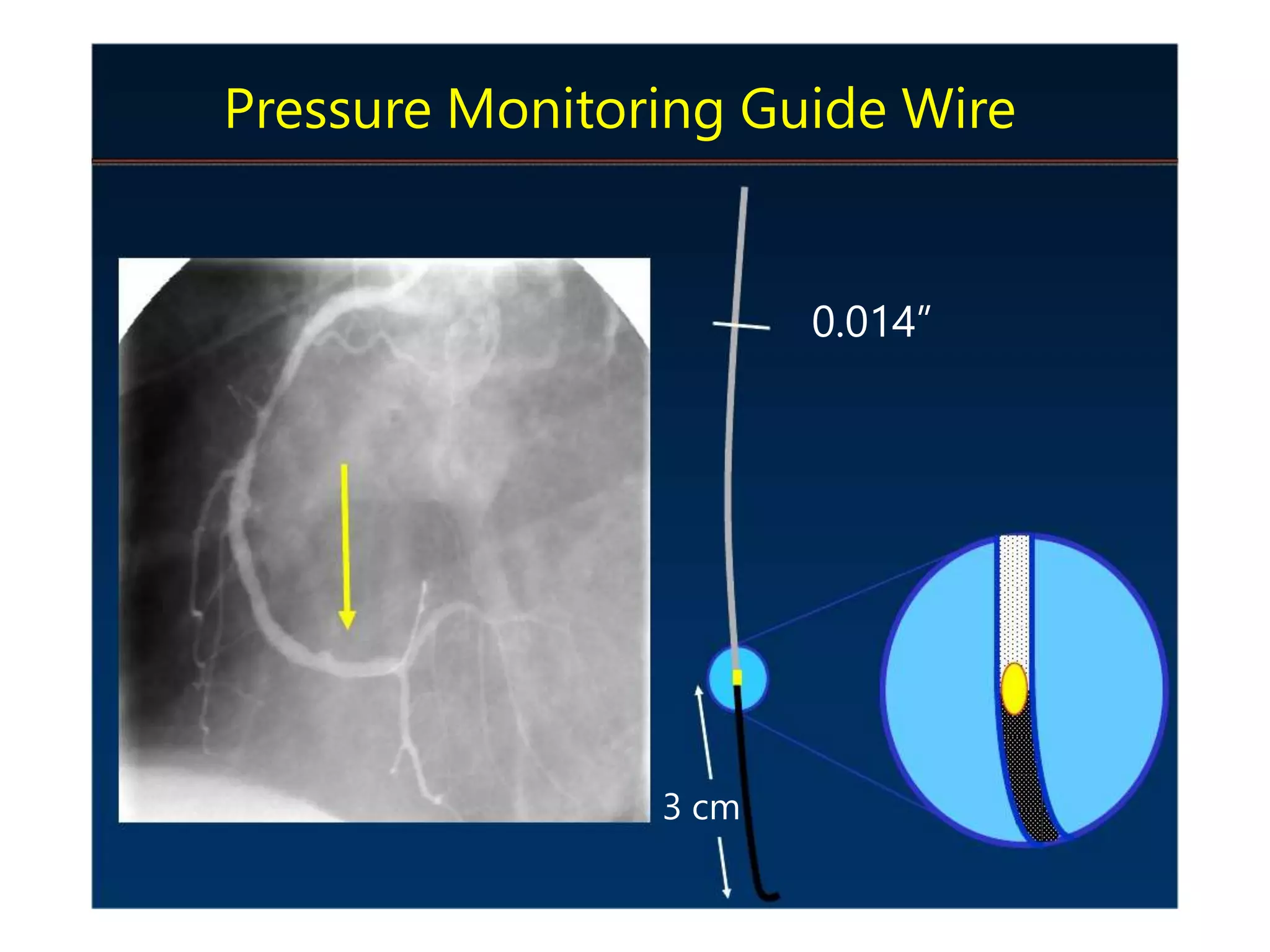
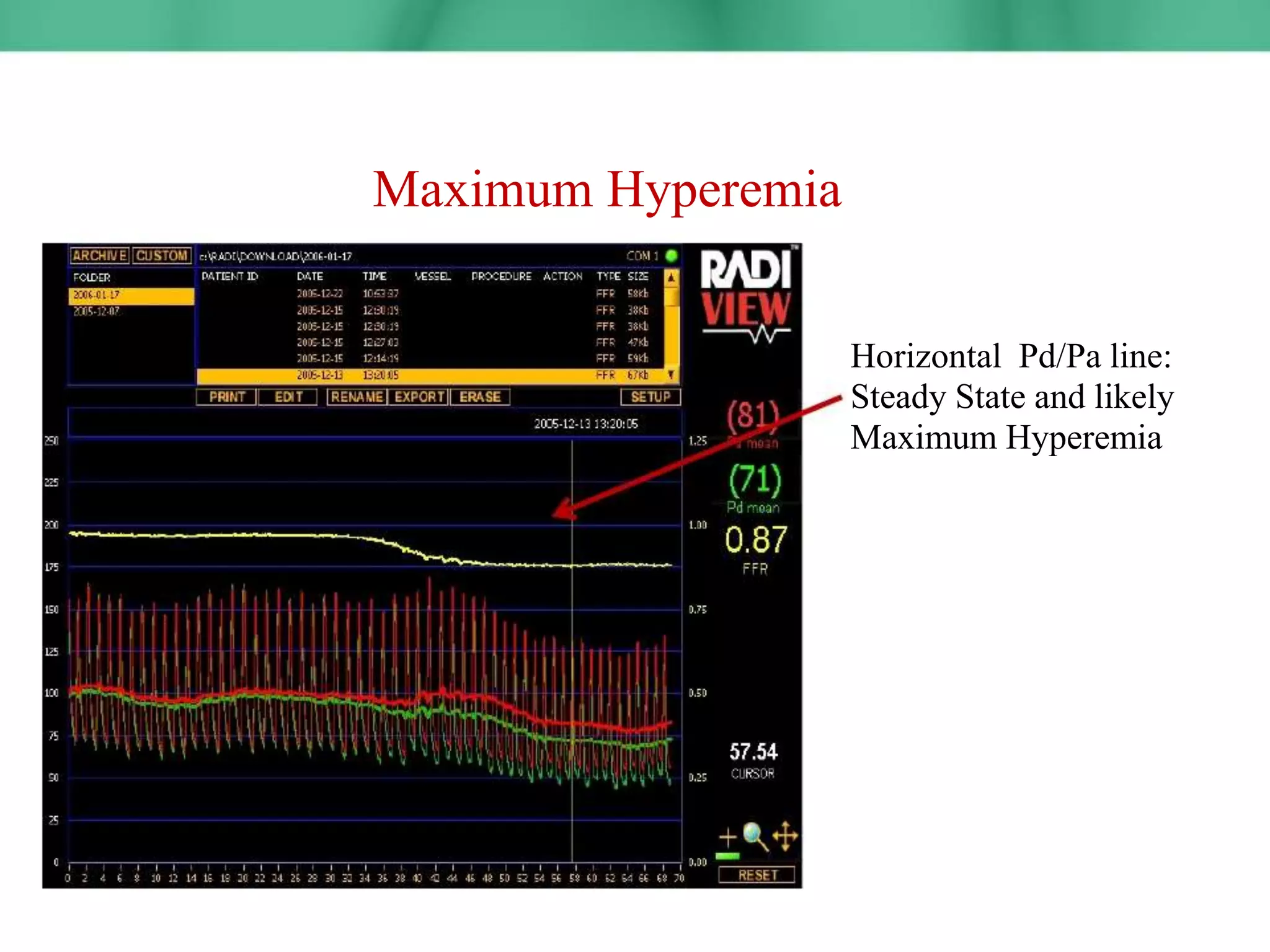
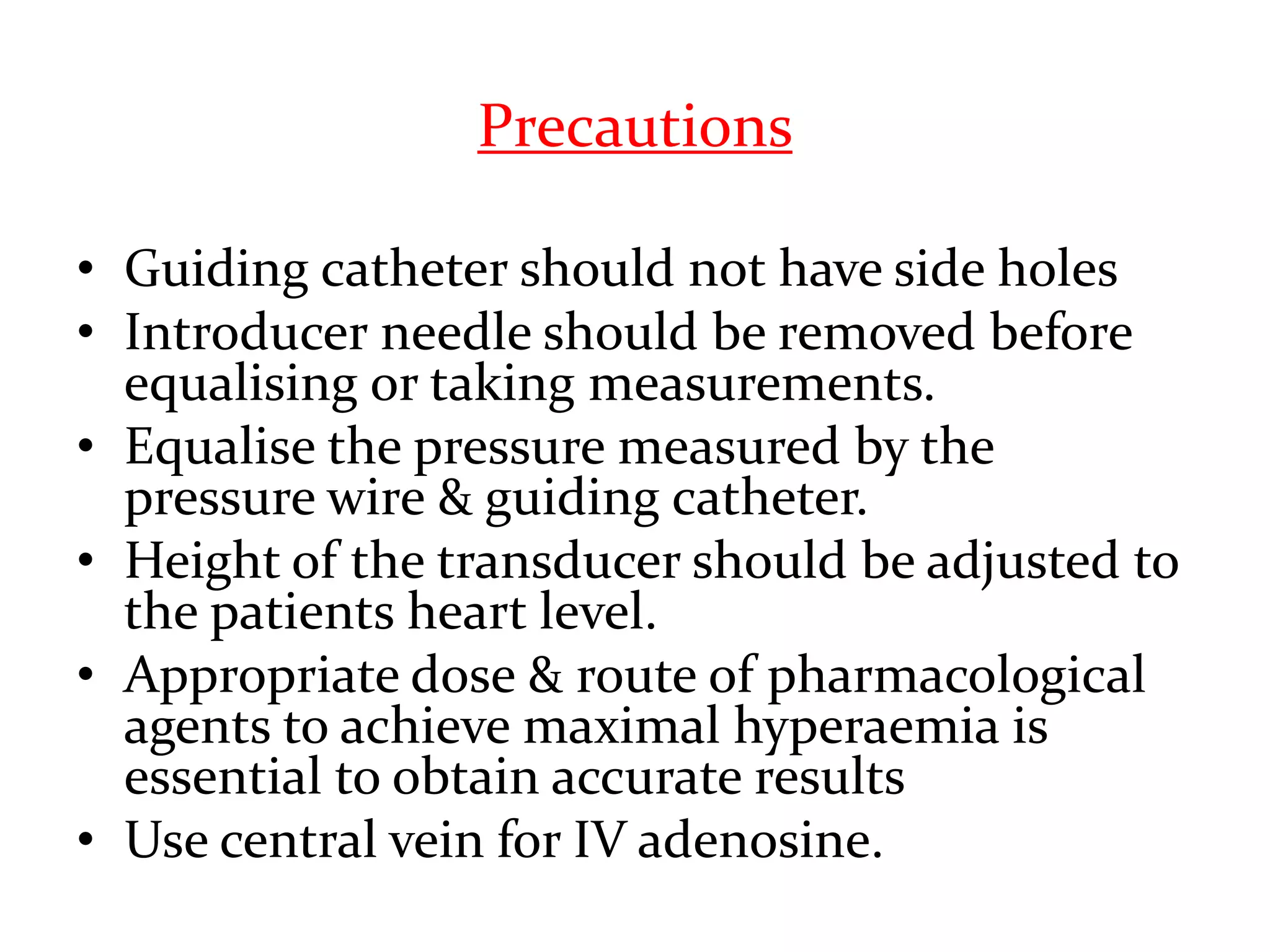
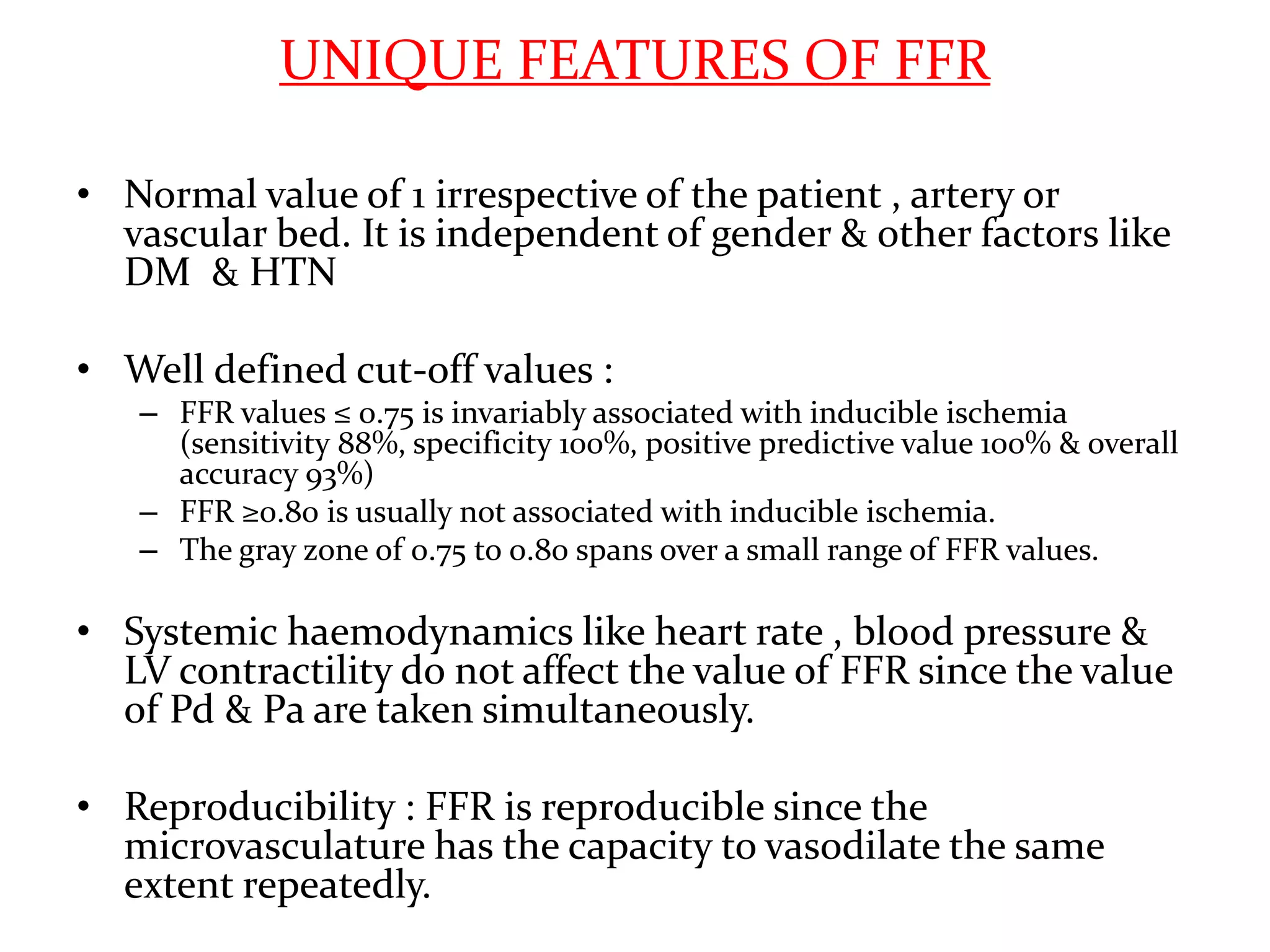
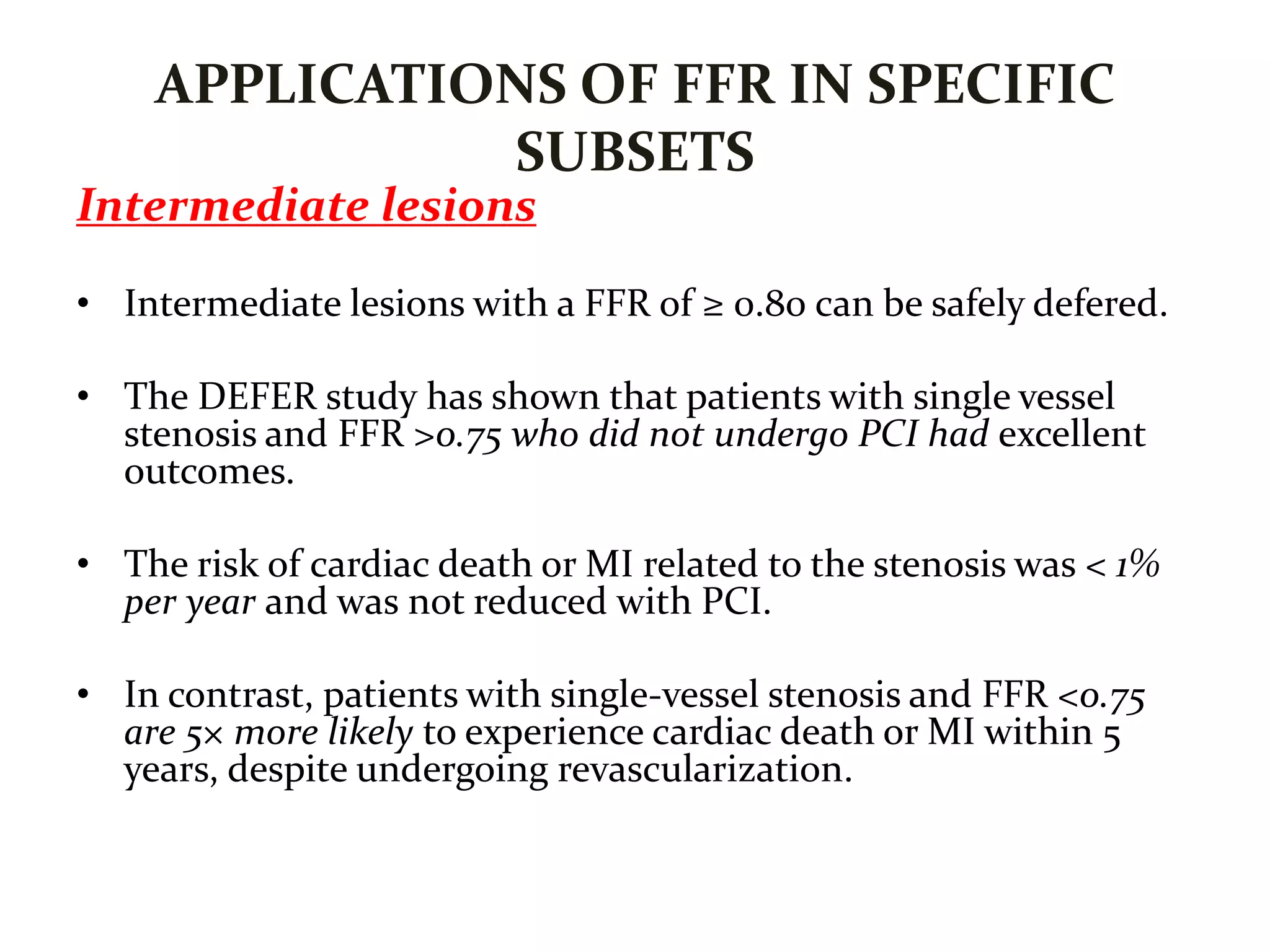
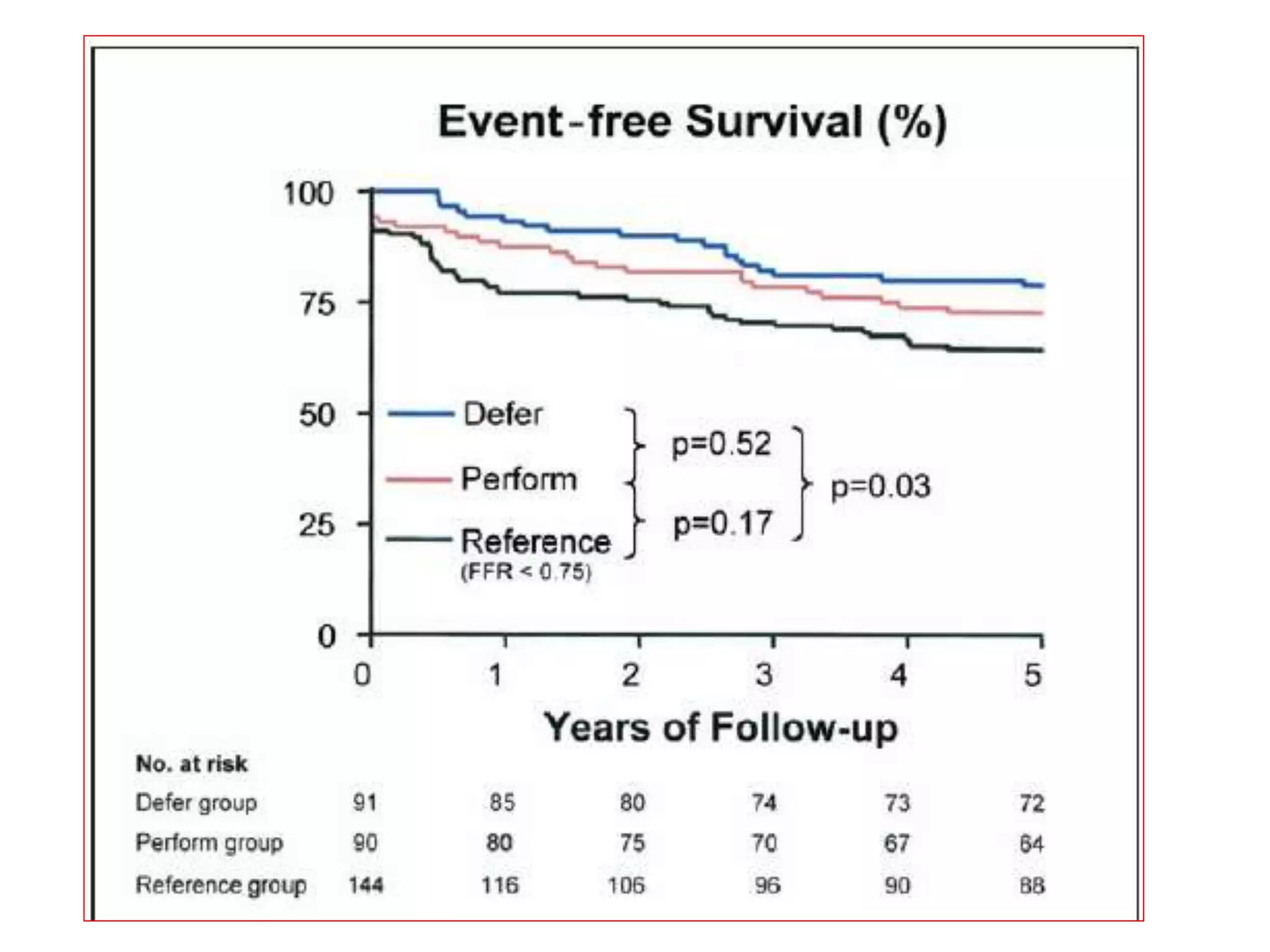
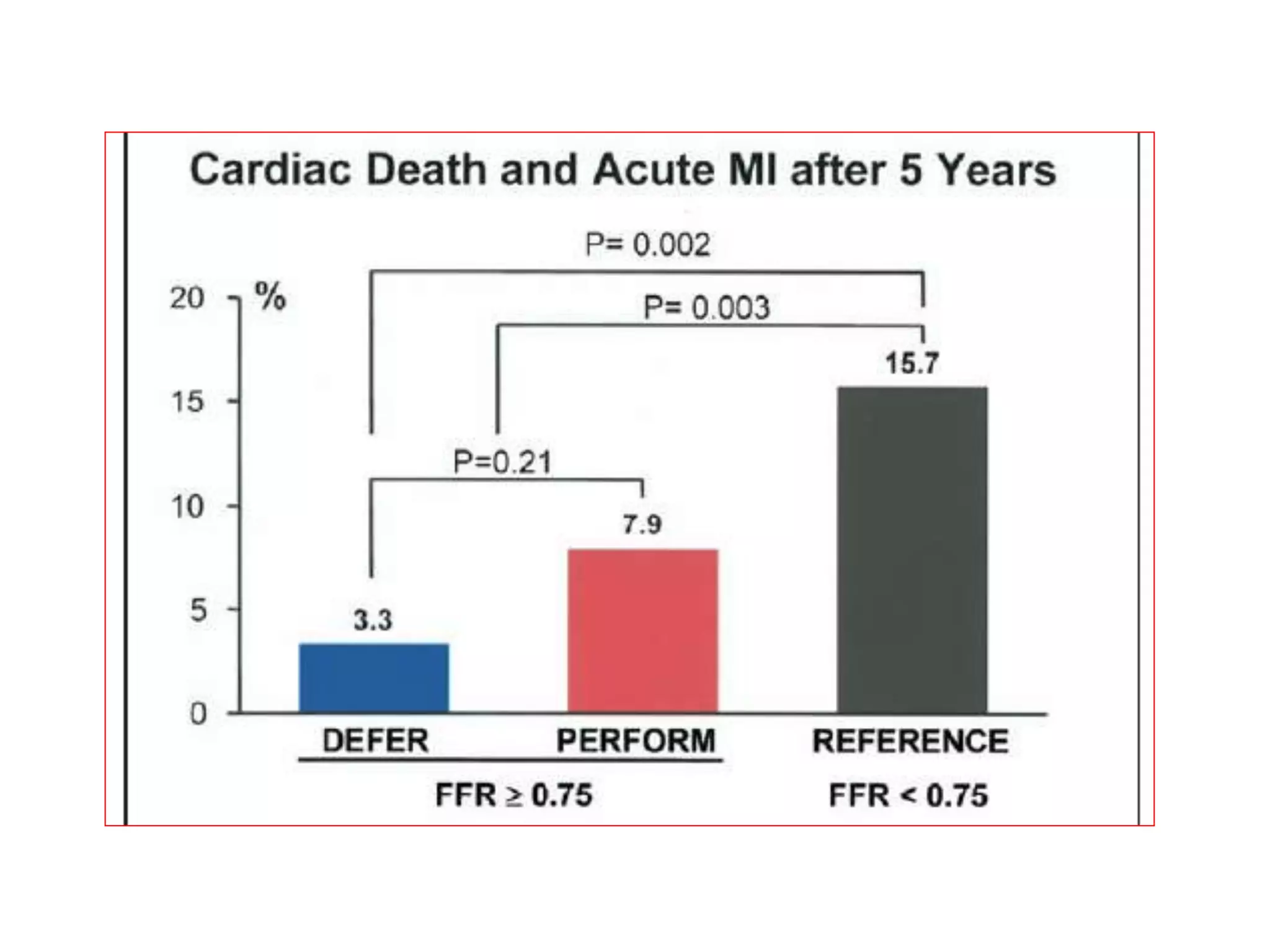
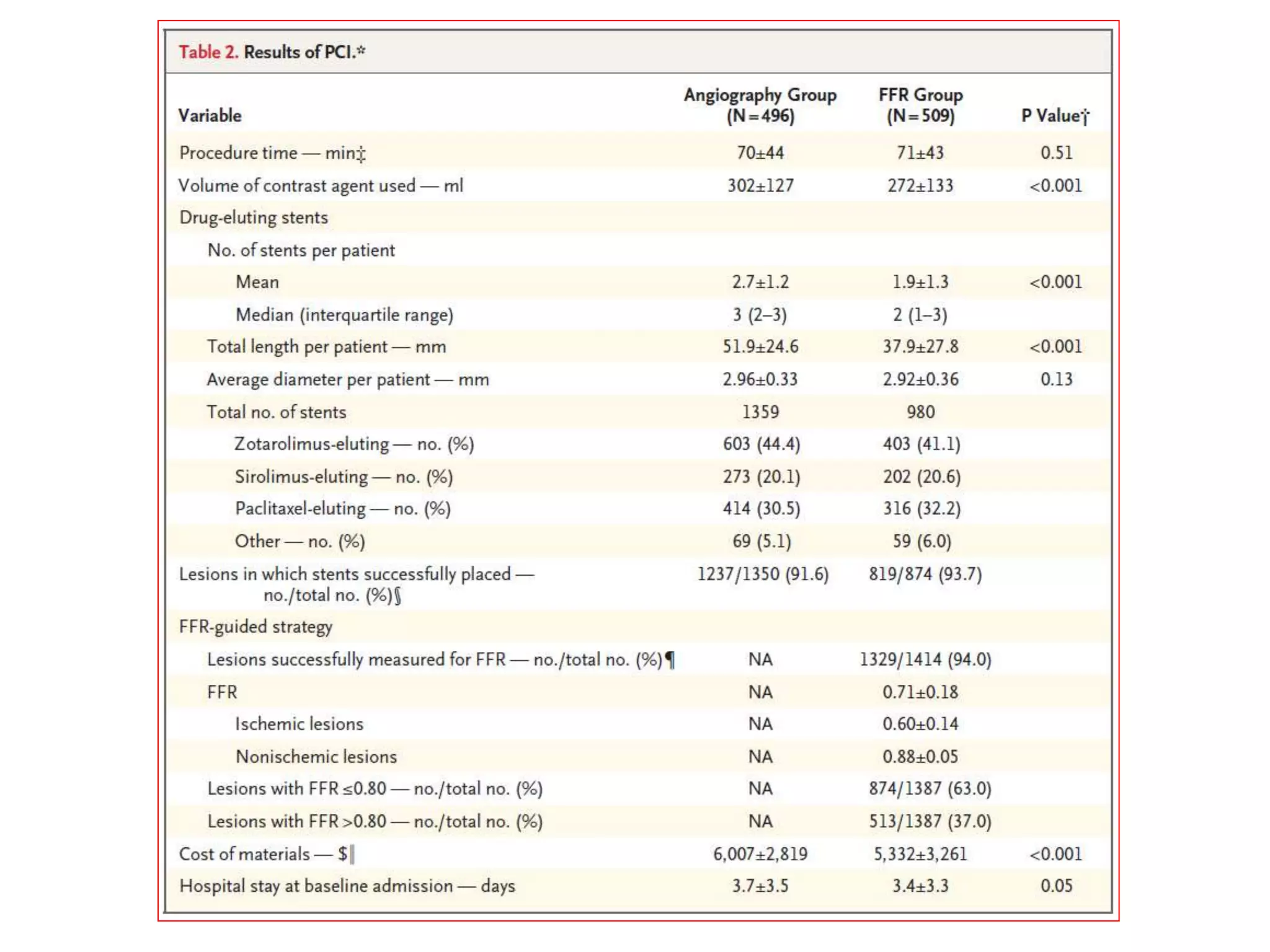
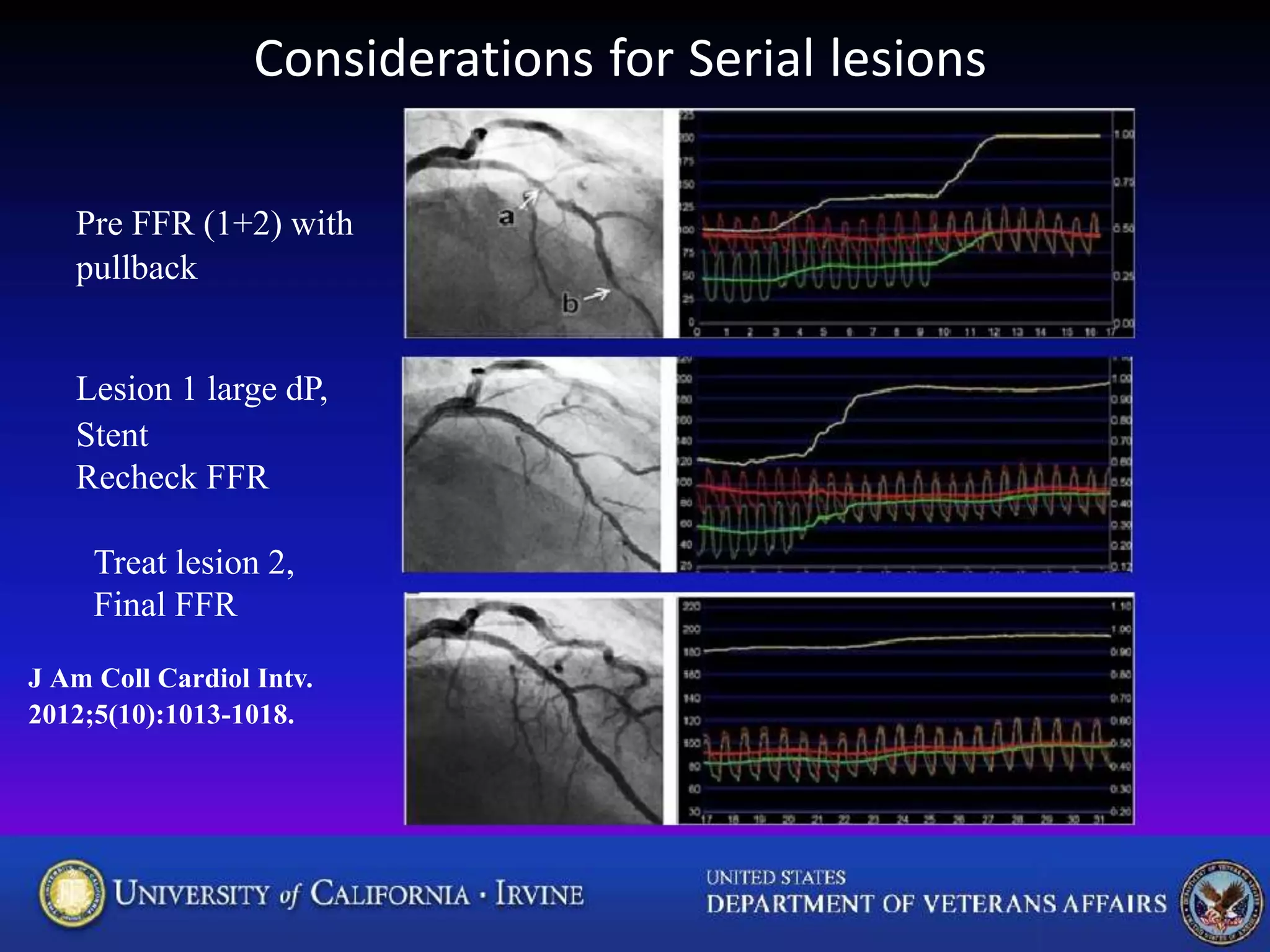
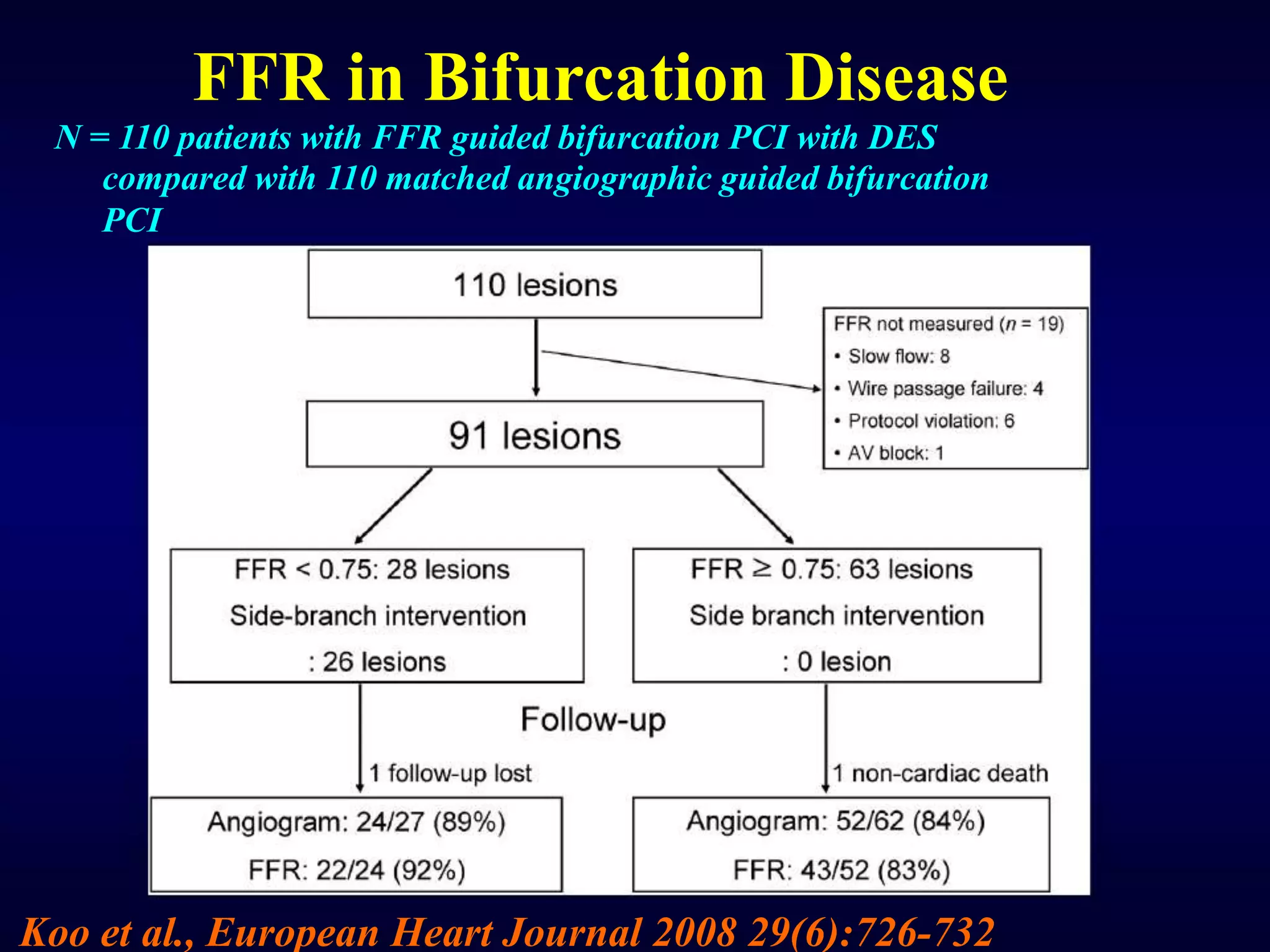
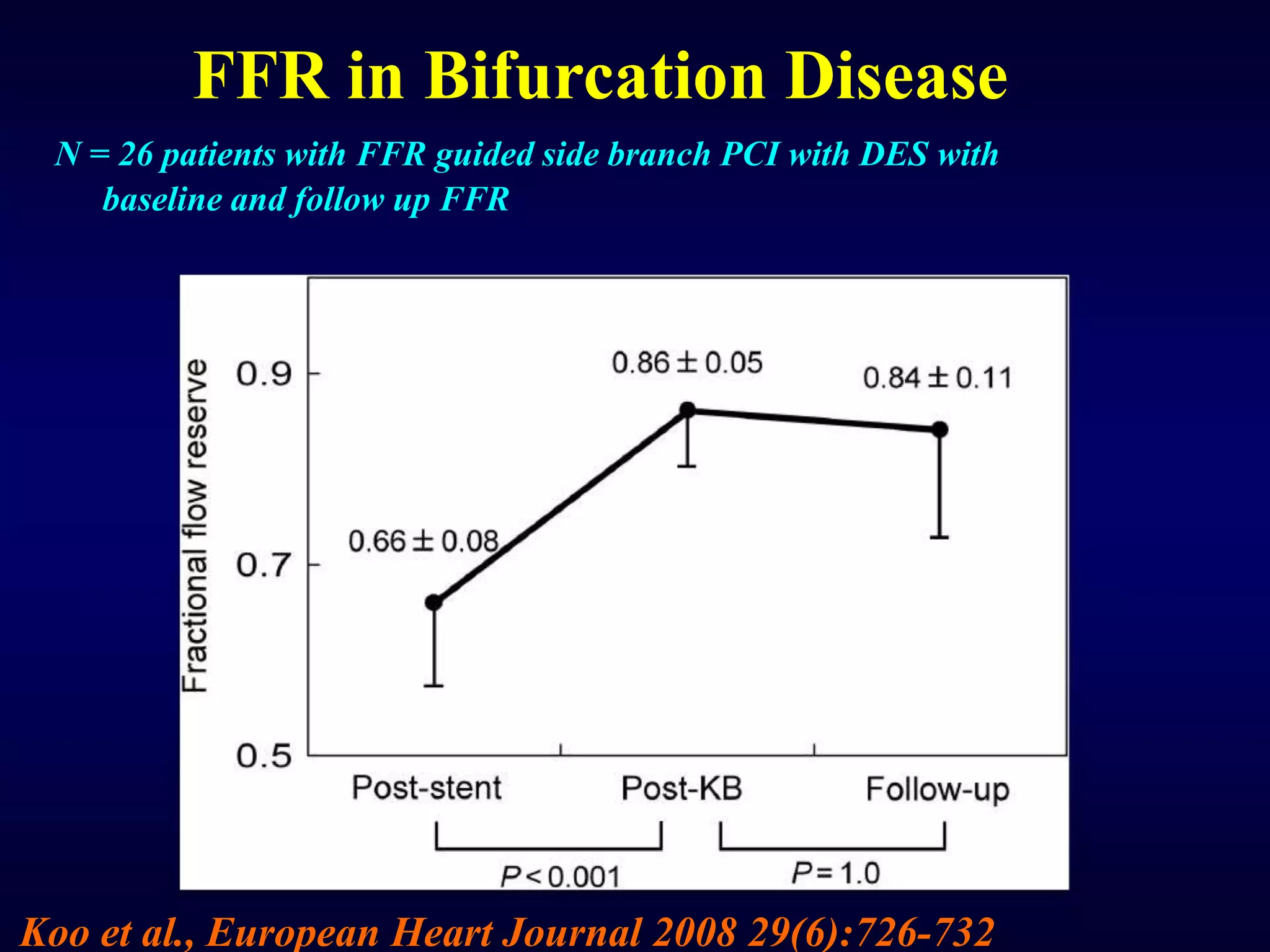
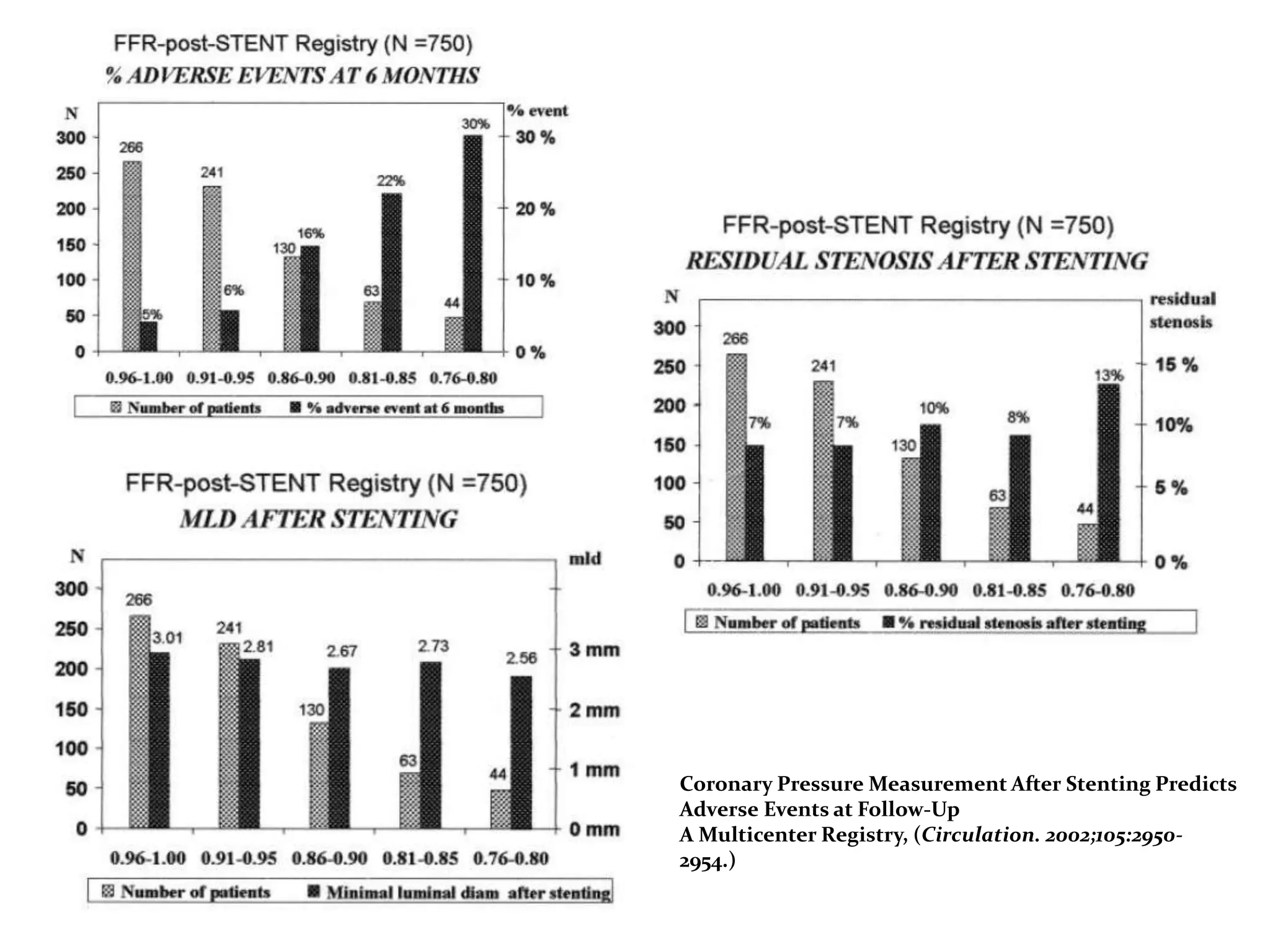
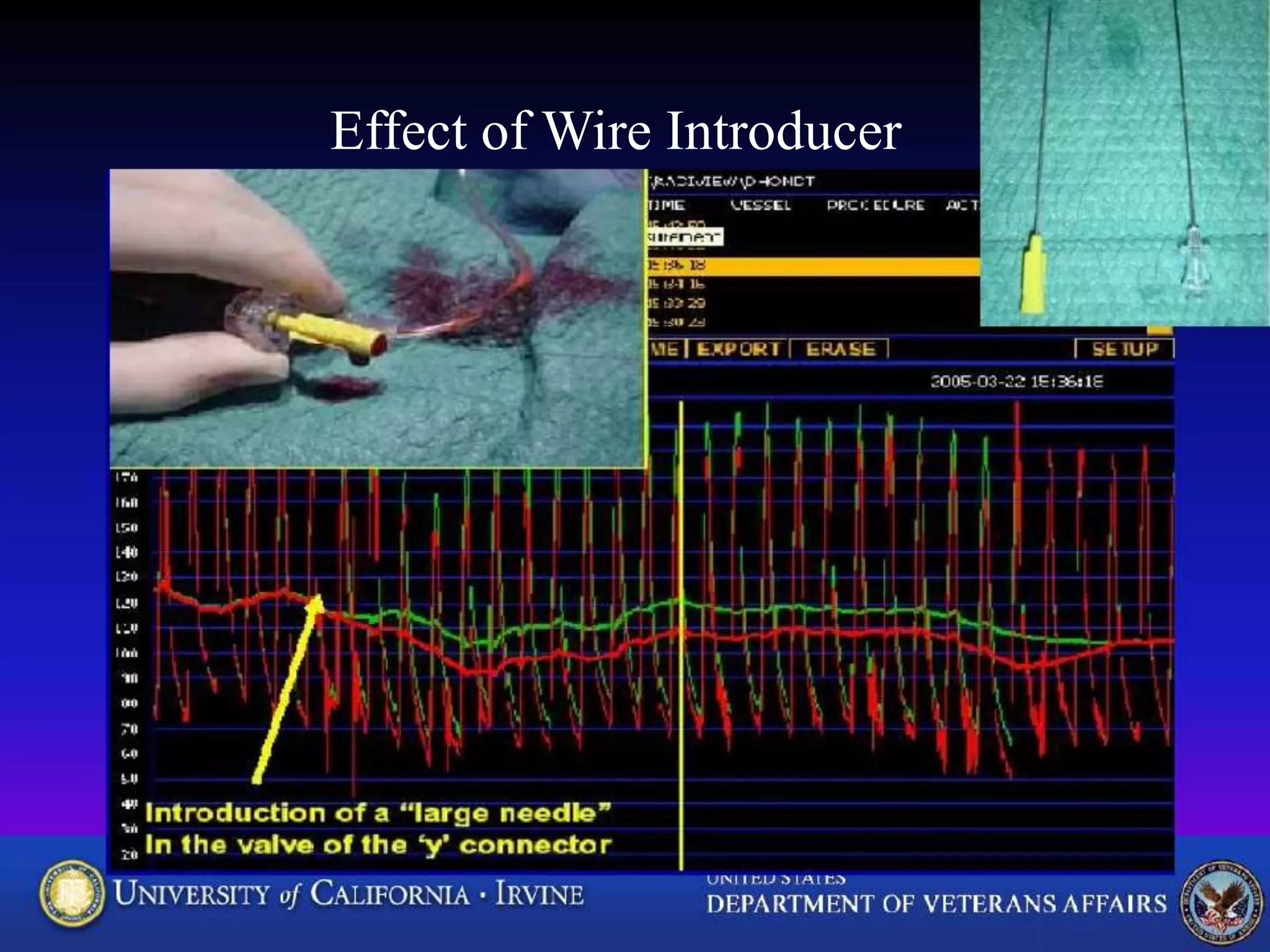
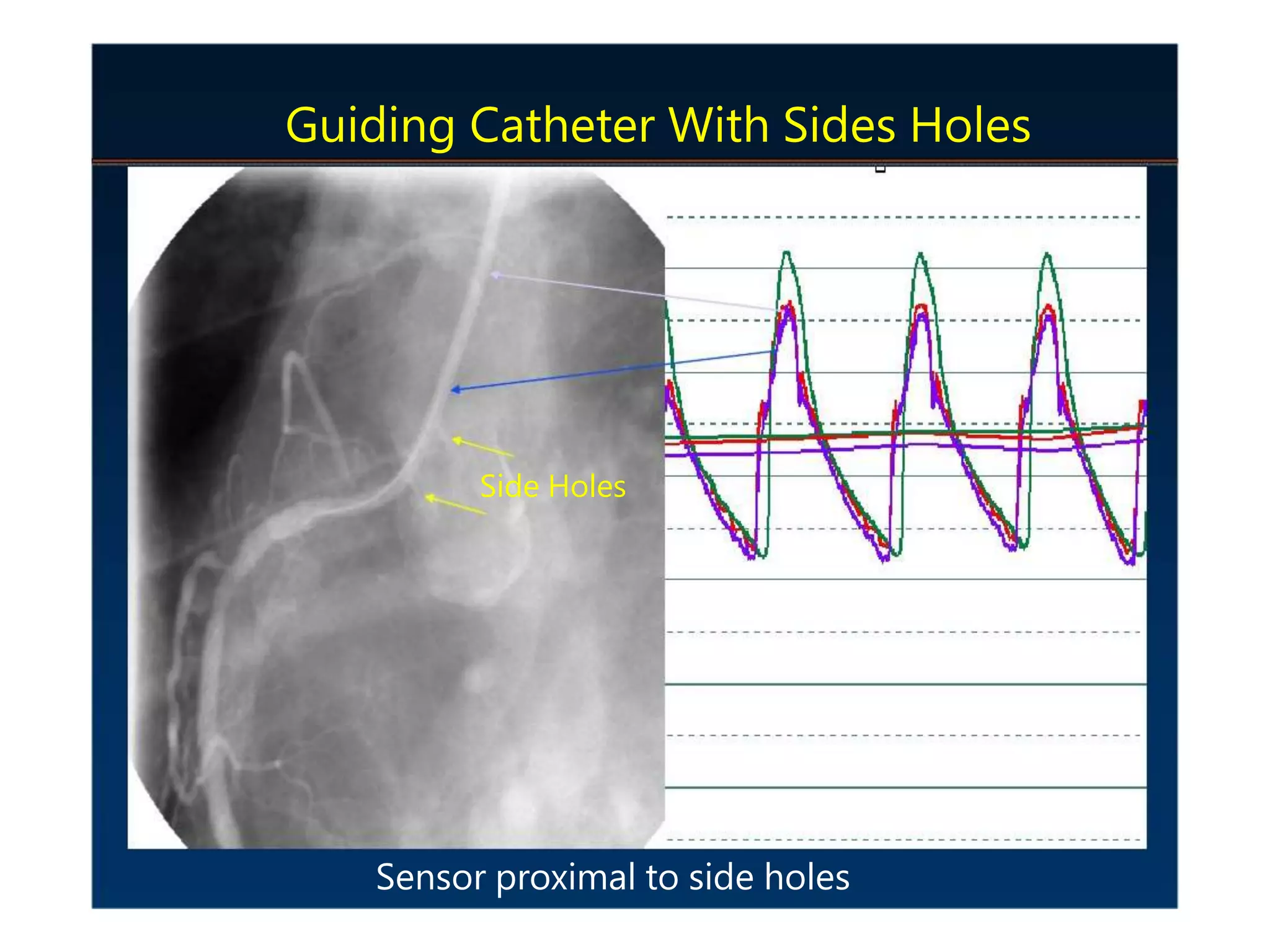
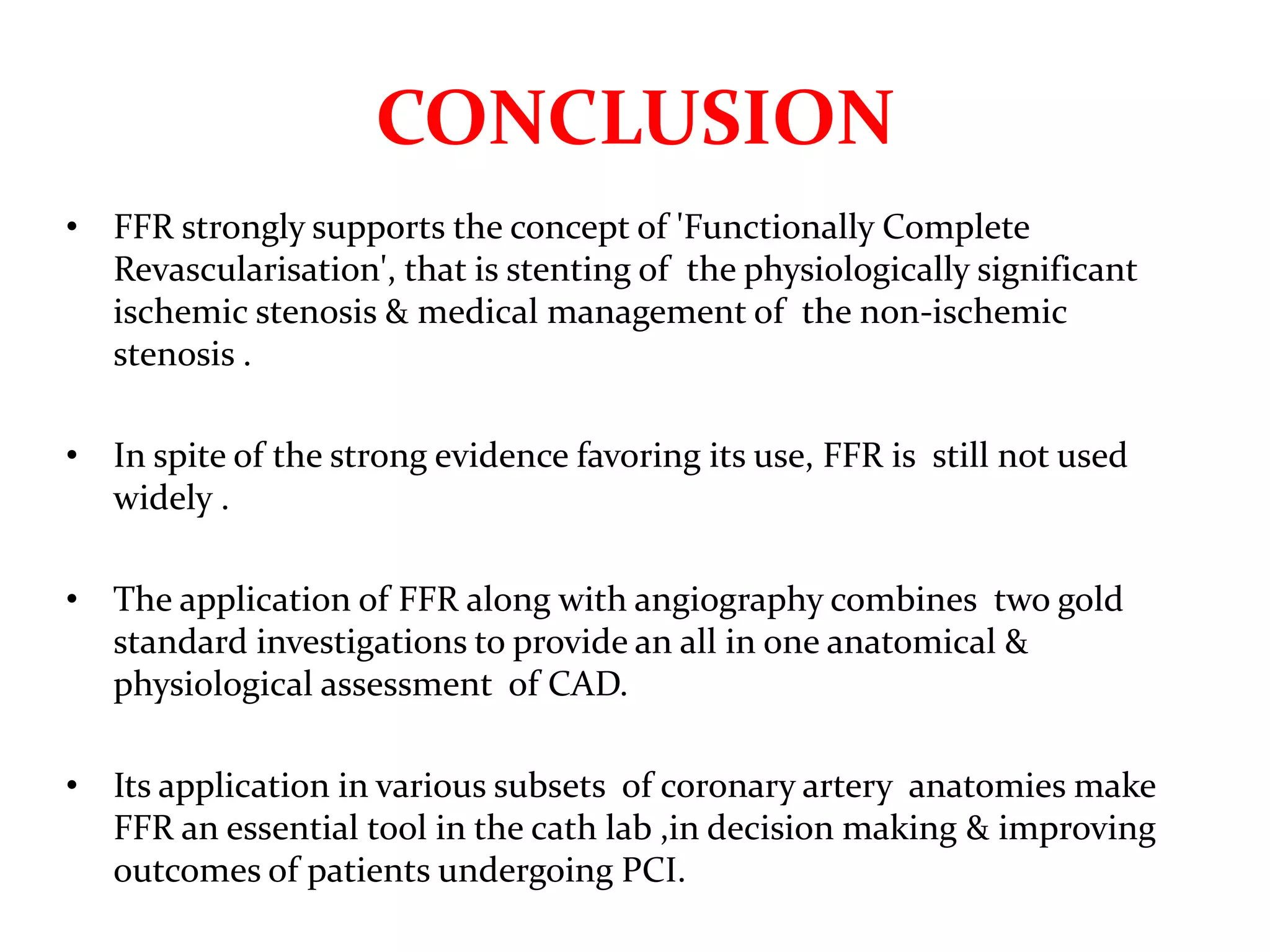
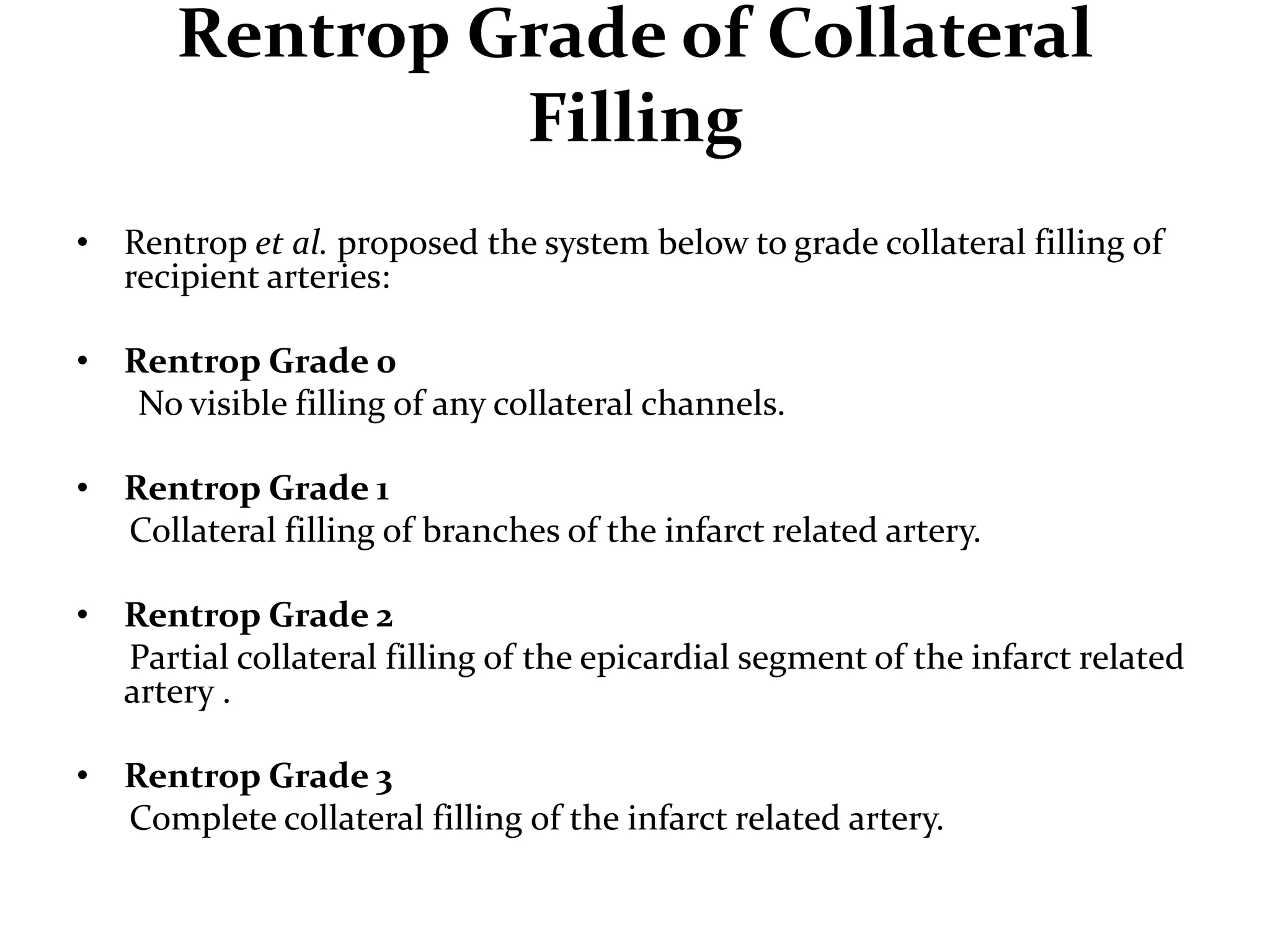
This document discusses fractional flow reserve (FFR), which is a technique used to functionally assess the significance of coronary artery stenosis. FFR is defined as the ratio of maximum blood flow in a stenotic artery to maximum blood flow if there was no stenosis. It is calculated as the ratio of mean distal coronary pressure (Pd) to mean aortic pressure (Pa) during maximal hyperemia induced by pharmacological agents. An FFR value below 0.75 is associated with inducible ischemia, while a value above 0.80 indicates an insignificant stenosis in most cases. FFR has advantages over angiography alone in evaluating stenosis as it accounts for vessel characteristics like length and takes collateral flow into consideration.