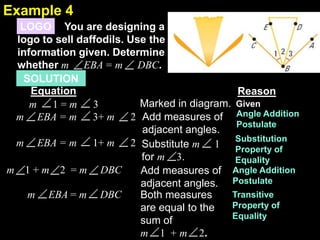
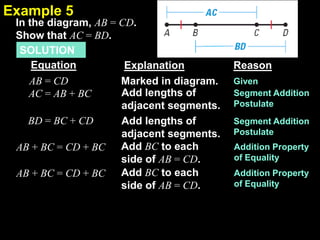
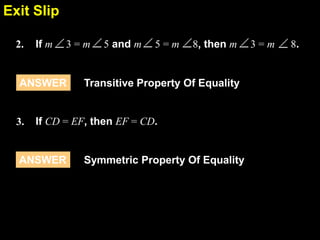
This document provides examples of solving equations and properties of equality. It contains 5 examples of solving equations with explanations and reasons provided for each step. It also discusses properties of equality like addition, subtraction, division, transitive, symmetric, and reflexive properties. The document provides guided practice problems for students to solve equations and identify properties of equality. It concludes with an exit slip for students to solve an equation with reasons and identify properties of equality.