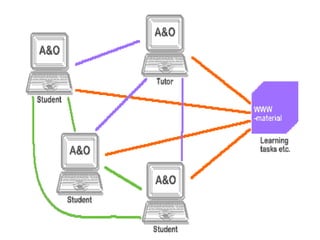
The document discusses Web Based Instruction (WBI) which refers to providing a learning environment that is mediated and supported via the Internet/Intranet. It describes WBI as utilizing the attributes and resources of the World Wide Web to create a meaningful learning environment. The document outlines the key features of WBI including its ability to include multimedia, hypertext/hypermedia capabilities, and allowing for distance/formal learning. It also discusses the different types of WBI (asynchronous and synchronous), the need and significance of WBI in enabling distance learning and reducing costs, and how instructional design models like ADDIE can be applied to develop effective WBI.