Embed presentation
Downloaded 28 times

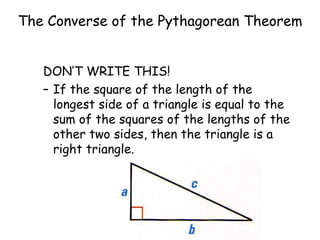
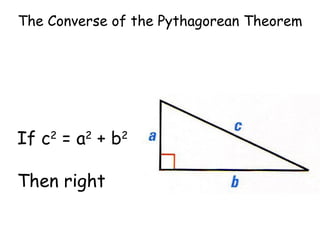
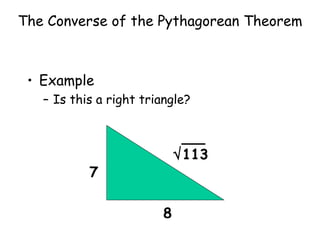
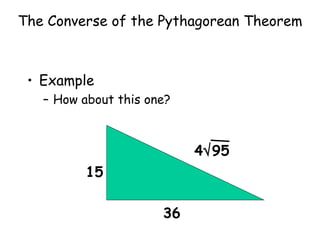

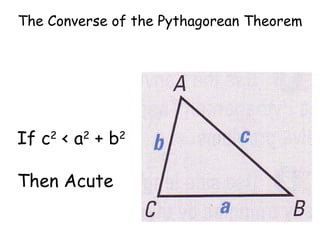

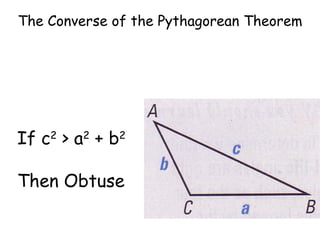



The document discusses the converse of the Pythagorean theorem, which states that if the square of the longest side of a triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, then the triangle is a right triangle. It further states that if the square of the longest side is less than the sum of the squares of the other two sides, the triangle is acute, and if it is greater, the triangle is obtuse. Examples are provided to illustrate applying the converse of the Pythagorean theorem to determine if a triangle is right, acute, or obtuse.










