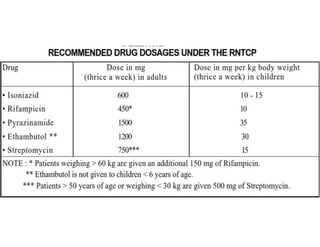
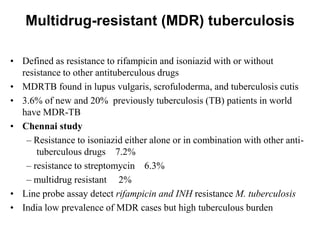
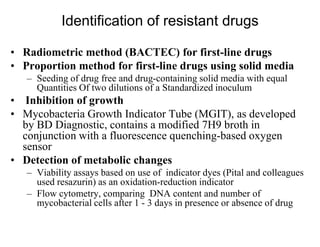
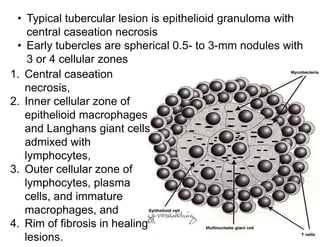
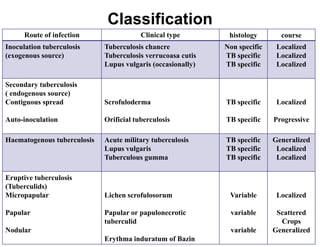
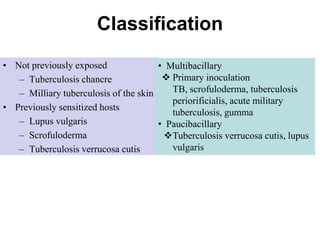
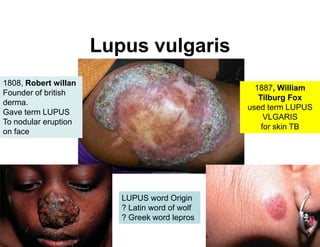
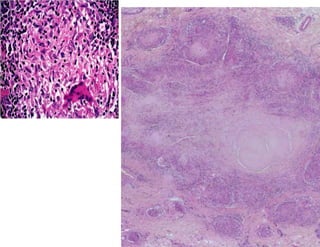
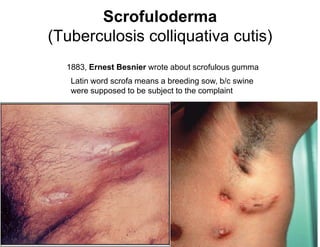
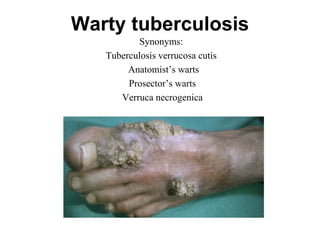
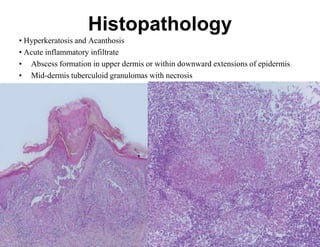
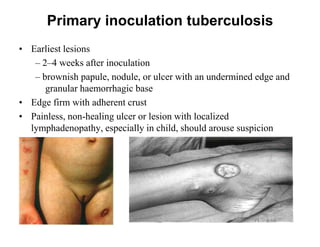
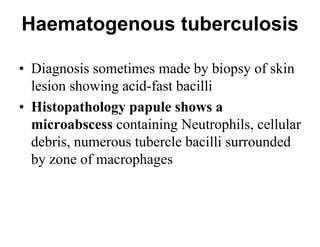
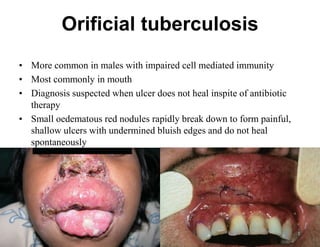
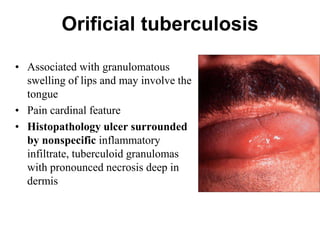
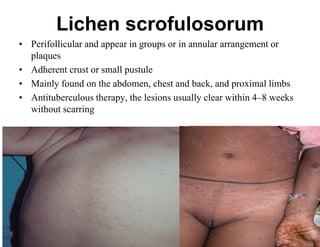
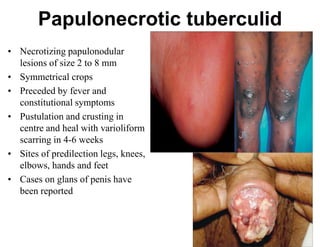
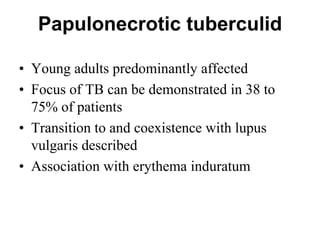
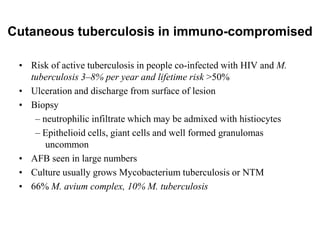
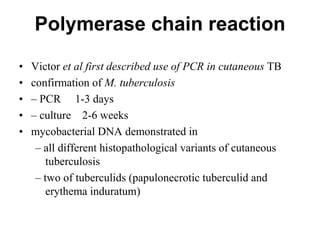
Cutaneous tuberculosis can present in several forms based on the route of infection and immune status of the host. Lupus vulgaris is the most common form in adults, presenting as slowly expanding reddish plaques on the head and neck. Scrofuloderma results from contiguous spread from underlying bone or lymph node infection, causing ulcerating nodules. Tuberculosis verrucosa cutis, or warty tuberculosis, occurs through inoculation and presents as painless verrucous plaques. Diagnosis involves biopsy showing granulomatous inflammation with caseation necrosis and occasionally visualizing acid-fast bacilli. Treatment involves anti-tubercular therapy targeting Mycobacterium tuberculosis.





























![Treatment
• WHO(2009) recommendations for cutaneous TB
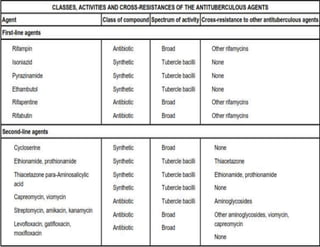
• HIV-negative individuals (adults as well as children) DOTS
– intensive phase 4 drugs H, R, Z, E x 2 mths
– continuation phase H and R x 4 mths
• Daily dosing (2HRZE/4HR) recommended for all newly diagnosed
• Alternatively
– [2HRZE/4(HR)3]: daily intensive phase followed by 3/wkly
continuation phase
– [2(HRZE)3/4(HR)3]: 3/weekly dosing throughout therapy,
provided every dose directly observed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarcut-140126084432-phpapp02/85/cutaneous-tuberculosis-61-320.jpg)