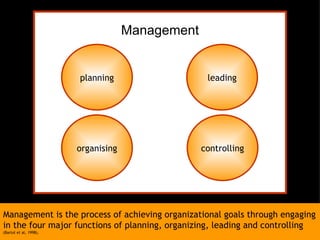
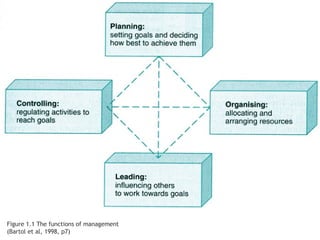
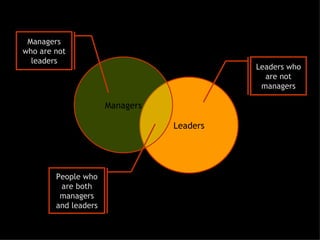
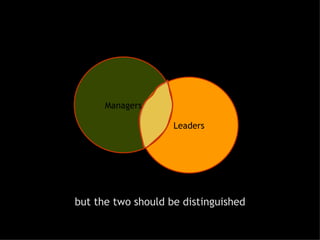
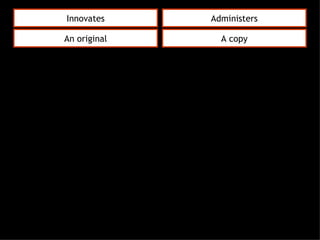
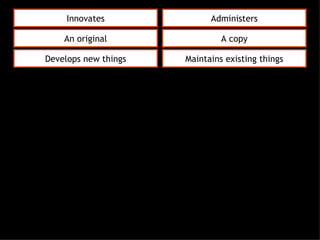
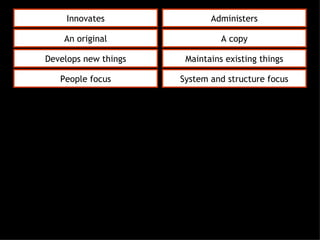
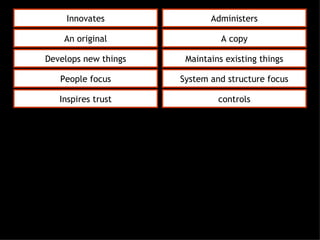
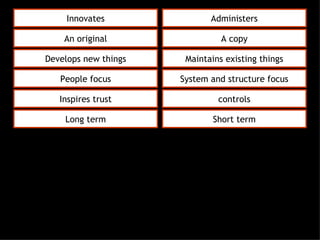
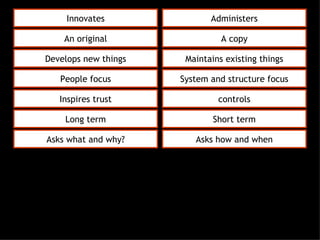
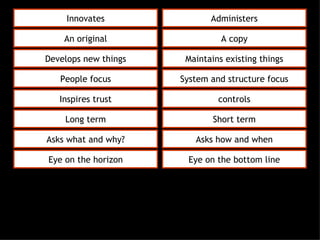
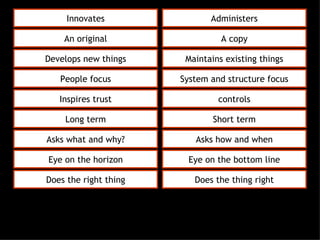
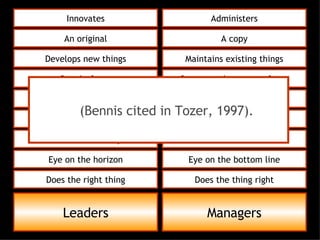
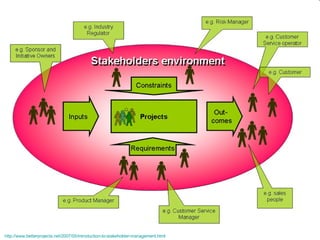
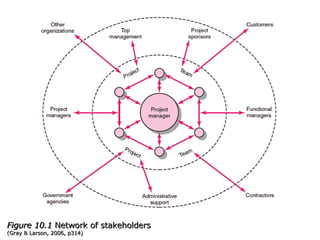
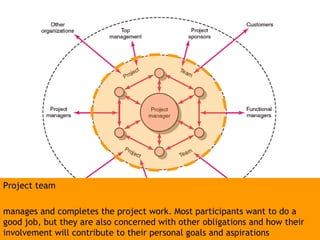
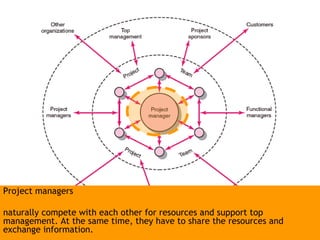
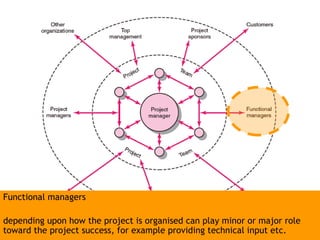
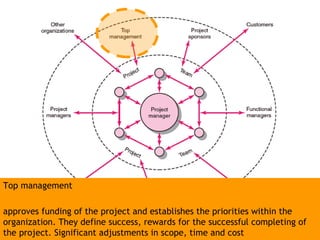
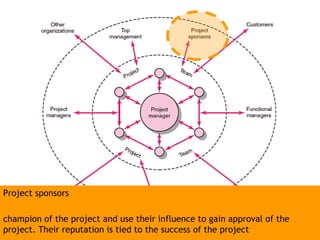
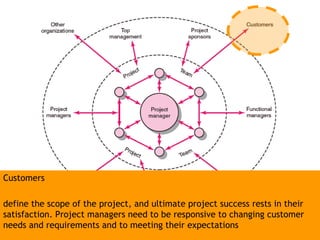
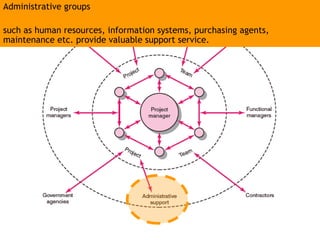
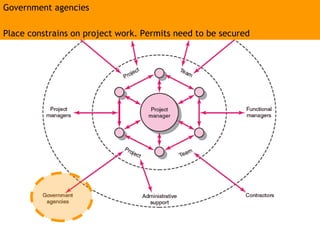
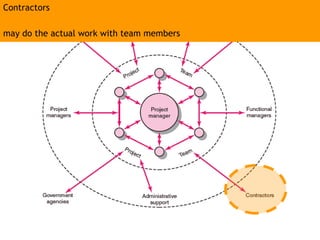
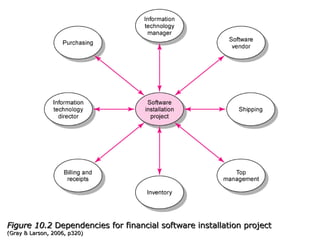
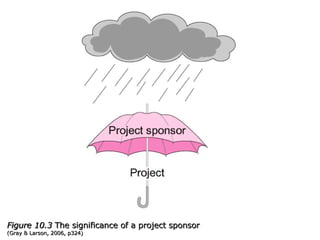
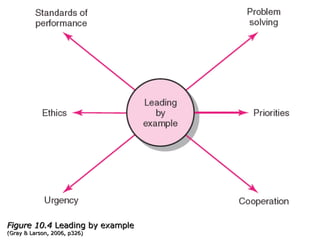
This document discusses project management and leadership. It defines management as achieving organizational goals through planning, organizing, leading and controlling. Leadership is defined as influencing others to achieve goals. The document contrasts managers and leaders, noting that some managers can function as leaders while not all leaders are managers. Effective project management requires both leadership and management skills to coordinate stakeholders, solve problems, and adapt to changes while achieving objectives on time and within budget.