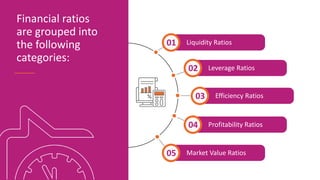
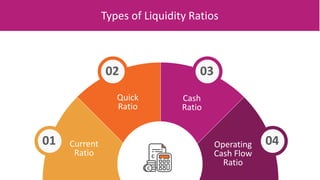
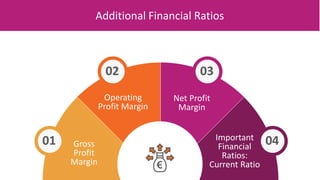
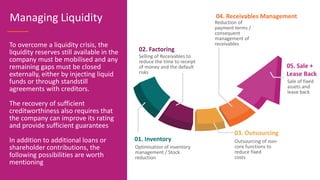
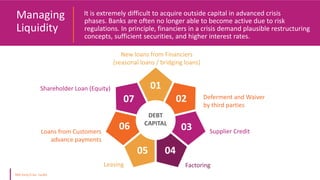
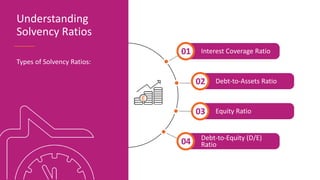
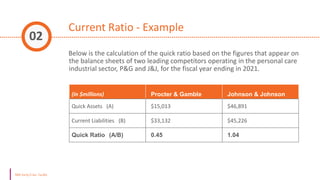
The document discusses various types of financial ratios used to analyze companies, including liquidity ratios and solvency ratios. It provides examples of key liquidity ratios like the current ratio, quick ratio, and cash ratio. The current ratio measures a company's ability to pay short-term debts with current assets. The quick ratio is similar but excludes inventory from current assets. The cash ratio measures a company's ability to pay debts with cash and cash equivalents. Solvency ratios measure long-term financial health and debt obligations, unlike liquidity ratios which focus on short-term obligations. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to calculate and interpret these important financial metrics.