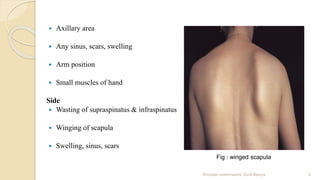
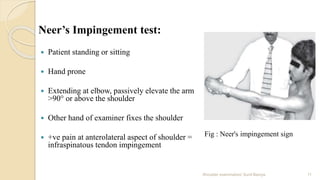
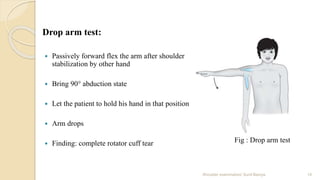
This document outlines a comprehensive shoulder examination protocol, detailing the various physical examination techniques to assess shoulder conditions. It includes assessment of chief complaints, visual inspection, palpation methods, active range of motion tests, and special tests for shoulder injuries. The document emphasizes the importance of confirming findings through specific tests such as impingement and rotator cuff evaluations.