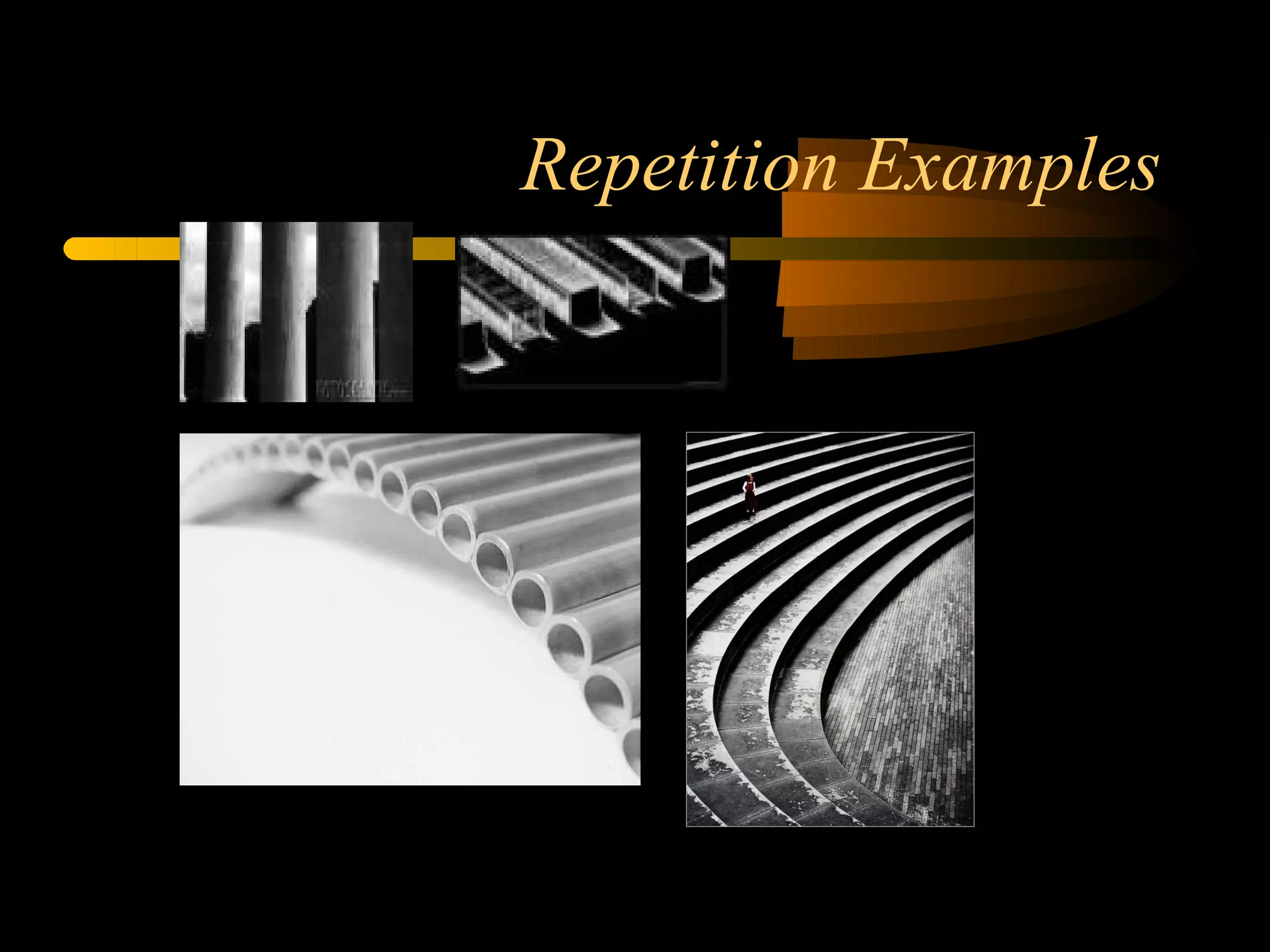
This document discusses the elements and principles of art as they relate to photography composition. The elements are line, shape, space, value, texture, and color. The principles are emphasis, balance, unity, contrast, movement/rhythm, and pattern/repetition. Understanding and using these elements and principles allows photographers to make intentional compositional choices that make their photographs more visually interesting and impactful.