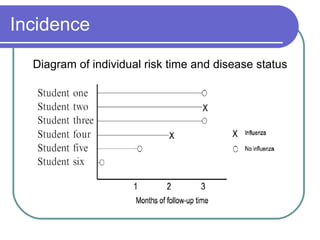
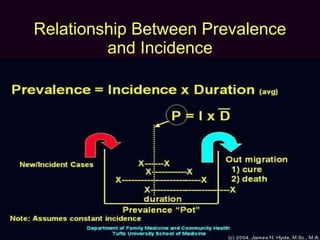
Incidence and prevalence measures provide information about disease frequency and burden in populations. Prevalence describes the proportion of people with a disease at a point in time, while incidence refers to the number of new cases that develop over time. Both measures can be stratified by person, place, and time to gain insights into a disease's pathogenesis and development.