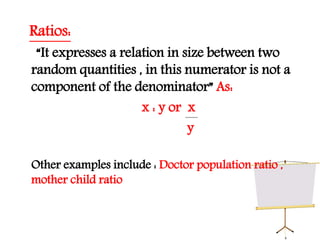
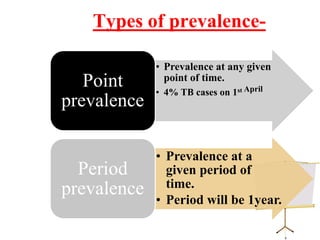
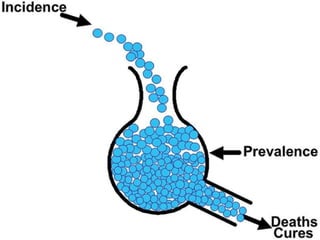
This document discusses various measurement tools used in epidemiology including rates, ratios, proportions, prevalence, and incidence. It provides examples of how to calculate crude rates, specific rates, ratios, and proportions. Prevalence refers to all existing cases at a point in time or over a period of time. Incidence refers only to new cases occurring over a time period. Relationships between incidence, prevalence, and duration of disease are also examined.