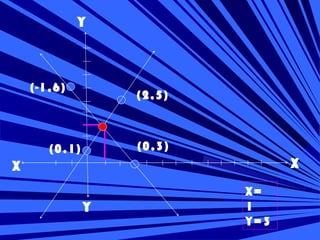
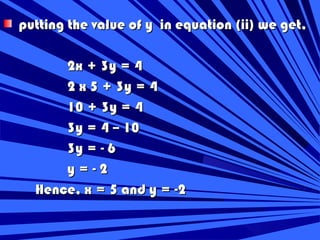The document discusses methods for solving systems of linear equations in two variables:
1) Graphical method involves plotting the lines defined by each equation on a graph and finding their point of intersection.
2) Algebraic methods include substitution, elimination by equating coefficients, and cross-multiplication. Elimination involves manipulating the equations to eliminate one variable and solve for the other.
3) Examples demonstrate solving a system using substitution and elimination to find the solution values for x and y.