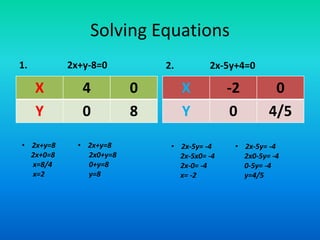
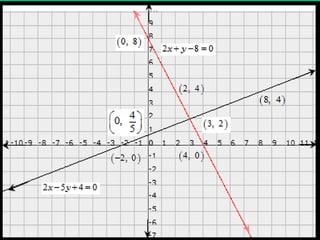
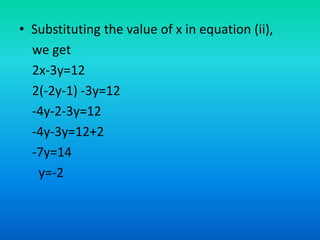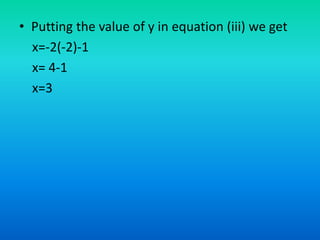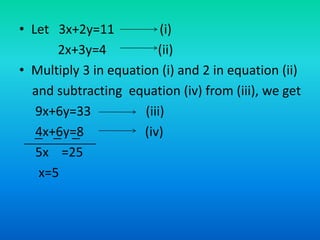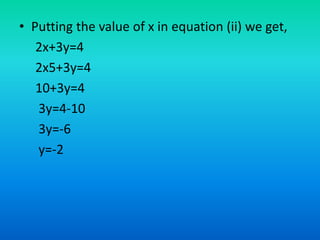The document discusses systems of linear equations and methods for solving them. It defines a system of linear equations as a pair of linear equations in two variables. It presents two examples of systems of linear equations. It then describes algebraic methods for solving systems, including elimination by substitution, elimination by equating coefficients, and cross multiplication. It provides examples of using elimination by substitution and elimination by equating coefficients to solve systems of two equations with two unknowns.