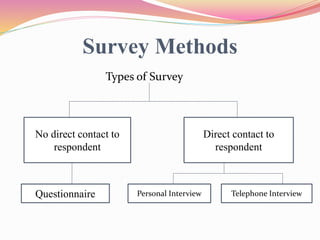
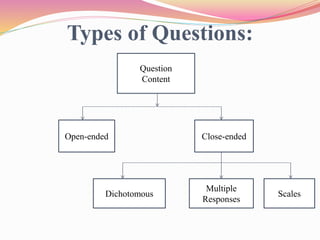
This document discusses different survey methods used for collecting data. It defines a survey and provides examples. The main survey methods discussed are questionnaires, personal interviews, and telephone interviews. For questionnaires, the document outlines different types of questions that can be included like open-ended, close-ended, dichotomous, multiple choice and scale questions. It also discusses personal interviews and telephone interviews as alternatives to questionnaires for direct contact with respondents.