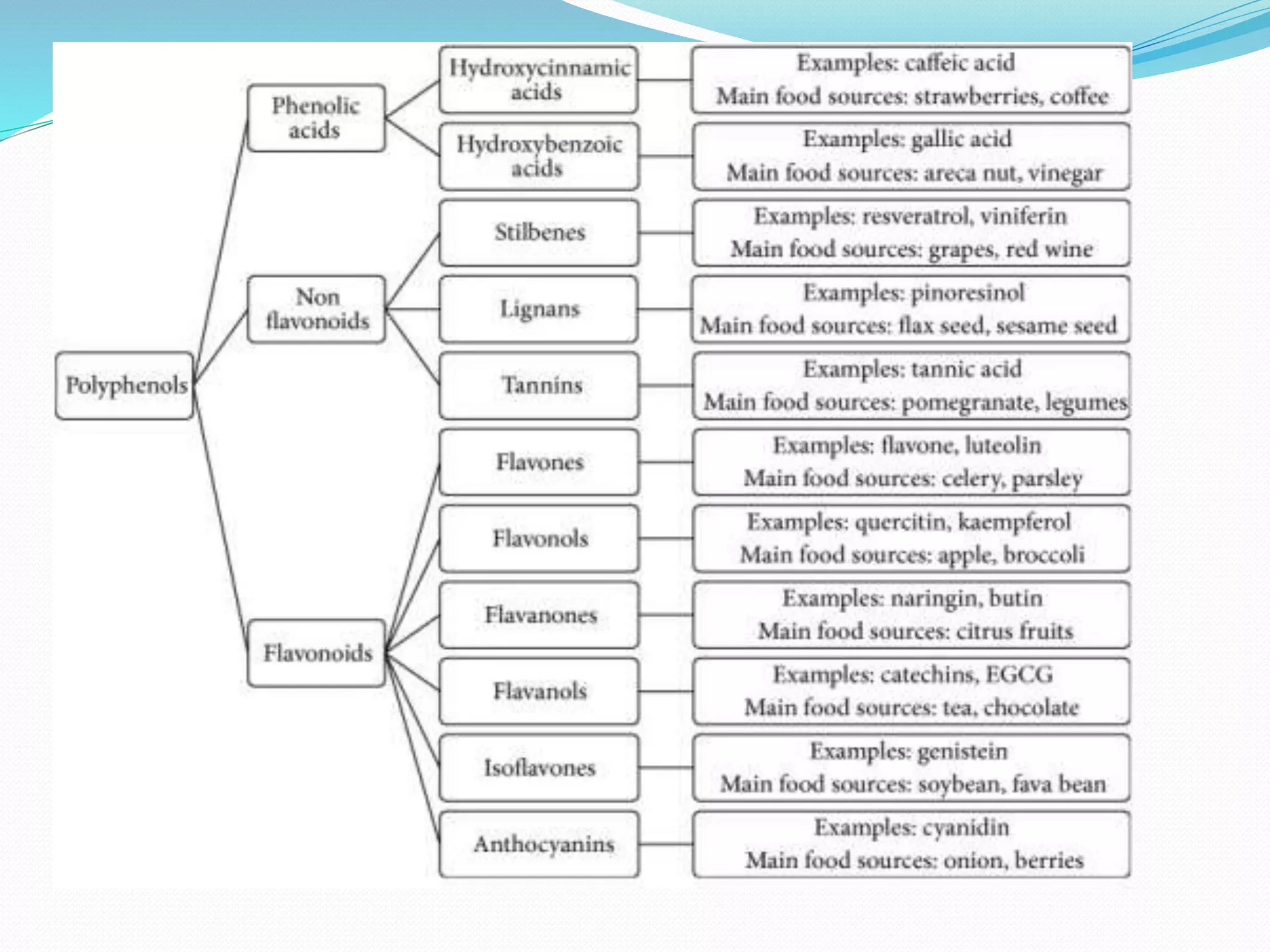
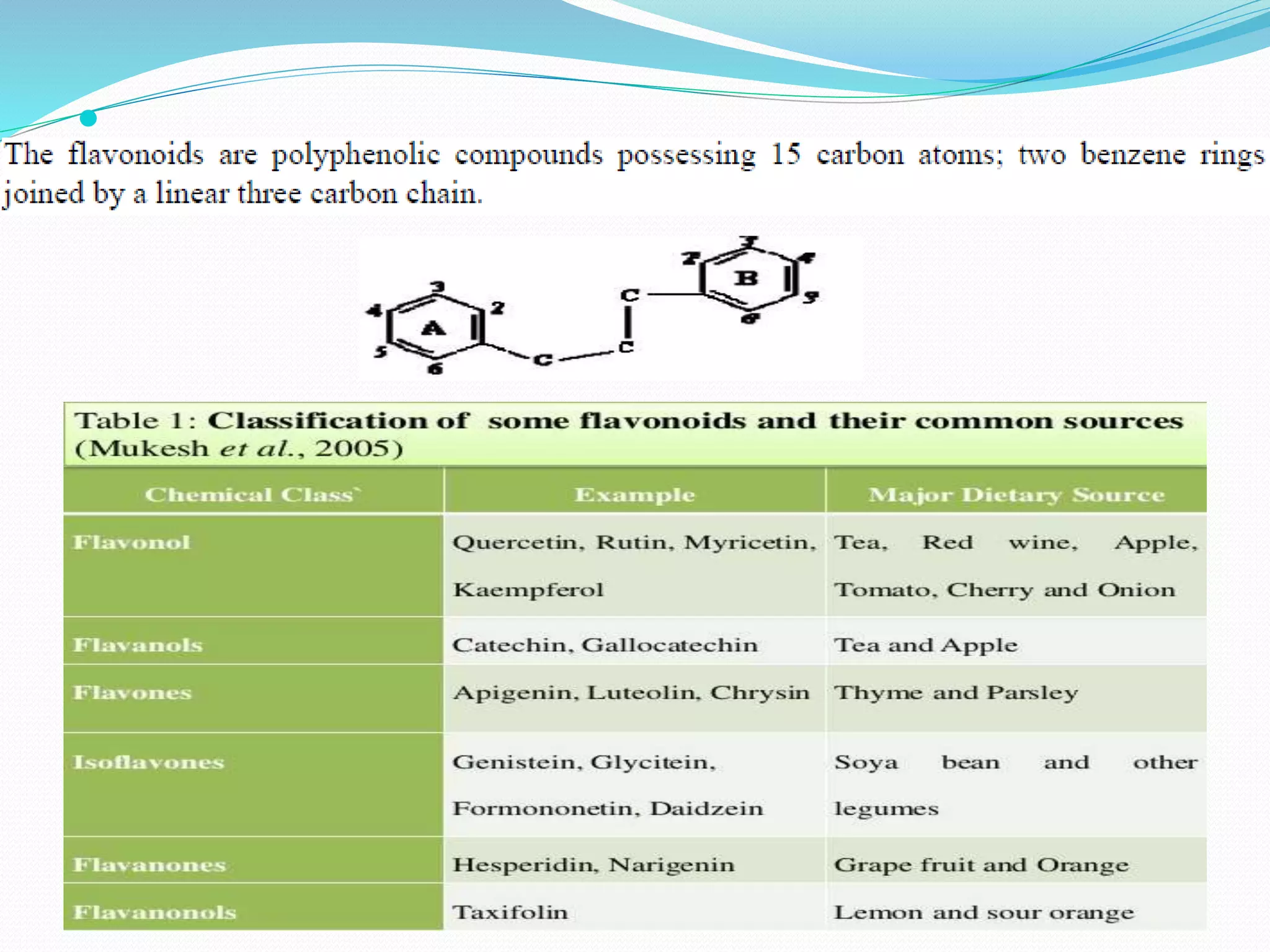
This document summarizes information about various carotenoids and polyphenols. It discusses their characteristics, uses, health benefits, and sources. Carotenoids are organic pigments found in plants and photosynthetic organisms. Over 600 are known, with beta-carotene, alpha-carotene, gamma-carotene, and beta-cryptoxanthin having vitamin A activity in humans. Polyphenols include flavonoids and tannins. Flavonoids include anthocyanidins, flavanols, flavones, and flavonones. They have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and other health benefits. Sources include fruits, vegetables, tea, cocoa. The document provides details on compounds